
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance.
The ISO 14000 family of standards by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) relate to environmental management that exists to help organizations (a) minimize how their operations negatively affect the environment ; (b) comply with applicable laws, regulations, and other environmentally oriented requirements; and (c) continually improve in the above.

Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a family of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options.
BACnet is a communication protocol for building automation and control (BAC) networks that use the ASHRAE, ANSI, and ISO 16484-5 standards protocol.

The Wi-Fi Alliance is a non-profit organization that owns the Wi-Fi trademark. Manufacturers may use the trademark to brand products certified for Wi-Fi interoperability. It is based in Austin, Texas.
The Khronos Group, Inc. is an open, non-profit, member-driven consortium of 170 organizations developing, publishing and maintaining royalty-free interoperability standards for 3D graphics, virtual reality, augmented reality, parallel computation, vision acceleration and machine learning. The open standards and associated conformance tests enable software applications and middleware to effectively harness authoring and accelerated playback of dynamic media across a wide variety of platforms and devices. The group is based in Beaverton, Oregon.
The Global Certification Forum, known as GCF, is an London-based partnership between mobile network operators, mobile device manufacturers and the test industry. GCF was founded in 1999, and its membership has been responsible for creating an independent certification programme to help ensure global interoperability between mobile devices and networks.

The PTCRB was established in 1997 as the certification forum by select North American cellular operators. Now a pseudo-acronym, it no longer stands for its original meaning of the PCS Type Certification Review Board.
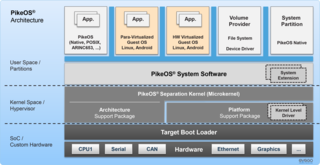
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) which features a separation kernel-based hypervisor. This hypervisor supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is engineered to support the creation of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring compliance with industry standards for quality, safety, and security across various sectors. In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is designed for critical real-time applications and provides up-to-standard safety and security.
ISO 13485Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes is a voluntary standard, published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for the first time in 1996, and contains a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices. The latest version of this standard supersedes earlier documents such as EN 46001 and EN 46002 (1996), the previously published ISO 13485, and ISO 13488.
Hardware certification is the process through which computer hardware is tested to ensure it is compatible with specific software packages, and operates as intended in critical situations. With ever dropping prices of hardware devices, the market for networking devices and systems is undergoing a kind of change that can be loosely termed as "generalization." Big established enterprises like Cisco, Novell, Sun Microsystems, etc., no longer manufacture all the hardware required in the market, instead they "license" or "certify" small hardware players operating in countries like Taiwan or China.
Mobile device management (MDM) is the administration of mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablet computers, and laptops. MDM is usually implemented with the use of a third-party product that has management features for particular vendors of mobile devices. Though closely related to Enterprise Mobility Management and Unified Endpoint Management, MDM differs slightly from both: unlike MDM, EMM includes mobile information management, BYOD, mobile application management and mobile content management, whereas UEM provides device management for endpoints like desktops, printers, IoT devices, and wearables as well.
IEC 60870 part 6 in electrical engineering and power system automation, is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed part 6 to provide a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems which is compatible with ISO standards and ITU-T recommendations.
The International Accreditation Forum, Inc. (IAF) is the worldwide association of conformity assessment accreditation bodies and other bodies interested in conformity assessment in the fields of management systems, products, services, personnel, processes, validation and verification and other similar programs of conformity assessment. Its primary function is to develop a single worldwide program of conformity assessment which reduces risk for businesses and their customers by assuring them that accredited certificates and validation and verification statements may be relied upon.
The (U)SIM interface is the connecting point of the mobile phone and the UICC with its SIM or USIM application.
CIPURSE is an open security standard for transit fare collection systems. It makes use of smart card technologies and additional security measures.

Voice over Long-Term Evolution is an LTE high-speed wireless communication standard for voice calls and SMS using mobile phones and data terminals. VoLTE has up to three times more voice and data capacity than older 3G UMTS and up to six times more than 2G GSM. It uses less bandwidth because VoLTE's packet headers are smaller than those of unoptimized VoIP/LTE. VoLTE calls are usually charged at the same rate as other calls.
Avnu Alliance is a consortium of member companies working together to create an interoperable ecosystem of low-latency, time-synchronized, highly reliable networking devices using the IEEE open standard, Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and its Pro AV networking protocol, Milan. Avnu Alliance creates comprehensive certification programs to ensure interoperability of network devices. In the Professional Audio Video (AV) industry, Alliance member companies worked together to develop Milan: a standards-based, user-driven deterministic network protocol for professional media, that through certification, assures devices will work together at new levels of convenience, reliability, and functionality. Milan™ is a standards-based deterministic network protocol for real time media. Avnu Members may use the Avnu-certified or Milan-certified logo on devices that pass the conformance tests from Avnu. Not every device based on AVB or TSN is submitted for certification to the Avnu Alliance. The lack of the Avnu logo does not necessarily imply a device is incompatible with other Avnu-certified devices. The Alliance, in conjunction with other complimentary standards bodies and alliances, provides a united network foundation for use in professional AV, automotive, industrial control and consumer segments.
The Banking Industry Architecture Network e.V. (BIAN) is an independent, member owned, not-for-profit association to establish and promote a common architectural framework for enabling banking interoperability. It was established in 2008.

oneM2M is a global partnership project founded in 2012 and constituted by 8 of the world's leading ICT standards development organizations, notably: ARIB (Japan), ATIS, CCSA (China), ETSI (Europe), TIA (USA), TSDSI (India), TTA (Korea) and TTC (Japan). The goal of the organization is to create a global technical standard for interoperability concerning the architecture, API specifications, security and enrolment solutions for Machine-to-Machine and IoT technologies based on requirements contributed by its members.






