STS-43, the ninth mission for Space Shuttle Atlantis, was a nine-day mission whose primary goal was launching the TDRS-E satellite (TDRS-5). The flight also tested an advanced heatpipe radiator for potential use on the then-future space station and conducted a variety of medical and materials science investigations.

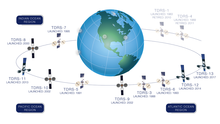
The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is a network of American communications satellites and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was designed to replace an existing network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions. The prime design goal was to increase the time spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. Many Tracking and Data Relay Satellites were launched in the 1980s and 1990s with the Space Shuttle and made use of the Inertial Upper Stage, a two-stage solid rocket booster developed for the shuttle. Other TDRS were launched by Atlas IIa and Atlas V rockets.
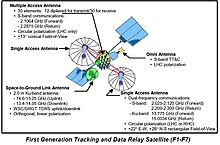
A tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft, the International Space Station, and remote bases like the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. This system was designed to replace an existing worldwide network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions and uncrewed satellites in low-Earth orbits. The primary system design goal was to increase the amount of time that these spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. These TDRSS satellites are all designed and built to be launched to and function in geosynchronous orbit, 35,786 km (22,236 mi) above the surface of the Earth.

The Spacecraft Tracking and Data (Acquisition) Network was established by NASA in the early 1960s to satisfy the requirement for long-duration, highly available space-to-ground communications. The network was the “follow-on” to the earlier Minitrack, which tracked the flights of Sputnik, Vanguard, Explorer, and other early space efforts (1957–1962). Real-time operational control and scheduling of the network was provided by the Network Operations Control Center (NOCC) at the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The Manned Space Flight Network was a set of tracking stations built to support the American Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Skylab space programs.

The Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program places the three prime NASA space communications networks, Space Network (SN), Near Earth Network (NEN), and the Deep Space Network (DSN), under one Management and Systems Engineering umbrella. It was established in 2006. It was previously known as the Space Communications & Data Systems (SCDS) Program.
The Near Earth Network provides orbital communications support for near-Earth orbiting customer platforms via various ground stations, operated by NASA and other space agencies. It uses a number of different dishes scattered around the globe. The antennas must be able to move fast for tracking of objects in low Earth orbit (LEO). The NEN and Space Network (SN) combined were previously referred to as the Spaceflight Tracking and Data Network (STDN).

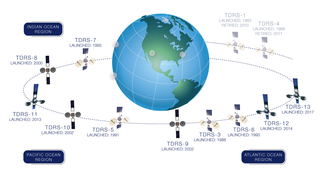
TDRS-B was an American communications satellite, of first generation, which was to have formed part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was destroyed in 1986 when the Space ShuttleChallenger disintegrated 73 seconds after launch.

TDRS-1, known before launch as TDRS-A, was an American communications satellite, operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW and launched by Space ShuttleChallenger on its maiden flight, STS-6.

The Merritt Island Spaceflight Tracking and Data Network station, known in NASA parlance as MILA, was a radio communications and spacecraft tracking complex located on 61 acres (0.25 km2) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. The name MILA was an acronym for the "Merritt Island Launch Annex" to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, which was how the site was referred to when spacecraft launches were primarily originating from the adjacent military installation. MILA's arrays of antennas provided various communications and data services between spacecraft and NASA centers, as well as tracked and ranged moving spacecraft. In its final years, it served as the primary voice and data link during the first 7½ minutes of Space Shuttle launches, and the final 13 minutes of shuttle landings at KSC. Though it occupied land at KSC, MILA was operated and managed by the Goddard Space Flight Center.

TDRS-5, known before launch as TDRS-E, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites.

TDRS-3, known before launch as TDRS-C, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW, and is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites.

TDRS-6, known before launch as TDRS-F, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW, and is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites.

TDRS-7, known before launch as TDRS-G, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW as a replacement for TDRS-B, which had been lost in the Challenger accident, and was the last first generation TDRS satellite to be launched.

TDRS-9, known before launch as TDRS-I, was an American communications satellite which was operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by the Boeing Satellite Development Center, formerly Hughes Space and Communications, and was based on the BSS-601 satellite bus. It was the second Advanced TDRS, or second-generation Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, to be launched.

The NASA (Ground) Communications System (NASCOM) manages terrestrial communications between ground stations, mission control centers, and other elements of spacecraft ground segments. Established in 1964, NASCOM provides worldwide, near real-time, transmission of commands, telemetry, voice, and television signals. It is managed out of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.

TDRS-11, known before launch as TDRS-K, is an American communications satellite which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. The eleventh Tracking and Data Relay Satellite is the first third-generation spacecraft.

TDRS-12, known before launch as TDRS-L, is an American communications satellite operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. The twelfth Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, it is the second third-generation spacecraft to be launched, following TDRS-11 in 2013.
Tianlian also known as CTDRS, is a Chinese data relay communication satellite constellation. The constellation serves to relay data from ground stations to spacecraft and rockets, most significantly China's crewed spaceflight program. The system currently consists of seven satellites in two generations, with the first satellite being launched in 2008.
Differenced one-way doppler (DOWD) is a method of spacecraft navigation. The process uses two TDRSS communications relay satellites receiving the same telemetry broadcast from a satellite. The Doppler shifts experienced by both TDRS satellites can be processed using ground equipment to generate trajectory estimates without the need for onboard GPS solutions. The Flight Dynamics Facility at GSFC provides this trajectory processing for NASA missions, though commercial software can also be used.