
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs about 10,000 civil servants and contractors. Named for American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard, it is one of ten major NASA field centers. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.

The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with energies from 20 keV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main telescopes in one spacecraft, covering X-rays and gamma rays, including various specialized sub-instruments and detectors. Following 14 years of effort, the observatory was launched from Space Shuttle Atlantis during STS-37 on April 5, 1991, and operated until its deorbit on June 4, 2000. It was deployed in low Earth orbit at 450 km (280 mi) to avoid the Van Allen radiation belt. It was the heaviest astrophysical payload ever flown at that time at 16,300 kilograms (35,900 lb).

John Mace Grunsfeld is an American physicist and a former NASA astronaut. He is a veteran of five Space Shuttle flights and has served as NASA Chief Scientist. His academic background includes research in high energy astrophysics, cosmic ray physics and the emerging field of exoplanet studies with specific interest in future astronomical instrumentation. After retiring from NASA in 2009, he served as the deputy director of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland. In January 2012, he returned to NASA and served as associate administrator of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD). Grunsfeld announced his retirement from NASA in April 2016.
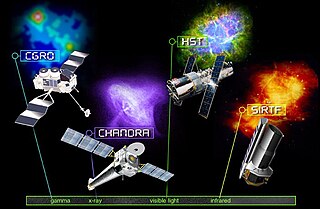
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.
Solar physics is the branch of astrophysics that specializes in the study of the Sun. It intersects with many disciplines of pure physics and astrophysics.

Nancy Grace Roman was an American astronomer who made important contributions to stellar classification and motions. The first female executive at NASA, Roman served as NASA's first Chief of Astronomy throughout the 1960s and 1970s, establishing her as one of the "visionary founders of the US civilian space program".
The US National Virtual Observatory'-NVO- was conceived to allow scientists to access data from multiple astronomical observatories, including ground and space-based facilities, through a single portal. Originally, the National Science Foundation (NSF) funded the information technology research that created the basic NVO infrastructure through a multi-organization collaborative effort. The NVO was more than a “digital library”; it was a vibrant, growing online research facility akin to a bricks-and-mortar observatory for professional astronomers.

Cornelis A. "Neil" Gehrels was an American astrophysicist specializing in the field of gamma-ray astronomy. He was Chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) from 1995 until his death, and was best known for his work developing the field from early balloon instruments to today's space observatories such as the NASA Swift mission, for which he was the principal investigator. He was leading the WFIRST wide-field infrared telescope forward toward a launch in the mid-2020s. He was a member of the National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.

Heidi B. Hammel is a planetary astronomer who has extensively studied Neptune and Uranus. She was part of the team imaging Neptune from Voyager 2 in 1989. She led the team using the Hubble Space Telescope to view Shoemaker-Levy 9's impact with Jupiter in 1994. She has used the Hubble Space Telescope and the Keck Telescope to study Uranus and Neptune, discovering new information about dark spots, planetary storms and Uranus' rings. In 2002, she was selected as an interdisciplinary scientist for the James Webb Space Telescope.

Goddard Space Flight Center is NASA's first, and oldest, space center. It is named after Robert H. Goddard, the father of modern rocketry. Throughout its history, the center has managed, developed, and operated many notable missions, including the Cosmic Background Explorer, the Hubble Space Telescope, the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS), the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, and the Solar Dynamics Observatory.

Space research is scientific study carried out in outer space, and by studying outer space. From the use of space technology to the observable universe, space research is a wide research field. Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine, and physics all apply to the space research environment. The term includes scientific payloads at any altitude from deep space to low Earth orbit, extended to include sounding rocket research in the upper atmosphere, and high-altitude balloons.

Dr. Thomas A. Prince is the Ira S. Bowen Professor of Physics at the California Institute of Technology and holds a joint appointment with Caltech’s NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) as a senior research scientist. Between May 2001 and June 2006, Prince was the chief scientist at JPL. He is currently the director and Allen V.C. Davis and Lenabelle Davis Leadership Chair for the W. M. Keck Institute for Space Studies at Caltech.

Charles Mattias ("Matt") Mountain is currently the President of the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) which designs, builds, and operates telescopes and observatories for the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). AURA's NASA center is the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI), responsible for the science mission for the Hubble Space Telescope, the science and operations for the James Webb Space Telescope, and the MAST data archive. AURA's NSF centers are Gemini Observatory, the National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO), and the National Solar Observatory (NSO). Dr. Mountain and AURA are also responsible for the NSF construction projects: the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST) on Haleakalā, Hawaii and the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) on Cerro Pachón in Chile.

Joan T. Schmelz is the Associate Director for Science and Public Outreach at the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) for the Universities Space Research Association (USRA). Previously, Schmelz was the Deputy Director of Arecibo Observatory and the Director of USRA Operations at Arecibo from 2015 through 2018. Before joining USRA, Schmelz was an NSF Program Director in the Astronomical Sciences Division, where she oversaw the Astronomy & Astrophysics Postdoctoral Fellowship program, and a professor of physics at the University of Memphis from 1996 to 2017. Schmelz's research focus is heliophysics, specifically investigating the coronal heating problem as well as the properties and dynamics of the solar atmosphere. She uses spectroscopic and image data in the X-ray and ultraviolet wavelength ranges obtained from NASA satellites and rockets. She has published over 80 refereed scientific journal articles and authored three books.

Erika Tobiason Hamden is an American astrophysicist and associate professor at the University of Arizona and Steward Observatory. Her research focuses on developing ultraviolet (UV) detector technology, ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV/VIS) instrumentation and spectroscopy, and galaxy evolution. She served as the project scientist and project manager of a UV multi-object spectrograph, FIREBall-2, that is designed to observe the circumgalactic medium (CGM). She is a 2019 TED fellow.

Padi Boyd is an American astrophysicist. She is the head of NASA's Exoplanets and Stellar Astrophysics Laboratory and an Associate Director at the Goddard Space Flight Center. She is the project scientist for NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission.

Rita M. Sambruna Commander OMRI (Hon) is an Italian-American astrophysicist and is the Deputy Director of the Astrophysics Science Division at National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Goddard Space Flight Center. From September 2022 to May 2023, she was the Acting Deputy Director of the Science Exploration Directorate at Goddard. Rita held the Clare Boothe Luce Professorship in Physics and Astronomy at George Mason University in 2000-2005.
Elizabeth Anne Hays is an American astrophysicist at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, where she is chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory and the project scientist for the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. Her research has included gamma-ray astronomy of the Crab Nebula, novae, and gamma-ray bursts.

Jane Rebecca Rigby is an American astrophysicist who works at the Goddard Space Flight Center and is Senior Project Scientist of the James Webb Space Telescope. She was selected one of Nature's 10 Ones to Watch in 2021 and Shape 2022. In 2024 she was awarded the Presidental Medal of Freedom by President Joe Biden.















