
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft.
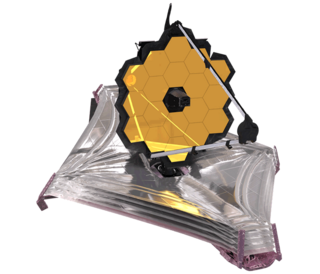
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. Its high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This enables investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the first stars and the formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.

STS-82 was the 22nd flight of the Space Shuttle Discovery and the 82nd mission of the Space Shuttle program. It was NASA's second mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope, during which Discovery's crew repaired and upgraded the telescope's scientific instruments, increasing its research capabilities. Discovery launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on February 11, 1997, returning to Earth on February 21, 1997, at Kennedy Space Center.
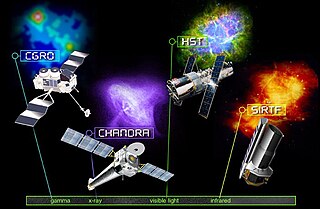
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.

The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) is a spectrograph, also with a camera mode, installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. Aerospace engineer Bruce Woodgate of the Goddard Space Flight Center was the principal investigator and creator of the STIS. It operated continuously from 1997 until a power supply failure in August 2004. After repairs, it began operating again in 2009. The spectrograph has made many important observations, including the first spectrum of the atmosphere of an extrasolar planet, HD 209458b.

The Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) is a scientific instrument for infrared astronomy, installed on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), operating from 1997 to 1999, and from 2002 to 2008. Images produced by NICMOS contain data from the near-infrared part of the light spectrum.

The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) is a third-generation axial instrument aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The initial design and scientific capabilities of ACS were defined by a team based at Johns Hopkins University. ACS was assembled and tested extensively at Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. and the Goddard Space Flight Center and underwent a final flight-ready verification at the Kennedy Space Center before integration in the cargo bay of the Columbia orbiter. It was launched on March 1, 2002, as part of Servicing Mission 3B (STS-109) and installed in HST on March 7, replacing the Faint Object Camera (FOC), the last original instrument. ACS cost US$86 million at that time.

The Faint Object Camera (FOC) was a camera installed on the Hubble Space Telescope from launch in 1990 until 2002. It was replaced by the Advanced Camera for Surveys. In December 1993, Hubble's vision was corrected on STS-61 by installing COSTARS, which corrected the problem with Hubble's mirror before it reached an instrument like FOC. Later instruments had this correction built in, which is why it was possible to later remove COSTARS itself and replace it with a new science instrument.

The Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) is a camera formerly installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. The camera was built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and is roughly the size of a baby grand piano. It was installed by servicing mission 1 (STS-61) in 1993, replacing the telescope's original Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC). WFPC2 was used to image the Hubble Deep Field in 1995, the Engraved Hourglass Nebula and Egg Nebula in 1996, and the Hubble Deep Field South in 1998. During STS-125, WFPC2 was removed and replaced with the Wide Field Camera 3 as part of the mission's first spacewalk on May 14, 2009. After returning to Earth, the camera was displayed briefly at the National Air and Space Museum and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory before returning to its final home at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum.

The Goddard High Resolution Spectrograph was an ultraviolet spectrograph installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during its original construction, and it was launched into space as part of that space telescope aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 (STS-31). The instrument is named after 20th century rocket pioneer Robert H. Goddard.

The Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WFPC) was a camera installed on the Hubble Space Telescope launched in April 1990 and operated until December 1993. It was one of the instruments on Hubble at launch, but its functionality was severely impaired by the defects of the main mirror optics which afflicted the telescope. However, it produced uniquely valuable high resolution images of relatively bright astronomical objects, allowing for a number of discoveries to be made by HST even in its aberrated condition.

The Space Telescope – European Coordinating Facility (ST-ECF) was an institution which provided a number of support and service functions primarily for European observers of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope (HST). It was established in 1984 by the European Space Agency (ESA) and the European Southern Observatory (ESO), and was located at the ESO headquarters in Garching bei München, Germany. The ST-ECF ceased operations on 31 December 2010.

International Ultraviolet Explorer, was the first space observatory primarily designed to take ultraviolet (UV) electromagnetic spectrum. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the United Kingdom's Science and Engineering Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA), formerly European Space Research Organisation (ESRO). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on 26 January 1978 aboard a NASA Thor-Delta 2914 launch vehicle. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.

The Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) is an optical correction instrument designed and built by NASA. It was created to correct the spherical aberration of the Hubble Space Telescope's primary mirror, which incorrectly focused light upon the Faint Object Camera (FOC), Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS), and Goddard High Resolution Spectrograph (GHRS) instruments.

The Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) is a science instrument that was installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during Servicing Mission 4 (STS-125) in May 2009. It is designed for ultraviolet (90–320 nm) spectroscopy of faint point sources with a resolving power of ≈1,550–24,000. Science goals include the study of the origins of large scale structure in the universe, the formation and evolution of galaxies, and the origin of stellar and planetary systems and the cold interstellar medium. COS was developed and built by the Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy (CASA-ARL) at the University of Colorado at Boulder and the Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corporation in Boulder, Colorado.

The Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) is the Hubble Space Telescope's last and most technologically advanced instrument to take images in the visible spectrum. It was installed as a replacement for the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 during the first spacewalk of Space Shuttle mission STS-125 on May 14, 2009.
A digicon detector is a spatially resolved light detector using the photoelectric effect directly. It uses magnetic and electric fields operating in a vacuum to focus the electrons released from a photocathode by incoming light onto a collection of silicon diodes. It is a photon-counting instrument, so most useful for weak sources. One of digicon's advantages is its very large dynamic range and it results from the short response and decay times of silicon diodes.

The NIRSpec is one of the four scientific instruments flown on the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The JWST is the follow-on mission to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and is developed to receive more information about the origins of the universe by observing infrared light from the first stars and galaxies. In comparison to HST, its instruments will allow looking further back in time and will study the so-called Dark Ages during which the universe was opaque, about 150 to 800 million years after the Big Bang.

Fine Guidance Sensor and Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS-NIRISS) is an instrument on the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) that combines a Fine Guidance Sensor and a science instrument, a near-infrared imager and a spectrograph. The FGS/NIRISS was designed by the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and built by Honeywell as part of an international project to build a large infrared space telescope with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the European Space Agency (ESA). FGS-NIRISS observes light from the wavelengths of 0.8 to 5.0 microns. The instrument has four different observing modes.

NIRCam is an instrument aboard the James Webb Space Telescope. It has two major tasks, as an imager from 0.6 to 5 μm wavelength, and as a wavefront sensor to keep the 18-section mirrors functioning as one. In other words, it is a camera and is also used to provide information to align the 18 segments of the primary mirror. It is an infrared camera with ten mercury-cadmium-telluride (HgCdTe) detector arrays, and each array has an array of 2048×2048 pixels. The camera has a field of view of 2.2×2.2 arcminutes with an angular resolution of 0.07 arcseconds at 2 μm. NIRCam is also equipped with coronagraphs, which helps to collect data on exoplanets near stars. It helps with imaging anything next to a much brighter object, because the coronagraph blocks that light.





















