Related Research Articles

Gene therapy is a medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.

The Holocene extinction, or Anthropocene extinction, is the ongoing extinction event caused by humans during the Holocene epoch. These extinctions span numerous families of plants and animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and invertebrates, and affecting not just terrestrial species but also large sectors of marine life. With widespread degradation of biodiversity hotspots, such as coral reefs and rainforests, as well as other areas, the vast majority of these extinctions are thought to be undocumented, as the species are undiscovered at the time of their extinction, which goes unrecorded. The current rate of extinction of species is estimated at 100 to 1,000 times higher than natural background extinction rates and is increasing. During the past 100–200 years, biodiversity loss and species extinction have accelerated, to the point that most conservation biologists now believe that human activity has either produced a period of mass extinction, or is on the cusp of doing so. As such, after the "Big Five" mass extinctions, the Holocene extinction event has also been referred to as the sixth mass extinction or sixth extinction; given the recent recognition of the Capitanian mass extinction, the term seventh mass extinction has also been proposed for the Holocene extinction event.

Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram. In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate.

microRNA are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21–23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals, and even some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes:

Heart rate is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute. The heart rate varies according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. It is also modulated by numerous factors, including genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness, as well as the interaction between these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse rate measured at any peripheral point.

Slavery in ancient Rome played an important role in society and the economy. Unskilled or low-skill slaves labored in the fields, mines, and mills with few opportunities for advancement and little chance of freedom. Skilled and educated slaves—including artisans, chefs, domestic staff and personal attendants, entertainers, business managers, accountants and bankers, educators at all levels, secretaries and librarians, civil servants, and physicians—occupied a more privileged tier of servitude and could hope to obtain freedom through one of several well-defined paths with protections under the law. The possibility of manumission and subsequent citizenship was a distinguishing feature of Rome's system of slavery, resulting in a significant and influential number of freedpersons in Roman society.

Takotsubo cardiomyopathy or takotsubo syndrome (TTS), also known as stress cardiomyopathy, is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy in which there is a sudden temporary weakening of the muscular portion of the heart. It usually appears after a significant stressor, either physical or emotional; when caused by the latter, the condition is sometimes called broken heart syndrome.
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and extinct organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago and evidence suggests that life emerged prior to 3.7 Ga. The similarities among all known present-day species indicate that they have diverged through the process of evolution from a common ancestor.
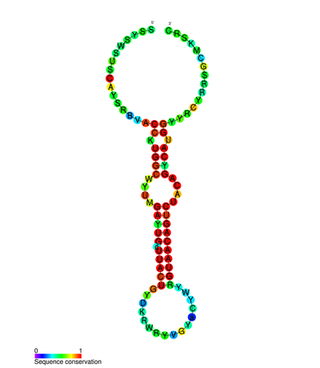
In molecular biology miR-132 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms, generally reducing protein levels through the cleavage of mRNAs or the repression of their translation. Several targets for miR-132 have been described, including mediators of neurological development, synaptic transmission, inflammation and angiogenesis.

Johann Bauersachs is a German internist, cardiologist, and full professor at the Hannover Medical School. He is widely recognized for his scholarly contributions to the domains of acute coronary syndrome, left ventricular repair and remodelling following ischemia, and acute and chronic heart failure.

Developmental bioelectricity is the regulation of cell, tissue, and organ-level patterning and behavior by electrical signals during the development of embryonic animals and plants. The charge carrier in developmental bioelectricity is the ion rather than the electron, and an electric current and field is generated whenever a net ion flux occurs. Cells and tissues of all types use flows of ions to communicate electrically. Endogenous electric currents and fields, ion fluxes, and differences in resting potential across tissues comprise a signalling system. It functions along with biochemical factors, transcriptional networks, and other physical forces to regulate cell behaviour and large-scale patterning in processes such as embryogenesis, regeneration, and cancer suppression.
This paleomammalogy list records new fossil mammal taxa that were described during the year 2018, as well as notes other significant paleomammalogy discoveries and events which occurred during that year.

This is a list of several significant scientific events that occurred or were scheduled to occur in 2021.
The following scientific events occurred in 2022.
References
- ↑ Batkai, Sandor; Genschel, Celina; Viereck, Janika; Rump, Steffen; Bär, Christian; Borchert, Tobias; Traxler, Denise; Riesenhuber, Martin; Spannbauer, Andreas; Lukovic, Dominika; Zlabinger, Katrin; Hašimbegović, Ena; Winkler, Johannes; Garamvölgyi, Rita; Neitzel, Sonja; Gyöngyösi, Mariann; Thum, Thomas (7 January 2021). "CDR132L improves systolic and diastolic function in a large animal model of chronic heart failure". European Heart Journal. 42 (2): 192–201. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa791 . PMC 7813625 . PMID 33089304.
- ↑ Taubel, Jorg; Hauke, Wilfried; Rump, Steffen; Viereck, Janika; Batkai, Sandor; Jenny, Poetzsch; Laura, Rode; Weigt, Henning; Genschel, Celina; Lorch, Ulrike; Theek, Carmen; Levin, Arthur A; Bauersachs, Johann B; Solomon, Scott D; Thum, Thomas (3 September 2021). "Abstract 114: Safety And Efficacy Of CDR132L, A Novel Antisense Therapeutic Which Targets MicroRNA-132 In Heart Failure Patients". Circulation Research. 129 (Suppl_1). doi:10.1161/res.129.suppl_1.114.
- ↑ Täubel, Jörg; Hauke, Wilfried; Rump, Steffen; Viereck, Janika; Batkai, Sandor; Poetzsch, Jenny; Rode, Laura; Weigt, Henning; Genschel, Celina; Lorch, Ulrike; Theek, Carmen; Levin, Arthur A; Bauersachs, Johann; Solomon, Scott D; Thum, Thomas (11 November 2020). "Novel antisense therapy targeting microRNA-132 in patients with heart failure: results of a first-in-human Phase 1b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study". European Heart Journal. 42 (2): 178–188. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa898 . ISSN 0195-668X. PMC 7954267 . PMID 33245749.