
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century, the development of the computer that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water.

Climatology or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. Climate concerns the atmospheric condition during an extended to indefinite period of time; weather is the condition of the atmosphere during a relative brief period of time. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. This topic of study is regarded as part of the atmospheric sciences and a subdivision of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology includes some aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry.

A logbook is a record of important events in the management, operation, and navigation of a ship. It is essential to traditional navigation, and must be filled in at least daily.
This is a list of meteorology topics. The terms relate to meteorology, the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere that focuses on weather processes and forecasting.

A Pacific hurricane is a tropical cyclone that develops within the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean to the east of 180°W, north of the equator. For tropical cyclone warning purposes, the northern Pacific is divided into three regions: the eastern, central, and western, while the southern Pacific is divided into 2 sections, the Australian region and the southern Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons. This separation between the two basins has a practical convenience, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific due to high vertical wind shear, and few cross the dateline.

The Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration seeks to correct and add new information about past North Atlantic hurricanes. It was started around 2000 to update HURDAT, the official hurricane database for the Atlantic Basin, which has become outdated since its creation due to various systematic errors introduced into the database over time. This effort has involved reanalyses of ship observations from the International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) as well as reanalyses done by other researchers over the years. It has been ongoing as of 2024.

A royal is a small sail flown immediately above the topgallant on square rigged sailing ships. It was originally called the "topgallant royal" and was used in light and favorable winds.

Surface weather observations are the fundamental data used for safety as well as climatological reasons to forecast weather and issue warnings worldwide. They can be taken manually, by a weather observer, by computer through the use of automated weather stations, or in a hybrid scheme using weather observers to augment the otherwise automated weather station. The ICAO defines the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), which is the model of the standard variation of pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity with altitude in the Earth's atmosphere, and is used to reduce a station pressure to sea level pressure. Airport observations can be transmitted worldwide through the use of the METAR observing code. Personal weather stations taking automated observations can transmit their data to the United States mesonet through the Citizen Weather Observer Program (CWOP), the UK Met Office through their Weather Observations Website (WOW), or internationally through the Weather Underground Internet site. A thirty-year average of a location's weather observations is traditionally used to determine the station's climate. In the US a network of Cooperative Observers make a daily record of summary weather and sometimes water level information.
The Hurricane Databases (HURDAT), managed by the National Hurricane Center (NHC), are two separate databases that contain details on tropical cyclones, that have occurred within the Atlantic Ocean and Eastern Pacific Ocean since 1851 and 1949 respectively.

The Ocean Prediction Center (OPC), established in 1995, is one of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction's (NCEP's) original six service centers. Until 2003, the name of the organization was the Marine Prediction Center. Its origins are traced back to the sinking of the RMS Titanic in 1912. The OPC issues forecasts up to five days in advance for ocean areas north of 31° north latitude and west of 35° west longitude in the Atlantic, and across the northeast Pacific north of 30° north latitude and east of 160° east longitude. Until recently, the OPC provided forecast points for tropical cyclones north of 20° north latitude and east of the 60° west longitude to the National Hurricane Center. OPC is composed of two branches: the Ocean Forecast Branch and the Ocean Applications Branch.
Ocean reanalysis is a method of combining historical ocean observations with a general ocean model driven by historical estimates of surface winds, heat, and freshwater, by way of a data assimilation algorithm to reconstruct historical changes in the state of the ocean.

The 14th Weather Squadron is a Geographically Separate Unit (GSU) of the 2nd Weather Group. The squadron is located in the Veach-Baley Federal Complex in Asheville, North Carolina. Its mission is military applied climatology. The 14 WS collects, protects and exploits authoritative climate data to optimize military and intelligence operations and planning in order to maximize the combat effectiveness of U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) personnel and weapons systems. It delivers environmental information worldwide to the United States Air Force (USAF), the Army, Unified Combatant Commands, the Intelligence Community, and the United States Department of Defense. The 14 WS also collaborates with the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI).
An atmospheric reanalysis is a meteorological and climate data assimilation project which aims to assimilate historical atmospheric observational data spanning an extended period, using a single consistent assimilation scheme throughout.

Old Weather is an online weather data project that currently invites members of the public to assist in digitising weather observations recorded in US log books dating from the mid-19th century onwards. It is an example of citizen science that enlists members of the public to help in scientific research. It contributes to the Atmospheric Circulation Reconstructions over the Earth initiative. Data collected by Old Weather has been used by at least five different climate reanalysis projects, including HURDAT, SODA and ECMWF. In February 2013, the project was awarded the Royal Meteorological Society IBM Award for Meteorological Innovation that Matters.

The International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) is a digital database of 261 million weather observations made by ships, weather ships, and weather buoys spanning the years 1662 to 2007. The database was initially constructed in 1985 and continues to be expanded upon and updated on a regular basis. From the original data, gridded datasets were created. ICOADS information has been useful in determining the reliability of ship and buoy wind measurements, helping to determine temperature trends in the sea surface temperature field, and updating the Atlantic hurricane database.

The 1859 Atlantic hurricane season featured seven hurricanes, the most recorded during an Atlantic hurricane season until 1870. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 has been estimated. Of the eight known 1859 cyclones, five were first documented in 1995 by Jose Fernandez-Partagás and Henry Diaz, which was largely adopted by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Atlantic hurricane reanalysis in their updates to the Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT), with some adjustments. HURDAT is the official source for hurricane data such as track and intensity, although due to sparse records, listings on some storms are incomplete.
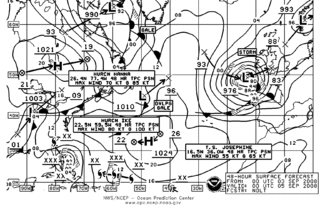
Marine weather forecasting is the process by which mariners and meteorological organizations attempt to forecast future weather conditions over the Earth's oceans. Mariners have had rules of thumb regarding the navigation around tropical cyclones for many years, dividing a storm into halves and sailing through the normally weaker and more navigable half of their circulation. Marine weather forecasts by various weather organizations can be traced back to the sinking of the Royal Charter in 1859 and the RMS Titanic in 1912.

The Mariners Weather Log is a triannual magazine that has been published by the United States Weather Bureau, the Environmental Science Services Administration, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration since 1957. It documents significant storms over and near the Earth's oceans and the Great Lakes of North America, tropical cyclones and extratropical cyclones alike. It is also used as an outreach tool to those who sail the high seas, in order to help gain greater weather reporting from ships at sea through the voluntary observing ship program, which became increasingly important during and after the decline of the weather ship and has taken up an increasing amount of the magazine recently. Although its coverage is primarily of the Northern Hemisphere, coverage of Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclones occurred between July 1973 and 1995.
The Atmospheric Circulation Reconstructions over the Earth, ACRE, is an international science project, began in 2008, that recovers historical weather observations to reconstruct past global and local weather patterns and so support meteorological reanalysis. The project aims to collect weather data from the past 250 years by linking international meteorological organisations to support data recovery projects and the imaging and digitisation of historical meteorological observations made at, for example, inland stations, lighthouses, or by ships at sea or in ports. The project aims to create historical datasets that are spatially and temporally complete, so as to be of value at a local, or regional level, as well as on a global scale. ACRE aims to recover millions of historic weather observations. This data will be deposited into two databases,