SPICE is a general-purpose, open-source analog electronic circuit simulator. It is a program used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.
In mathematics and transportation engineering, traffic flow is the study of interactions between travellers and infrastructure, with the aim of understanding and developing an optimal transport network with efficient movement of traffic and minimal traffic congestion problems.
Microsimulation is a category of computerized analytical tools that perform highly detailed analysis of activities such as highway traffic flowing through an intersection, financial transactions, or pathogens spreading disease through a population. Microsimulation is often used to evaluate the effects of proposed interventions before they are implemented in the real world. For example, a traffic microsimulation model could be used to evaluate the effectiveness of lengthening a turn lane at an intersection, and thus help decide whether it is worth spending money on actually lengthening the lane.
Ngspice is a mixed-level/mixed-signal electronic circuit simulator. It is a successor of the latest stable release of Berkeley SPICE, version 3f.5, which was released in 1993. A small group of maintainers and the user community contribute to the ngspice project by providing new features, enhancements and bug fixes.
STREAMS Integrated Intelligent Transport System is an enterprise traffic management system designed to operate in the Microsoft Windows environment. Like most traffic management systems, STREAMS is an array of institutional, human, hardware, and software components designed to monitor, control, and manage traffic on streets and highways. Advanced traffic management systems come under the banner of ITS. ITS is the application of information and communications technology to transport operations in order to reduce operating costs, improve safety and maximise the capacity of existing infrastructure. STREAMS provides traffic signal management, incident management, motorway management, vehicle priority, traveller information, flood monitoring and parking guidance within a single integrated system. STREAMS is developed by Transmax.
TRANSIMS is an integrated set of tools developed to conduct regional transportation system analyses. With the goal of establishing TRANSIMS as an ongoing public resource available to the transportation community, TRANSIMS is made available under the NASA Open Source Agreement Version 1.3
The National Transportation Communications for Intelligent Transportation System Protocol (NTCIP) is a family of standards designed to achieve interoperability and interchangeability between computers and electronic traffic control equipment from different manufacturers.
TransModeler is the name of a based traffic simulation platform for doing wide-area traffic planning, traffic management, and emergency evacuation studies that is developed by Caliper Corporation. It can animate the behavior of multi-modal traffic systems to show the flow of vehicles, the operation of traffic signals, and the overall performance of the transportation network.
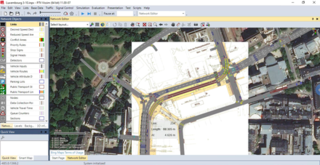
PTV Vissim is a microscopic multi-modal traffic flow simulation software package developed by PTV Planung Transport Verkehr AG in Karlsruhe, Germany. The name is derived from "Verkehr In Städten - SIMulationsmodell". PTV Vissim was first developed in 1992 and is today a global market leader.

AnyLogic is a multimethod simulation modeling tool developed by The AnyLogic Company. It supports agent-based, discrete event, and system dynamics simulation methodologies. AnyLogic is cross-platform simulation software that works on Windows, macOS and Linux. AnyLogic is used to simulate:markets and competition, healthcare, manufacturing, supply chains and logistics, retail, business processes, social and ecosystem dynamics, defense, project and asset management, pedestrian dynamics and road traffic, IT, aerospace.
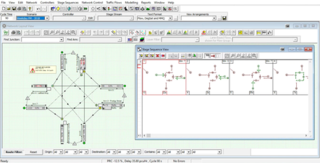
LinSig is a software tool by JCT Consultancy which allows traffic engineers to model traffic signals and their effect on traffic capacities and queuing. As well as modelling the effects of traffic signals LinSig also optimises signal timings to reduce delay or increase capacity at a junction or group of interlinked junctions.

The Canadian Capacity Guide for Signalized Intersections (CCG) is a publication of the Canadian Institute of Transportation Engineers (CITE). It provides a methodology that allows Traffic Engineers to plan, design, and evaluate traffic signal controlled roadway intersections.

Traffic simulation or the simulation of transportation systems is the mathematical modeling of transportation systems through the application of computer software to better help plan, design, and operate transportation systems. Simulation of transportation systems started over forty years ago, and is an important area of discipline in traffic engineering and transportation planning today. Various national and local transportation agencies, academic institutions and consulting firms use simulation to aid in their management of transportation networks.

EPANET is a public domain, water distribution system modeling software package developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Water Supply and Water Resources Division. It performs extended-period simulation of hydraulic and water-quality behavior within pressurized pipe networks and is designed to be "a research tool that improves our understanding of the movement and fate of drinking-water constituents within distribution systems". EPANET first appeared in 1993.
Paramics is traffic microsimulation software, originally developed by Quadstone Ltd. There is a related pedestrian microsimulation product called the Urban Analytics Framework.
TRANSYT-7F is a traffic simulation and signal timing optimization program. The primary application of TRANSYT-7F is signal timing design and optimization. TRANSYT-7F features genetic algorithm optimization of cycle length, phasing sequence, splits, and offsets. TRANSYT-7F combines a detailed optimization process with a detailed macroscopic simulation model.
PTV AG is a German company specialising in software and consulting services for traffic and transportation, mobility, and logistics. "Vision Traffic Suite", their transport planning software, and "PTV Map&Guide", their program for route planning, comprise the PTV AG's product portfolio. According to the manufacturer, over 2,000 customers in more than 90 countries use the Vision Traffic Suite in the fields of transport modelling and traffic flow calculation. PTV ranks among the top 1,000 global market leaders in Germany according to Germany's Manager Magazin. The German company PTV Planung Transport Verkehr AG is a member of PTV Group.
Sidra Intersection is a software package used for intersection (junction) and network capacity, level of service and performance analysis, and signalised intersection and network timing calculations by traffic design, operations and planning professionals.
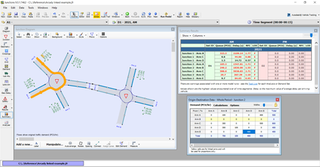
Junctions is a software package by Transport Research Laboratory. It incorporates the previously separate programs ARCADY, PICADY and OSCADY. The latest version, Junctions 10, was launched Wednesday 3 February 2021.

TRANSYT is traffic engineering software developed by the Transport Research Laboratory. It is used to model signalised highway networks and has the ability to model platooning.







