Pattern recognition is the task of assigning a class to an observation based on patterns extracted from data. While similar, pattern recognition (PR) is not to be confused with pattern machines (PM) which may possess (PR) capabilities but their primary function is to distinguish and create emergent patterns. PR has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power.
Unsupervised learning is a framework in machine learning where, in contrast to supervised learning, algorithms learn patterns exclusively from unlabeled data. Other frameworks in the spectrum of supervisions include weak- or semi-supervision, where a small portion of the data is tagged, and self-supervision. Some researchers consider self-supervised learning a form of unsupervised learning.
Edge detection includes a variety of mathematical methods that aim at identifying edges, defined as curves in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities. The same problem of finding discontinuities in one-dimensional signals is known as step detection and the problem of finding signal discontinuities over time is known as change detection. Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing, machine vision and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction.
CRM114 is a program based upon a statistical approach for classifying data, and especially used for filtering email spam.
Template matching is a technique in digital image processing for finding small parts of an image which match a template image. It can be used for quality control in manufacturing, navigation of mobile robots, or edge detection in images.
The scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) is a computer vision algorithm to detect, describe, and match local features in images, invented by David Lowe in 1999. Applications include object recognition, robotic mapping and navigation, image stitching, 3D modeling, gesture recognition, video tracking, individual identification of wildlife and match moving.
In machine learning and pattern recognition, a feature is an individual measurable property or characteristic of a phenomenon. Choosing informative, discriminating and independent features is a crucial element of effective algorithms in pattern recognition, classification and regression. Features are usually numeric, but structural features such as strings and graphs are used in syntactic pattern recognition. The concept of "feature" is related to that of explanatory variable used in statistical techniques such as linear regression.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computer vision:
Computer audition (CA) or machine listening is the general field of study of algorithms and systems for audio interpretation by machines. Since the notion of what it means for a machine to "hear" is very broad and somewhat vague, computer audition attempts to bring together several disciplines that originally dealt with specific problems or had a concrete application in mind. The engineer Paris Smaragdis, interviewed in Technology Review, talks about these systems — "software that uses sound to locate people moving through rooms, monitor machinery for impending breakdowns, or activate traffic cameras to record accidents."
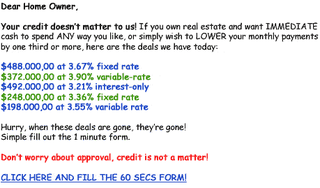
Image-based spam, or image spam, is a kind of email spam where the textual spam message is embedded into images, that are then attached to spam emails. Since most of the email clients will display the image file directly to the user, the spam message is conveyed as soon as the email is opened.
Articulated body pose estimation in computer vision is the study of algorithms and systems that recover the pose of an articulated body, which consists of joints and rigid parts using image-based observations. It is one of the longest-lasting problems in computer vision because of the complexity of the models that relate observation with pose, and because of the variety of situations in which it would be useful.
The histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) is a feature descriptor used in computer vision and image processing for the purpose of object detection. The technique counts occurrences of gradient orientation in localized portions of an image. This method is similar to that of edge orientation histograms, scale-invariant feature transform descriptors, and shape contexts, but differs in that it is computed on a dense grid of uniformly spaced cells and uses overlapping local contrast normalization for improved accuracy.
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different view points, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades.
Automatic target recognition (ATR) is the ability for an algorithm or device to recognize targets or other objects based on data obtained from sensors.
The principal curvature-based region detector, also called PCBR is a feature detector used in the fields of computer vision and image analysis. Specifically the PCBR detector is designed for object recognition applications.

The Point Cloud Library (PCL) is an open-source library of algorithms for point cloud processing tasks and 3D geometry processing, such as occur in three-dimensional computer vision. The library contains algorithms for filtering, feature estimation, surface reconstruction, 3D registration, model fitting, object recognition, and segmentation. Each module is implemented as a smaller library that can be compiled separately. PCL has its own data format for storing point clouds - PCD, but also allows datasets to be loaded and saved in many other formats. It is written in C++ and released under the BSD license.
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a regularized type of feed-forward neural network that learns features by itself via filter optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently have been replaced -- in some cases -- by more recent deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by using regularized weights over fewer connections. For example, for each neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded convolution kernels, only 25 neurons are required to process 5x5-sized tiles. Higher-layer features are extracted from wider context windows, compared to lower-layer features.
Nicolai Petkov is Dutch computer scientist, and professor of Intelligent Systems and Computer Science at the University of Groningen, known for his contributions in the fields of brain-inspired computing, pattern recognition, machine learning, and parallel computing.
Oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF (ORB) is a fast robust local feature detector, first presented by Ethan Rublee et al. in 2011, that can be used in computer vision tasks like object recognition or 3D reconstruction. It is based on the FAST keypoint detector and a modified version of the visual descriptor BRIEF (Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features). Its aim is to provide a fast and efficient alternative to SIFT.
In signal processing it is useful to simultaneously analyze the space and frequency characteristics of a signal. While the Fourier transform gives the frequency information of the signal, it is not localized. This means that we cannot determine which part of a signal produced a particular frequency. It is possible to use a short time Fourier transform for this purpose, however the short time Fourier transform limits the basis functions to be sinusoidal. To provide a more flexible space-frequency signal decomposition several filters have been proposed. The Log-Gabor filter is one such filter that is an improvement upon the original Gabor filter. The advantage of this filter over the many alternatives is that it better fits the statistics of natural images compared with Gabor filters and other wavelet filters.

