
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees.

Influenza A virus (IAV) is the only species of the genus Alphainfluenzavirus of the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as causing seasonal flu in humans. Mammals in which different strains of IAV circulate with sustained transmission are bats, pigs, horses and dogs; other mammals can occasionally become infected.

Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A virus, which is enzootic in many bird populations.

Antigenic shift is the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains. The term is often applied specifically to influenza, as that is the best-known example, but the process is also known to occur with other viruses, such as visna virus in sheep. Antigenic shift is a specific case of reassortment or viral shift that confers a phenotypic change.

Influenza hemagglutinin (HA) or haemagglutinin[p] is a homotrimeric glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza viruses and is integral to its infectivity.

Orthomyxoviridae is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: Alphainfluenzavirus, Betainfluenzavirus, Gammainfluenzavirus, Deltainfluenzavirus, Isavirus, Thogotovirus, and Quaranjavirus. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates. The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods).
Antigenic drift is a kind of genetic variation in viruses, arising from the accumulation of mutations in the virus genes that code for virus-surface proteins that host antibodies recognize. This results in a new strain of virus particles that is not effectively inhibited by the antibodies that prevented infection by previous strains. This makes it easier for the changed virus to spread throughout a partially immune population. Antigenic drift occurs in both influenza A and influenza B viruses.

Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which causes influenza (flu), predominantly in birds. It is enzootic in many bird populations, and also panzootic. A/H5N1 virus can also infect mammals that have been exposed to infected birds; in these cases, symptoms are frequently severe or fatal.

Envelope glycoprotein GP120 is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1984. The 120 in its name comes from its molecular weight of 120 kDa. Gp120 is essential for virus entry into cells as it plays a vital role in attachment to specific cell surface receptors. These receptors are DC-SIGN, Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and a specific interaction with the CD4 receptor, particularly on helper T-cells. Binding to CD4 induces the start of a cascade of conformational changes in gp120 and gp41 that lead to the fusion of the viral membrane with the host cell membrane. Binding to CD4 is mainly electrostatic although there are van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonds.

Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 (A/H3N2) is a subtype of influenza A virus (IAV). Some human-adapted strains of A/H3N2 are endemic in humans and are one cause of seasonal influenza (flu). Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs and in birds. Subtypes of IAV are defined by the combination of the antigenic H and N proteins in the viral envelope; for example, "H1N1" designates an IAV subtype that has a type-1 hemagglutinin (H) protein and a type-1 neuraminidase (N) protein.

The genetic structure of H5N1, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, is characterized by a segmented RNA genome consisting of eight gene segments that encode for various viral proteins essential for replication, host adaptation, and immune evasion.
Antigenic variation or antigenic alteration refers to the mechanism by which an infectious agent such as a protozoan, bacterium or virus alters the proteins or carbohydrates on its surface and thus avoids a host immune response, making it one of the mechanisms of antigenic escape. It is related to phase variation. Antigenic variation not only enables the pathogen to avoid the immune response in its current host, but also allows re-infection of previously infected hosts. Immunity to re-infection is based on recognition of the antigens carried by the pathogen, which are "remembered" by the acquired immune response. If the pathogen's dominant antigen can be altered, the pathogen can then evade the host's acquired immune system. Antigenic variation can occur by altering a variety of surface molecules including proteins and carbohydrates. Antigenic variation can result from gene conversion, site-specific DNA inversions, hypermutation, or recombination of sequence cassettes. The result is that even a clonal population of pathogens expresses a heterogeneous phenotype. Many of the proteins known to show antigenic or phase variation are related to virulence.

Antonio Lanzavecchia is an Italian and Swiss immunologist. As a fellow of Collegio Borromeo he obtained a degree with honors in Medicine in 1976 from the University of Pavia where he specialized in Pediatrics and Infectious Diseases. He is Head Human Immunology Program, Istituto Nazionale di Genetica Molecolare-INGM, Milan and SVP Senior research Fellow, Humabs/Vir Biotechnology, Bellinzona and San Francisco (USA). Since 2017, he is also Professor at the Faculty of Biomedical Sciences of the Università della Svizzera italiana (USI).

Influenza, commonly known as "the flu" or just "flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease.
A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. Neutralization renders the particle no longer infectious or pathogenic. Neutralizing antibodies are part of the humoral response of the adaptive immune system against viruses, bacteria and microbial toxin. By binding specifically to surface structures (antigen) on an infectious particle, neutralizing antibodies prevent the particle from interacting with its host cells it might infect and destroy.

Peter Palese is a United States microbiologist, researcher, inventor and the Horace W. Goldsmith Professor in the Department of Microbiology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, and an expert in the field of RNA viruses.
FI6 is an antibody that targets a protein found on the surface of all influenza A viruses called hemagglutinin. FI6 is the only known antibody found to bind all 16 subtypes of the influenza A virus hemagglutinin and is hoped to be useful for a universal influenza virus therapy.

A H5N1 vaccine is an influenza vaccine intended to provide immunization to influenza A virus subtype H5N1.
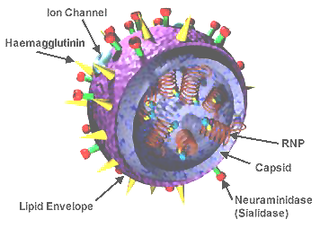
A universal flu vaccine would be a flu vaccine effective against all human -adapted strains of influenza A and influenza B regardless of the virus sub type, or any antigenic drift or antigenic shift. Hence it should not require modification from year to year in order to keep up with changes in the influenza virus. As of 2024 no universal flu vaccine had been successfully developed, however several candidate vaccines were in development, with some undergoing early stage clinical trial.
Type A influenza vaccine is for the prevention of infection of influenza A virus and also the influenza-related complications. Different monovalent type A influenza vaccines have been developed for different subtypes of influenza A virus including H1N1 and H5N1. Both intramuscular injection or intranasal spray are available on market. Unlike the seasonal influenza vaccines which are used annually, they are usually used during the outbreak of certain strand of subtypes of influenza A. Common adverse effects includes injection site reaction and local tenderness. Incidences of headache and myalgia were also reported with H1N1 whereas cases of fever has also been demonstrated with H5N1 vaccines. It is stated that immunosuppressant therapies would reduce the therapeutic effects of vaccines and that people with egg allergy should go for the egg-free preparations.











