PlanetMath is a free, collaborative, mathematics online encyclopedia. Intended to be comprehensive, the project is currently hosted by the University of Waterloo. The site is owned by a US-based nonprofit corporation, "PlanetMath.org, Ltd".
In mathematics, a perfect magic cube is a magic cube in which not only the columns, rows, pillars, and main space diagonals, but also the cross section diagonals sum up to the cube's magic constant.
MathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign.

The versine or versed sine is a trigonometric function found in some of the earliest trigonometric tables. The versine of an angle is 1 minus its cosine.

Wolfram Research, Inc. is an American multinational company that creates computational technology. Wolfram's flagship product is the technical computing program Wolfram Mathematica, first released on June 23, 1988. Other products include WolframAlpha, Wolfram SystemModeler, Wolfram Workbench, gridMathematica, Wolfram Finance Platform, webMathematica, the Wolfram Cloud, and the Wolfram Programming Lab. Wolfram Research founder Stephen Wolfram is the CEO. The company is headquartered in Champaign, Illinois, United States.
Eric Wolfgang Weisstein is an American scientist, mathematician, and encyclopedist who created and maintains the encyclopedias MathWorld and ScienceWorld. In addition, he is the author of the CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics. He works for Wolfram Research.
In mathematics, the boustrophedon transform is a procedure which maps one sequence to another. The transformed sequence is computed by an "addition" operation, implemented as if filling a triangular array in a boustrophedon manner—as opposed to a "Raster Scan" sawtooth-like manner.
Edgar van Tuyll was the chief quantitative strategist of Pictet & Cie, where he worked from 1995 to 2017. He has been extensively quoted by the media for his prediction of the 2000 Dot-com bubble crash and of the bull market beginning in March 2003. He is among the minority of strategists expecting a US recession in 2007–2008. His website Links to unsolved problems, prizes and research is top ranked by Google for list of unsolved problems in mathematics and physics. He is the author of several entries in the "CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics", Chapman & Hall, 2002. He is the grandson of Antti Johannes Rantamaa.
In mathematics, an operation is a function which takes zero or more input values to a well-defined output value. The number of operands is the arity of the operation.

In geometry, the great ditrigonal icosidodecahedron (or great ditrigonary icosidodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U47. It has 32 faces (20 triangles and 12 pentagons), 60 edges, and 20 vertices. It has 4 Schwarz triangle equivalent constructions, for example Wythoff symbol 3 | 3 5⁄4 gives Coxeter diagram = . It has extended Schläfli symbol a{5⁄2,3} or c{3,5⁄2}, as an altered great stellated dodecahedron or converted great icosahedron.
In mathematics, the following matrix was given by Indian mathematician Brahmagupta:

In the mathematical field of knot theory, the tricolorability of a knot is the ability of a knot to be colored with three colors subject to certain rules. Tricolorability is an isotopy invariant, and hence can be used to distinguish between two different (non-isotopic) knots. In particular, since the unknot is not tricolorable, any tricolorable knot is necessarily nontrivial.

Edward Taylor Pegg Jr. is an expert on mathematical puzzles and is a self-described recreational mathematician. He wrote an online puzzle column called Ed Pegg Jr.'s Math Games for the Mathematical Association of America during the years 2003–2007. His puzzles have also been used by Will Shortz on the puzzle segment of NPR's Weekend Edition Sunday. He was a fan of Martin Gardner and regularly participated in Gathering 4 Gardner conferences. In 2009 he teamed up with Tom M. Rodgers and Alan Schoen to edit two Gardner tribute books.
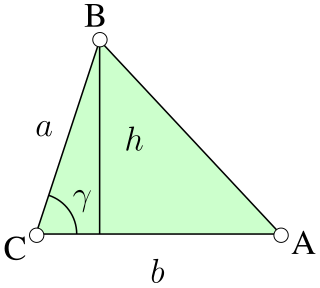
In geometry, an edge is a particular type of line segment joining two vertices in a polygon, polyhedron, or higher-dimensional polytope. In a polygon, an edge is a line segment on the boundary, and is often called a polygon side. In a polyhedron or more generally a polytope, an edge is a line segment where two faces meet. A segment joining two vertices while passing through the interior or exterior is not an edge but instead is called a diagonal.
In mathematics, the theta operator is a differential operator defined by
A tetradicnumber, also known as a four-waynumber, is a number that remains the same when flipped back to front, flipped front to back, mirrored up-down, or flipped up-down. The only numbers that remain the same which turned up-side-down or mirrored are 0, 1, and 8, so a tetradic number is a palindromic number containing only 0, 1, and 8 as digits. The first few tetradic numbers are 1, 8, 11, 88, 101, 111, 181, 808, 818, ....

In geometry, the Hart circle is derived from three given circles that cross pairwise to form eight circular triangles. For any one of these eight triangles, and its three neighboring triangles, there exists a Hart circle, tangent to the inscribed circles of these four circular triangles. Thus, the three given circles have eight Hart circles associated with them. The Hart circles are named after their discover, Andrew Searle Hart. They can be seen as analogous to the nine-point circle of straight-sided triangles.