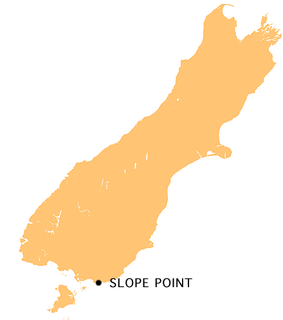
Slope Point is the southernmost point of the South Island of New Zealand.

Albert Town is located to the east of Wanaka in Otago, New Zealand. Until recently only a farming settlement, the population boom in this area has led to much new development. The confluence of the Clutha and Hāwea Rivers is located here. The town was named after Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. Albert Town was formerly called Newcastle.

Owaka is a small town in the Clutha District of South Otago, in the South Island of New Zealand. It is the largest community in the rugged, forested Catlins area, close to the border with Southland, some 35 km (22 mi) south of Balclutha on the Southern Scenic Route. The town's population was 334 in the 2006 census, a decrease of 39 from 2001. In the census figures, 72.9% of the population were European, and 15% were Māori.
The Catlins River flows southeastward through The Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. Its total length is 42 kilometres (26 mi), and it flows into the Pacific Ocean at Pounawea, 28 kilometres (17 mi) south of Balclutha. Its upper estuary is called Catlins Lake, and its lower estuary is shared with the Owaka River.
The Tahakopa River flows southeastward through the Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. Its total length is 32 kilometres (20 mi), and it flows into the Pacific Ocean 30 kilometres (19 mi) east of Waikawa, close to the settlement of Papatowai.

Curio Bay is a coastal embayment in the Southland District of New Zealand, best known as the site of a petrified forest some 180 million years old. It also hosts a yellow-eyed penguin colony, arguably the rarest of penguin species, with approximately 1600 breeding pairs in the extant population. The bay, along with neighbouring Porpoise Bay, is home to the endemic Hector's dolphin. Southern right whales are occasionally observed offshore, as on numerous parts of the country's coast. Located near the southernmost point of the South Island, Curio Bay is one of the major attractions in the Catlins, attracting around 100,000 visitors per year. The town of Waikawa has an information center for tourists.
The Catlins Ranges are a series of rugged, roughly parallel hill ranges in the southeastern corner of New Zealand's South Island.
Pounawea is a small settlement in The Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. It is located four kilometres southwest of Owaka, at the mouth of the Catlins River. It is a popular holiday spot with a seasonal population, there are numerous cribs at the settlement.

Jack's Bay is a small settlement in The Catlins, an area on the southeastern corner of the South Island of New Zealand. It is located six kilometres southwest of Owaka, close to the mouth of the Catlins River. A popular holiday spot with a seasonal population, there are numerous cribs at the settlement. Jack's Bay is noted for a large blowhole, known as Jack's Blowhole, a 55-metre-deep blowhole that formed when part of a sea cavern's roof collapsed. The blowhole is 200 metres from the sea.

Maclennan is a small settlement in The Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. It is located 20 kilometres southwest of Owaka. From 1915 until its closure on 27 February 1971, the Catlins River Branch railway passed through the village, and the station building and goods shed still stand today.

Kaka Point is a small settlement at the northern edge of The Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. It is located 14 km south of Balclutha and 8 km north of the headland of Nugget Point. It has a seasonally fluctuating population, and there are numerous cribs at the settlement. It has a permanent population of about 100. The settlement's best known resident was Māori poet Hone Tuwhare, who lived in Kaka Point for many years until his death in 2008. Kaka Point is named for the New Zealand kaka bird, whose signature call is "ka-aa." There is a restaurant, a motel, bed and breakfasts and a camping ground(s) there. http://www.lonelyplanet.com/new-zealand/the-catlins/things-to-do

Glenomaru is a small settlement in The Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. It is located 10 kilometres north of Owaka on the main road to Balclutha. On 7 July 1891, a branch line railway from the Main South Line in Balclutha was opened to Glenomaru, and the village remained the terminus of the line until it was extended to Tahora on 16 December 1895. This line ultimately terminated in Tahakopa and was known as the Catlins River Branch. It closed on 27 February 1971 and a sawmill now exists on the site of Glenomaru station, though some of the railway's old formation can be seen in the surrounding area and the Hunts Road tunnel is in the vicinity and can be walked.

Tautuku Peninsula is a rocky headland in the Catlins on the south coast of Otago on the South Island of New Zealand. It is located 25 km (15 mi) east of Waikawa, at the western end of Tautuku Bay.

Tahakopa is a small settlement in The Catlins, an area of the southern South Island of New Zealand. It is located 25 kilometres northeast of Waikawa on the Tahakopa River. On 17 February 1915, Tahakopa became the terminus of the Catlins River Branch railway and retained this status until the branch line was closed on 27 February 1971. From the line's opening until 12 August 1956, a railway locomotive depot was based in the village. The old station building and goods shed still stand today.

Clarksville is a small township located three kilometres southwest of Milton in the Otago region of the South Island of New Zealand. State Highways 1 and 8 meet in Clarksville. The town was also once the location of a railway junction, where the Roxburgh Branch left the Main South Line. Construction of this branch line began in the 1870s and Clarksville acted as the junction until 1907, when an extension of the branch was built alongside the Main South Line into Milton to improve operations. This led to Milton being the junction until 1960, when the extension was removed and Clarksville regained its status as a junction until the branch was entirely closed in 1968.

Waikawa is a small settlement in Southland, New Zealand, at the southwestern edge of The Catlins.
The Fleming River is a river of the eastern Catlins, New Zealand. A tributary of the Tautuku River, it rises west of Soaker Hill in the Maclennan Range and flows south-eastward through the Catlins Forest Park to join that river at Tautuku.
Waiwera South is a small settlement in the South Island of New Zealand, close to the boundary between the Otago and Southland regions. The settlement is located between Balclutha and Clinton, immediately to the south of State Highway 1, between branches of the Waiwera River and Kaihiku Stream, two minor tributaries of the Clutha River. The South Island Main Trunk railway also runs through the township. The settlement's population is around 100.

Wangaloa is a small coastal settlement in South Otago, New Zealand. It is located to the north of the mouths of the Clutha River the beach area, close to the town of Kaitangata. There is access to Wangaloa Beach from the Kaitangata Golf course. Wangaloa is connected to Toko Mouth, 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) to the north, by a coastal road, and to Kaitangata, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) to the west, by a road which crests a low range of coastal hills.

Port Molyneux is a tiny settlement on the coast of South Otago, New Zealand, close to the northeasternmost point of The Catlins. Now home only to farmland, it was a thriving port in the early years of New Zealand's European settlement.









