This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2009) |



A cactus fence is a hedge or fence made of closely spaced cactus plants, sometimes with barbed wire or wood interwoven with the cacti.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2009) |



A cactus fence is a hedge or fence made of closely spaced cactus plants, sometimes with barbed wire or wood interwoven with the cacti.
Such fences are inexpensive to develop in regions where cacti are common, and can provide an extreme deterrent to any but a determined human intruder. Often their primary function is to keep wandering large animals off a private property.
Sometimes, cacti are used as barriers without being formed into a structured fence. Prickly pears (mostly Opuntia stricta ) were imported into Australia in the 19th century for use as a natural agricultural fence and to establish a cochineal dye industry, but quickly became a widespread weed.
Closely spaced columnar cacti such as Trichocereus or Mexican fencepost cactus can be used for more structured, space-saving fences. [1] [2]
In the American southwest, ocotillo stems are often set in the ground to form a structure similar to a cactus fence.

A cactus is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family of the order Caryophyllales comprising about 127 genera with some 1,750 known species. The word cactus derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek word κάκτος (káktos), a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. They are native to the Americas, ranging from Patagonia in the south to parts of western Canada in the north, with the exception of Rhipsalis baccifera, which is also found in Africa and Sri Lanka. Cacti are adapted to live in very dry environments, including the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth. Because of this, cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. For example, almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti where this vital process takes place. Most species of cacti have lost true leaves, retaining only spines, which are highly modified leaves. As well as defending against herbivores, spines help prevent water loss by reducing air flow close to the cactus and providing some shade. In the absence of true leaves, cacti's enlarged stems carry out photosynthesis.

Euphorbia is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae.

Fouquieria splendens is a plant indigenous to the Mojave Desert, Sonoran Desert, Chihuahuan Desert and Colorado Desert in the Southwestern United States, and northern Mexico.

Schlumbergera is a small genus of cacti with six to nine species found in the coastal mountains of south-eastern Brazil. These plants grow on trees or rocks in habitats that are generally shady with high humidity, and can be quite different in appearance from their desert-dwelling cousins. Most species of Schlumbergera have stems which resemble leaf-like pads joined one to the other and flowers which appear from areoles at the joints and tips of the stems. Two species have cylindrical stems more similar to other cacti.

Stenocereus eruca, commonly known as the creeping devil, is a member of the family Cactaceae. It is one of the most distinctive cacti, a member of the relatively small genus Stenocereus.

Ariocarpus is a small genus of succulent, subtropical plants of the family Cactaceae.

Pediocactus is a genus of cacti native to the Western United States. The genus comprises between 6 and 11 species, depending upon the authority. Species of this genus are referred to as hedgehog cacti, though that name is also applied to plants from the genera Echinocereus and Echinopsis. Species may also be referred to as pincushion cacti, a common name which is also applied to other genera.

Lophocereus is a genus of cacti. It has often been merged into the genus Pachycereus, but was separated in a 2019 revision of Pachycereus, and is accepted by Plants of the World Online as of March 2021.

Echinopsis lageniformis, synonyms including Echinopsis scopulicola and Trichocereus bridgesii, is a cactus native to Bolivia. It is known as the Bolivian torch cactus. Among the indigenous populations of Bolivia, it is sometimes called achuma or wachuma, although these names are also applied to related species such as Trichocereus macrogonus which are also used for their psychedelic effects.

Cactoblastis cactorum, the cactus moth, South American cactus moth or nopal moth, is native to Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay and southern Brazil. It is one of five species in the genus Cactoblastis that inhabit South America, where many parasitoids, predators and pathogens control the expansion of the moths' population. This species has been introduced into many areas outside its natural range, including Australia, the Caribbean, and South Africa. In some locations, it has spread uncontrollably and was consequently classified an invasive species. However, in other places such as Australia, it has gained favor for its role in the biological control of cacti from the genus Opuntia, such as prickly pear.

Trichocereus macrogonus var. pachanoi is a fast-growing columnar cactus found in the Andes at 2,000–3,000 m (6,600–9,800 ft) in altitude. It is one of a number of kinds of cacti known as San Pedro cactus. It is native to Ecuador, Peru and Colombia, but also found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Venezuela and cultivated in other parts of the world. Uses for it include traditional medicine and traditional veterinary medicine, and it is widely grown as an ornamental cactus. It has been used for healing and religious divination in the Andes Mountains region for over 3,000 years.

Opuntia humifusa, commonly known as the devil's-tongue, eastern prickly pear or Indian fig, is a cactus of the genus Opuntia present in parts of the eastern United States and northeastern Mexico.
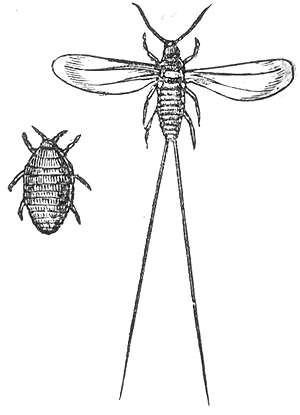
The cochineal is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessile parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North America, this insect lives on cacti in the genus Opuntia, feeding on plant moisture and nutrients. The insects are found on the pads of prickly pear cacti, collected by brushing them off the plants, and dried.

In botany, succulent plants, also known as succulents, are plants with parts that are thickened, fleshy, and engorged, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions. The word succulent comes from the Latin word sucus, meaning "juice" or "sap".

The saguaro is a tree-like cactus species in the monotypic genus Carnegiea that can grow to be over 12 meters tall. It is native to the Sonoran Desert in Arizona, the Mexican state of Sonora, and the Whipple Mountains and Imperial County areas of California. The saguaro blossom is the state wildflower of Arizona. Its scientific name is given in honor of Andrew Carnegie. In 1933, Saguaro National Park, near Tucson, Arizona, was designated to help protect this species and its habitat.

Opuntia, commonly called the prickly pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae, many known for their flavorful fruit and showy flowers. Cacti are well-adapted to aridity; however, they are still vulnerable to alterations in precipitation and temperature driven by climate change. Prickly pear alone is more commonly used to refer exclusively to the fruit, but may also be used for the plant itself; in addition, other names given to the plant and its specific parts include tuna (fruit), sabra, sabbar, nopal from the Nahuatl word nōpalli, nostle (fruit) from the Nahuatl word nōchtli, and paddle cactus. The genus is named for the Ancient Greek city of Opus, where, according to Theophrastus, an edible plant grew and could be propagated by rooting its leaves. The most common culinary species is the "Barbary fig".

Pelecyphora sneedii is a rare species of cactus known by the common names Sneed's pincushion cactus and carpet foxtail cactus. It is endemic to the Chihuahuan Desert of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. It is a small, variable cactus with a lengthy taxonomic history, and is often subdivided into a number of subspecies or varieties. It is usually found on steep, rocky habitats, primarily of limestone geology, in desert scrub or coniferous forest. A species of conservation concern, P. sneedii faces threats from poaching, urban encroachment, and wildfires.

Cereus ( "serious") is a genus of cacti including around 33 species of large columnar cacti from South America. The name is derived from Greek (κηρός) and Latin words meaning "wax", "torch" or "candle". Cereus was one of the first cactus genera to be described; the circumscription varies depending on the authority. The term "cereus" is also sometimes used for a ceroid cactus, any cactus with a very elongated body, including columnar growth cacti and epiphytic cacti.

Hatiora salicornioides, the bottle cactus, dancing-bones, drunkard's-dream, or spice cactus, is a species of flowering plant in the cactus family. A member of the tribe Rhipsalideae, it often grows as an epiphyte, natively in eastern Brazil and ornamentally elsewhere.
Cactodera cacti, also known as the cactus cyst nematode or cactus cyst eelworm, is a plant pathogenic nematode. It is a pest of plants in the families Cactaceae, Apiaceae, and Euphorbiaceae.