Related Research Articles

Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the 3+1⁄2-mile (5.6-kilometer) wide, 295-foot deep Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; geologically, the two bodies are a single lake that is, by area, the largest freshwater lake in the world.

The Illinois and Michigan Canal connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. In Illinois, it ran 96 miles (154 km) from the Chicago River in Bridgeport, Chicago to the Illinois River at LaSalle-Peru. The canal crossed the Chicago Portage, and helped establish Chicago as the transportation hub of the United States, before the railroad era. It was opened in 1848. Its function was partially replaced by the wider and deeper Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal in 1900, and it ceased transportation operations with the completion of the Illinois Waterway in 1933.

Blue Island is a city in Cook County, Illinois, United States, located approximately 16 miles (26 km) south of Chicago's Loop. Blue Island is adjacent to the city of Chicago and shares its northern boundary with that city's Morgan Park neighborhood. The population was 22,558 at the 2020 United States Census.

The Calumet River is a system of heavily industrialized rivers and canals in the region between the south side of Chicago, Illinois, and the city of Gary, Indiana. Historically, the Little Calumet River and the Grand Calumet River were one, the former flowing west from Indiana into Illinois, then turning back east to its mouth at Lake Michigan at Marquette Park in Gary. Now the system is part of the Chicago Area Waterway System and through the use of locks flows away from Lake Michigan to the Cal-Sag Channel.

The city of Chicago is located in northern Illinois, United States, at the south western tip of Lake Michigan. It sits on the Saint Lawrence Seaway continental divide at the site of the Chicago Portage, an ancient trade route connecting the Mississippi River and the Great Lakes watersheds.

Riverdale is one of the 77 official community areas of Chicago, Illinois and is located on the city's far south side.

The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal, historically known as the Chicago Drainage Canal, is a 28-mile-long (45 km) canal system that connects the Chicago River to the Des Plaines River. It reverses the direction of the Main Stem and the South Branch of the Chicago River, which now flows out of Lake Michigan rather than into it. The related Calumet-Saganashkee Channel does the same for the Calumet River a short distance to the south, joining the Chicago canal about halfway along its route to the Des Plaines. The two provide the only navigation for ships between the Great Lakes Waterway and the Mississippi River system.
The Calumet Region is the geographic area drained by the Grand Calumet River and the Little Calumet River of northeastern Illinois and northwestern Indiana in the United States. It is part of the Great Lakes Basin, which eventually reaches the Atlantic Ocean. It is a sub-region of the greater Northwest Indiana region and the even larger Great Lakes region.

The Illinois Waterway system consists of 336 miles (541 km) of navigable water from the mouth of the Calumet River at Chicago to the mouth of the Illinois River at Grafton, Illinois. Based primarily on the Illinois River, it is a system of rivers, lakes, and canals that provide a shipping connection from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico via the Illinois and Mississippi rivers.

Lake Chicago was a prehistoric proglacial lake that is the ancestor of what is now known as Lake Michigan, one of North America's five Great Lakes. Formed about 13,000 years ago and fed by retreating glaciers, it drained southwest through the Chicago Outlet River.

Wolf Lake is an 804-acre (325.4 ha) lake that straddles the Indiana and Illinois state line near Lake Michigan. It is smaller than it was prior to settlement by European colonizers because of infilling for development around the edges. Despite years of environmental damage caused by heavy industries, transportation infrastructure, urban runoff and filling of wetlands, it is one of the most important biological sites in the Chicago region.

The Calumet-Saganashkee Channel, usually shortened to the Cal-Sag Channel, is a 16-mile-long (26 km) drainage and shipping canal in southern Cook County, Illinois, operated by the Metropolitan Water Reclamation District of Greater Chicago (MWRD). A component of the Chicago Area Waterway System, it connects the Little Calumet River at its eastern end to the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal at its western end.
William W. Powers State Recreation Area is an Illinois state park administered by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources on 580 acres (230 ha) in the Hegewisch community area of the City of Chicago in Cook County, Illinois, United States. The area includes 419 acres (170 ha) of water in Wolf Lake that provides about 6 miles (10 km) of shoreline to fishermen. The park hosts about half a million visitors annually. The park contains numerous species, and is one of the most important biological sites in the Chicago region.

The Valparaiso Moraine is a recessional moraine that forms an immense U around the southern Lake Michigan basin in North America. It is a band of hilly terrain composed of glacial till and sand. The Valparaiso Moraine defines part of the continental divide known as the Saint Lawrence River Divide, bounding the Great Lakes Basin. It begins near the border of Wisconsin and Illinois and extends south through Lake, McHenry, Cook, DuPage and Will counties in Illinois, and then turns southeast, going through northwestern Indiana. From this point, the moraine curves northeast through Lake, Porter, and LaPorte counties of Indiana into Michigan. It continues into Michigan as far as Montcalm County.
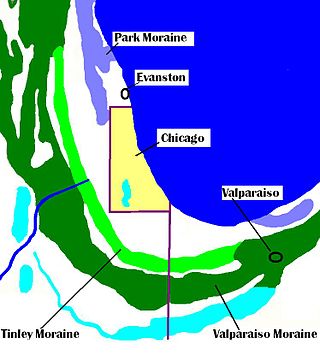
The Tinley Moraine is a moraine around the Lake Michigan basin in North America. It was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation and is younger than the higher and wider terminal moraine called the Valparaiso Moraine, which is located farther from the lake than the Tinley Moraine. Compared to the Valparaiso Moraine, the Tinley Moraine is much narrower and occupies a similar swath, about 6 miles (10 km) closer to Lake Michigan, and passes through the communities of Flossmoor, Western Springs, and Arlington Heights. The moraine was named after the village of Tinley Park, a village southwest of Chicago that lies on the moraine.

The Calumet Shoreline is an ancient shoreline of Lake Michigan located in the Lake Michigan Basin. It can be clearly seen as a sand ridge along Ridge Road south of Chicago. Closer to the lake from the Calumet Shoreline, there are the Tolleston shorelines and farther from the lake are the Glenwood Shoreline, the Tinley Moraine, and the Valparaiso Moraine. The shoreline is named after the Calumet Region of Northern Indiana.

The Chicago Area Waterway System (CAWS) is a complex of natural and artificial waterways extending through much of the Chicago metropolitan area, covering approximately 87 miles altogether. It straddles the Chicago Portage and is the sole navigable inland link between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River and makes up the northern end of the Illinois Waterway.

The Grand Calumet River is a 13.0-mile-long (20.9 km) river that flows primarily into Lake Michigan. Originating in Miller Beach in Gary, it flows through the cities of Gary, East Chicago and Hammond, as well as Calumet City and Burnham on the Illinois side. The majority of the river's flow drains into Lake Michigan via the Indiana Harbor and Ship Canal, sending about 1,500 cubic feet (42 m3) per second of water into the lake. A smaller part of the flow, at the river's western end, enters the Calumet River, and through the Illinois ultimately drains into the Mississippi River.

Thomas J. O'Brien Lock & Dam is a stop lock in the Hegewisch neighborhood on the South Side of Chicago at the confluence of the Grand Calumet River and Little Calumet River, which form the Calumet River. It is a component of the Chicago Area Waterway System (CAWS), which is, itself, a part of the Illinois Waterway, which links the Mississippi River and the Great Lakes.
References
- 1 2 3 Juhl, Arlan. "History of Flood Control & Drainage in Northeastern Illinois". Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved 2015-02-02.
- ↑ Andreas, Alfred Theodore (1884). History of Chicago: Ending with the year 1857. A. T. Andreas. p. 172.
- 1 2 Howe 1956, p. 92.
- ↑ Howe 1956, pp. 145–148.
- ↑ Howe 1956, pp. 92, 146.
- 1 2 3 Howe 1956, p. 146.
- ↑ Schoon, Kenneth J. (2003). Calumet Beginnings: Ancient Shorelines and Settlements at the Southern End of Lake Michigan. Indiana University Press. p. 112. ISBN 025334218X.
- ↑ Howe 1956, p. 151.
- ↑ Sanitary Dist. of Chicago v. Chicago & A.R. Co. Vol. 108. West Publishing Company. 1915. pp. 312, 313.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)