
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, submarine, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top, or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.

A ship is a large vessel that travels the world's oceans and other navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce.

Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.

Maritime transport or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people (passengers) or goods (cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by sea has been widely used throughout recorded history. The advent of aviation has diminished the importance of sea travel for passengers, though it is still popular for short trips and pleasure cruises. Transport by water is cheaper than transport by air or ground, but significantly slower for longer distances. Maritime transport accounts for roughly 80% of international trade, according to UNCTAD in 2020.
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water. Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin nauticus, from Greek nautikos, from nautēs: "sailor", from naus: "ship".

A bulk carrier or bulker is a merchant ship specially designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo—such as grain, coal, ore, steel coils, and cement—in its cargo holds. Since the first specialized bulk carrier was built in 1852, economic forces have led to increased size and sophistication of these ships. Today's bulk carriers are specially designed to maximize capacity, safety, efficiency, and durability.

Deadweight tonnage or tons deadweight (DWT) is a measure of how much weight a ship can carry. It is the sum of the weights of cargo, fuel, fresh water, ballast water, provisions, passengers, and crew.
Ballast is extra weight placed low in ships to lower their centre of gravity, which increases stability. Insufficiently ballasted boats tend to tip or heel excessively in high winds. Too much heel may result in the vessel capsizing. If a sailing vessel needs to voyage without cargo, then ballast of little or no value will be loaded to keep the vessel upright. Some or all of this ballast will then be discarded when cargo is loaded.

A third mate (3/M) or third officer is a licensed member of the deck department of a merchant ship. The third mate is a watchstander and customarily the ship's safety officer and fourth-in-command. The position is junior to a second mate. Other duties vary depending on the type of ship, its crewing, and other factors.
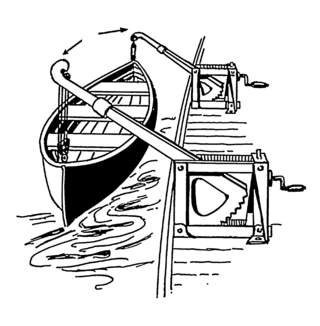
A davit is any of various crane-like devices used on a ship for supporting, raising, and lowering equipment such as boats and anchors.

The bow is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern.

The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer sides of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water.

A vessel's length at the waterline is the length of a ship or boat at the level where it sits in the water. The LWL will be shorter than the length of the boat overall as most boats have bows and stern protrusions that make the LOA greater than the LWL. As a ship becomes more loaded, it will sit lower in the water and its ambient waterline length may change; but the registered L.W.L is measured from a default load condition.

Length overall is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth.

A sea captain, ship's captain, captain, master, or shipmaster, is a high-grade licensed mariner who holds ultimate command and responsibility of a merchant vessel. The captain is responsible for the safe and efficient operation of the ship, including its seaworthiness, safety and security, cargo operations, navigation, crew management, and legal compliance, and for the persons and cargo on board.

The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation.

Ship stability is an area of naval architecture and ship design that deals with how a ship behaves at sea, both in still water and in waves, whether intact or damaged. Stability calculations focus on centers of gravity, centers of buoyancy, the metacenters of vessels, and on how these interact.

Seakeeping ability or seaworthiness is a measure of how well-suited a watercraft is to conditions when underway. A ship or boat which has good seakeeping ability is said to be very seaworthy and is able to operate effectively even in high sea states.

The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used.
Oil tankers generally have from 8 to 12 tanks. Each tank is split into two or three independent compartments by fore-and-aft bulkheads. The tanks are numbered with tank one being the forwardmost. Individual compartments are referred to by the tank number and the athwartships position, such as "one port", "three starboard", or "six center."













