
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, submarine, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top, or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.
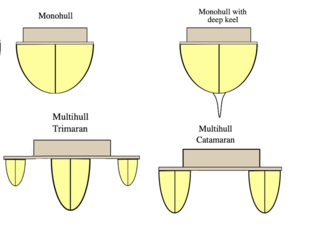
A multihull is a boat or ship with more than one hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull. The most common multihulls are catamarans, and trimarans. There are other types, with four or more hulls, but such examples are very rare and tend to be specialised for particular functions.

Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.

A yacht is a sail- or motor-propelled watercraft made for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a yacht, as opposed to a boat, such a pleasure vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and may have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities.
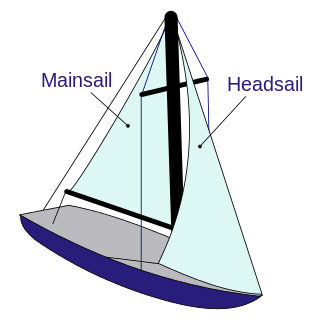
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.

A catamaran is a watercraft with two parallel hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is required. Catamarans typically have less hull volume, smaller displacement, and shallower draft (draught) than monohulls of comparable length. The two hulls combined also often have a smaller hydrodynamic resistance than comparable monohulls, requiring less propulsive power from either sails or motors. The catamaran's wider stance on the water can reduce both heeling and wave-induced motion, as compared with a monohull, and can give reduced wakes.

Boat building is the design and construction of boats — and their on-board systems. This includes at minimum the construction of a hull, with any necessary propulsion, mechanical, navigation, safety and other service systems as the craft requires.

A deck is a permanent covering over a compartment or a hull of a ship. On a boat or ship, the primary or upper deck is the horizontal structure that forms the "roof" of the hull, strengthening it and serving as the primary working surface. Vessels often have more than one level both within the hull and in the superstructure above the primary deck, similar to the floors of a multi-storey building, that are also referred to as decks, as are certain compartments and decks built over specific areas of the superstructure. Decks for some purposes have specific names.

Hobie Cat is a company that manufactures watercraft and other products as the Hobie Cat Company. "Hobie Cat" can also refer to specific products of the company, notably its sailing catamarans. Its fiberglass catamaran models range in nominal length between 14 feet (4.3 m) and 18 feet (5.5 m). Rotomolded catamaran models range in length between 12 feet (3.7 m) and 17 feet (5.2 m). Other sailing vessels in the Hobie Cat lineup include, monocats, dinghies, and trimarans, ranging in length between 9 feet (2.7 m) and 20 feet (6.1 m). Its largest product was the Hobie 33, 33 feet (10 m) in length. The company's non-sailing product line includes surfboards, kayaks, stand-up paddle boards, pedalboards, eyeware, and e-bikes. It was founded in 1961 by Hobart (Hobie) Alter, who originally manufactured surfboards.

A vessel's length at the waterline is the length of a ship or boat at the level where it sits in the water. The LWL will be shorter than the length of the boat overall as most boats have bows and stern protrusions that make the LOA greater than the LWL. As a ship becomes more loaded, it will sit lower in the water and its ambient waterline length may change; but the registered L.W.L is measured from a default load condition.
The term beachcat is an informal name for one of the most common types of small recreational sailboats, minimalist 14 to 20 foot catamarans, almost always with a cloth "trampoline" stretched between the two hulls, typically made of fiberglass or more recently rotomolded plastic. The name comes from the fact that they are designed to be sailed directly off a sand beach, unlike most other small boats which are launched from a ramp. The average 8 foot width of the beachcat means it can also sit upright on the sand and is quite stable in this position, unlike a monohull of the same size. The Hobie 14 and Hobie 16 are two of the earliest boats of this type that achieved widespread popularity, and popularized the term as well as created the template for this type of boat.

Length overall is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth.

Length between perpendiculars is the length of a ship along the summer load line from the forward surface of the stem, or main bow perpendicular member, to the after surface of the sternpost, or main stern perpendicular member. When there is no sternpost, the centerline axis of the rudder stock is used as the aft end of the length between perpendiculars.
A mast-aft rig is a sailboat sail-plan that uses a single mast set in the aft half of the hull. The mast supports fore-sails that may consist of a single jib, multiple staysails, or a crab claw sail. The mainsail is either small or completely absent. Mast-aft rigs are uncommon, but are found on a few custom, and production sailboats.

The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation.

A sailing yacht, is a leisure craft that uses sails as its primary means of propulsion. A yacht may be a sail or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, so the term applies here to sailing vessels that have a cabin with amenities that accommodate overnight use. To be termed a "yacht", as opposed to a "boat", such a vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities. Sailboats that do not accommodate overnight use or are smaller than 30 feet (9.1 m) are not universally called yachts. Sailing yachts in excess of 130 feet (40 m) are generally considered to be superyachts.
Ship measurements consist of a multitude of terms and definitions specifically related to ships and measuring or defining their characteristics.

The F-31 Sport Cruiser is a family of American trailerable trimaran sailboats that was designed by New Zealander Ian Farrier and first built in 1991.
The Bahia 22, also called the Bahia 23, is a French trailerable sailboat that was designed by Philippe Harlé as a pocket cruiser and first built in 1983.















