Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority, mostly as or through Filipino. Its standardized, codified, national or nationalized, intellectualized, more linguistically inclusive, more linguistically dynamic, and expanded or broaden form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of the latter's two official languages, alongside English. Tagalog, like the other and as one of the regional languages of the Philippines, which majority are Austronesian, is one of the auxiliary official languages of the Philippines in the regions and also one of the auxiliary media of instruction therein.

Calabarzon, sometimes referred to as Southern Tagalog and designated as Region IV‑A, is an administrative region in the Philippines. The region comprises five provinces: Batangas, Cavite, Laguna, Quezon, and Rizal; and one highly urbanized city, Lucena. It is the most populous region in the Philippines, according to the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA), having over 16.1 million inhabitants in 2020, and is also the country's second most densely populated after the National Capital Region. It is situated southeast of Metro Manila, and is bordered by Manila Bay and South China Sea to the west, Lamon Bay and the Bicol Region to the east, Tayabas Bay and the Sibuyan Sea to the south, and Central Luzon to the north. It is home to places like Mount Makiling near Los Baños, Laguna, and Taal Volcano in Batangas. Calamba is the regional center while Antipolo is the most populous city in the region.

Batangas, officially the Province of Batangas, is a first class province of the Philippines located in the southwestern part of Luzon in the Calabarzon region. Its capital is the city of Batangas, and is bordered by the provinces of Cavite and Laguna to the north, and Quezon to the east. Across the Verde Island Passages to the south is the island of Mindoro and to the west lies the South China Sea. Poetically, Batangas is often referred to by its ancient name, Kumintáng.

Mindoro is the seventh largest and eighth-most populous island in the Philippines. With a total land area of 10,571 km2, it has a population of 1,408,454, as of the 2020 census. It is located off the southwestern coast of Luzon and northeast of Palawan. Mindoro is divided into two provinces: Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro. Calapan is the only city in the island while San Jose is the largest settlement on the island with a total population of 143,430 inhabitants as of 2015. The southern coast of Mindoro forms the northeastern extremum of the Sulu Sea. Mount Halcon is the highest point on the island, standing at 8,484 feet (2,586 m) above sea level located in Oriental Mindoro. Mount Baco is the island's second highest mountain with an elevation of 8,163 feet (2,488 m), located in the province of Occidental Mindoro.

Batangas City, officially the City of Batangas, is a 1st class component city and capital of the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 351,437 people.

Ilog, officially the Municipality of Ilog, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,855 people.

Mabini, officially the Municipality of Mabini, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 50,858 people.
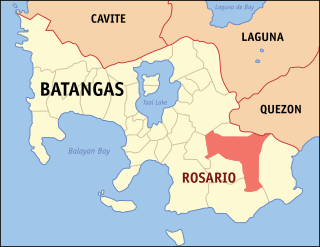
Rosario, officially the Municipality of Rosario, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 128,352 people.

San Juan, officially the Municipality of San Juan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 114,068 people.

Taysan, officially the Municipality of Taysan, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 40,146 people.

The Señor Santo Niño de Cebú is a Catholic title of the Child Jesus associated with a religious image of the Christ Child widely venerated as miraculous by Filipino Catholics. It is the oldest Christian artifact in the Philippines, originally a gift from the Conquistador Ferdinand Magellan to Rajah Humabon and his wife and chief consort, Hara Humamay on account of their Christian baptism in 1521. The image is the only canonically crowned image of Jesus Christ in the Philippines.

Montenegro Shipping Lines, Inc. (MSLI) is a Philippine domestic shipping line based at Batangas City, Philippines. The office is located at Montenegro Corporate office, along Bolbok Diversion Road, Bolbok Batangas City. It operates passenger, cargo and RORO vessels to various destinations in the Philippines under the brands Montenegro Lines and Marina Ferries.

The Santa Cruz River is a river system in Santa Cruz, Laguna, on the island of Luzon, in the Philippines.

Batangas State University, The National Engineering University is a state university in the province of Batangas, Philippines. Established in 1903 as a training school, Batangas State University is the oldest higher education institution in the region. It was granted a state college status in 1968, renamed Pablo Borbon Memorial Institute of Technology, and was finally elevated into a state university in 2001. At present, the university has eleven campuses in Batangas.

Indigenous Philippine shrines and sacred grounds are places regarded as holy within the indigenous Philippine folk religions. These places usually serve as grounds for communication with the spirit world, especially to the deities and ancestral spirits. In some cases, they also function as safeguards for the caskets of ancestors, as well as statues or other objects depicting divine entities.

2GO Travel or 2GO Sea Solutions, also known simply as 2GO, is a ferry company based in Manila, Philippines, the shipping arm of 2GO Group, and the only remaining Manila-based major interisland ferry company, with its hubs located in Pier 4 at the Manila North Harbor and Batangas International Port.

The Batangas International Port or locally known as the Batangas Pier is a seaport in Barangay Santa Clara, Batangas City primarily serving the Calabarzon region of the Philippines. The seaport covers an area of about 150 hectares.



















