
Functional neuroimaging is the use of neuroimaging technology to measure an aspect of brain function, often with a view to understanding the relationship between activity in certain brain areas and specific mental functions. It is primarily used as a research tool in cognitive neuroscience, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and social neuroscience.
Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) is a statistical technique for examining differences in brain activity recorded during functional neuroimaging experiments. It was created by Karl Friston. It may alternatively refer to software created by the Wellcome Department of Imaging Neuroscience at University College London to carry out such analyses.

Analysis of Functional NeuroImages (AFNI) is an open-source environment for processing and displaying functional MRI data—a technique for mapping human brain activity.

Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative research studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is highly multidisciplinary involving neuroscience, computer science, psychology and statistics, and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging is sometimes confused with neuroradiology.
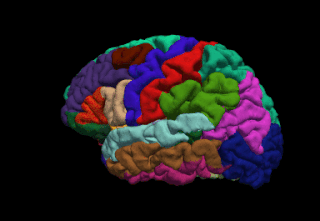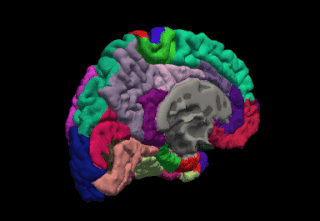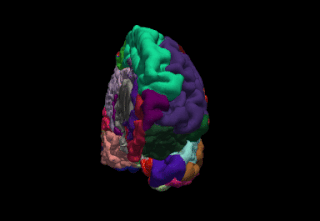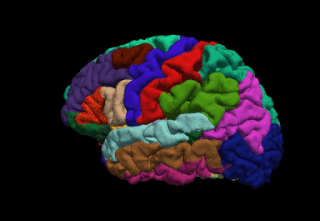
FreeSurfer is brain imaging software originally developed by Bruce Fischl, Anders Dale, Martin Sereno, and Doug Greve. Development and maintenance of FreeSurfer is now the primary responsibility of the Laboratory for Computational Neuroimaging at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging. FreeSurfer contains a set of programs with a common focus of analyzing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of brain tissue. It is an important tool in functional brain mapping and contains tools to conduct both volume based and surface based analysis. FreeSurfer includes tools for the reconstruction of topologically correct and geometrically accurate models of both the gray/white and pial surfaces, for measuring cortical thickness, surface area and folding, and for computing inter-subject registration based on the pattern of cortical folds.

The FMRIB Software Library, abbreviated FSL, is a software library containing image analysis and statistical tools for functional, structural and diffusion MRI brain imaging data.
The Wolfson Brain Imaging Centre (WBIC) is a UK Biomedical Imaging Centre, located at Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, England, on the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus at the southwestern end of Hills Road. It is a division of the Department of Clinical Neurosciences of the University of Cambridge.
Robert Turner is a British neuroscientist, physicist, and social anthropologist. He has been a director and professor at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, Germany, and is an internationally recognized expert in brain physics and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Coils inside every MRI scanner owe their shape to his ideas.
Mark Steven Cohen is an American neuroscientist and early pioneer of functional brain imaging using magnetic resonance imaging. He is a currently a professor of psychiatry, neurology, radiology, psychology, biomedical physics, and biomedical engineering at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior and the Staglin Center for Cognitive Neuroscience. He is also a performing musician.

Resting state fMRI is a method of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) that is used in brain mapping to evaluate regional interactions that occur in a resting or task-negative state, when an explicit task is not being performed. A number of resting-state brain networks have been identified, one of which is the default mode network. These brain networks are observed through changes in blood flow in the brain which creates what is referred to as a blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) signal that can be measured using fMRI.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to brain mapping:

Katya Rubia is a professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at the MRC Social, Genetic and Developmental Psychiatry Centre and Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, both part of the Institute of Psychiatry, King's College London.

The Neuroimaging Tools and Resources Collaboratory is a neuroimaging informatics knowledge environment for MR, PET/SPECT, CT, EEG/MEG, optical imaging, clinical neuroinformatics, imaging genomics, and computational neuroscience tools and resources.
Bruce Rosen is an American physicist and radiologist and a leading expert in the area of functional neuroimaging. His research for the past 30 years has focused on the development and application of physiological and functional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques, as well as new approaches to combine functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data with information from other modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), magnetoencephalography (MEG) and noninvasive optical imaging. The techniques his group has developed to measure physiological and metabolic changes associated with brain activation and cerebrovascular insult are used by research centers and hospitals throughout the world.
Gemma A. Calvert FRSA is a British neuroscientist and pioneer of neuromarketing. She is the founder of Neurosense Limited, the world's first neuromarketing agency established in 1999, and in 2016 she co-founded Split Second Research, a company which provides implicit research for companies worldwide. Calvert is a professor of marketing at the Nanyang Business School at the Nanyang Technological University in Singapore.

CONN is a Matlab-based cross-platform imaging software for the computation, display, and analysis of functional connectivity in fMRI in the resting state and during task.
Edward Thomas Bullmore is a British neuropsychiatrist, neuroscientist and academic. Since 1999, he has been Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Cambridge and was Head of the Department of Psychiatry between 2014 and 2021. In 2005, he became Vice-President of Experimental Medicine at GlaxoSmithKline while maintaining his post at University of Cambridge.
Joaquim Radua is a Spanish psychiatrist and developer of methods for meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. He has been named as one of the most cited researchers in Psychiatry / Psychology.








