Related Research Articles

Sir John Sparrow David Thompson was a Canadian lawyer, judge and politician who served as the fourth prime minister of Canada from 1892 until his death. He had previously been fifth premier of Nova Scotia for a brief period in 1882.
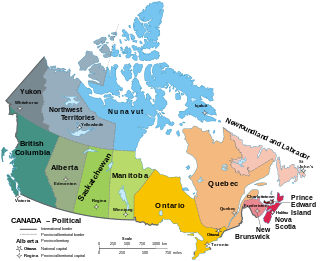
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.
The Canadian order of precedence is a nominal and symbolic hierarchy of important positions within the governing institutions of Canada. It has no legal standing, but is used to dictate ceremonial protocol.
The Progressive Party of Canada, formally the National Progressive Party, was a federal-level political party in Canada in the 1920s until 1930. It was linked with the provincial United Farmers parties in several provinces, and it spawned the Progressive Party of Saskatchewan, and the Progressive Party of Manitoba, which formed the government of that province. The Progressive Party was part of the farmers' political movement that included federal and provincial Progressive and United Farmers' parties.

Events from the year 1918 in Canada.

The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to Canada.

Events from the year 1902 in Canada.

Events from the year 1894 in Canada.
The harmonized sales tax (HST) is a consumption tax in Canada. It is used in provinces where both the federal goods and services tax (GST) and the regional provincial sales tax (PST) have been combined into a single value-added sales tax.

St. Francis Xavier University is a public undergraduate liberal arts university located in Antigonish, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is a member of the Maple League, a group of primarily undergraduate universities in Eastern Canada.
Canadian securities regulation is managed through the laws and agencies established by Canada's 10 provincial and 3 territorial governments. Each province and territory has a securities commission or equivalent authority with its own provincial or territorial legislation.
Local government in Canada can be defined as all elected local authorities which are legally empowered to make decisions on behalf of its electors, excluding the federal government, provincial and territorial governments, and First Nations, Métis and Inuit governments. This can include municipalities, school boards, health authorities, and so on.

The Boston Christmas Tree is the City of Boston, Massachusetts' official Christmas tree. A tree has been lit each year since 1941, and since 1971 it has been given to the people of Boston by the people of Nova Scotia in thanks for their assistance after the 1917 Halifax Explosion. The tree is lit in the Boston Common throughout the Christmas season.

The Nova Scotia Society for the Prevention of Cruelty is a not-for-profit charitable society organized under the Animal Protection Act of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. The Society is dedicated to the prevention of cruelty to animals and to the promotion of respect and humane care for animals. Its members are committed to providing humane leadership in animal advocacy, protection, education, and veterinary care.

The Challenge Trophy is a national amateur soccer cup in Canada contested by the champions of individual provincial soccer competitions. It is one of the oldest soccer competitions in Canada, being held since 1913. It is run by the Canadian Soccer Association.

The Canadian Agricultural Safety Association was established in 1993 in response to an identified need for a national farm safety networking and coordinating agency to address problems of illness, injuries and accidental death in farmers, their families and agricultural workers. Since then, CASA has worked to improve the health and safety conditions of those who live and work on Canadian farms.

Christmas tree cultivation is an agricultural, forestry, and horticultural occupation which involves growing pine, spruce, and fir trees specifically for use as Christmas trees.

Christmas tree production in Canada totals from 3 to 6 million trees annually. Trees are produced in many of the provinces of Canada but the nation's leading producers are found in Quebec, Nova Scotia and Ontario, which account for 80 percent of Canadian tree production. Of the 900,000 trees produced annually in British Columbia, most are cut from native pine stands.
The National Christmas Tree Association (NCTA) is a professional organization in the United States of over 5,100 "Christmas tree professionals" in various capacities. The group focuses its work into three areas: promotion and research, federal representation, and professional education. The association was founded in 1955 and has more than 1,800 members.

Higher education in Nova Scotia refers to education provided by higher education institutions. In Canada, education is the responsibility of the provinces and there is no Canadian federal ministry governing education. Nova Scotia has a population of less than one million people, but is home to ten public universities and the Nova Scotia Community College, which offers programs at 13 locations.
References
- 1 2 Sandberg, Anders L. and Clancy, Peter L. Against the Grain: Foresters and Politics in Nova Scotia, (Google Books), UBC Press, 2000, pp. 228-229, ( ISBN 0774807660).
- ↑ "Minister MacKay helps donate Christmas Trees to Military Families Archived 2009-08-23 at the Wayback Machine ", (Press release), Canadian Forces Personnel Support Agency, December 7, 2007, accessed April 5, 2009.
- 1 2 "PM supports the Christmas Trees for Troop Families program Archived 2010-01-13 at the Wayback Machine ", (Press release), Prime Minister of Canada , December 5, 2008, accessed April 5, 2009.
- ↑ "Who We Are Archived 2009-04-08 at the Wayback Machine ", Canadian Christmas Tree Growers Association, accessed April 5, 2009.
- ↑ "Canada's Provincial Christmas Tree Associations Archived 2009-04-08 at the Wayback Machine ", Canadian Christmas Tree Growers Association, accessed April 5, 2009.