Related Research Articles

The interurban is a type of electric railway, with tram-like electric self-propelled railcars which run within and between cities or towns. The term "interurban" is usually used in North America, with other terms used outside it. They were very prevalent in many parts of the world before the Second World War and were used primarily for passenger travel between cities and their surrounding suburban and rural communities. Interurban as a term encompassed the companies, their infrastructure, their cars that ran on the rails, and their service. In the United States, the early 1900s interurban was a valuable economic institution, when most roads between towns, many town streets were unpaved, and transportation and haulage was by horse-drawn carriages and carts.

The Rochester Industrial and Rapid Transit Railway, more commonly known as the Rochester subway, was a light rail rapid transit line in the city of Rochester, New York that operated from 1927 to 1956. The subway was constructed in the bed of the old Erie Canal, which allowed the route to be grade-separated for its entire length. Two miles (3.2 km) of the route through downtown were constructed in a cut-and-cover tunnel that became Broad Street, and the only underground portion of the subway.

New York State Railways was a subsidiary of the New York Central Railroad that controlled several large city streetcar and electric interurban systems in upstate New York. It included the city transit lines in Rochester, Syracuse, Utica, Oneida and Rome, plus various interurban lines connecting those cities. New York State Railways also held a 50% interest in the Schenectady Railway Company, but it remained a separate independent operation. The New York Central took control of the Rochester Railway Company, the Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway and the Rochester and Sodus Bay Railway in 1905, and the Mohawk Valley Company was formed by the railroad to manage these new acquisitions. New York State Railways was formed in 1909 when the properties controlled by the Mohawk Valley Company were merged. In 1912 it added the Rochester and Suburban Railway, the Syracuse Rapid Transit Railway, the Oneida Railway, and the Utica and Mohawk Valley Railway. The New York Central Railroad was interested in acquiring these lines in an effort to control the competition and to gain control of the lucrative electric utility companies that were behind many of these streetcar and interurban railways. Ridership across the system dropped through the 1920s as operating costs continued to rise, coupled with competition from better highways and private automobile use. New York Central sold New York State Railways in 1928 to a consortium led by investor E. L. Phillips, who was looking to gain control of the upstate utilities. Phillips sold his stake to Associated Gas & Electric in 1929, and the new owners allowed the railway bonds to default. New York State Railways entered receivership on December 30, 1929. The company emerged from receivership in 1934, and local operations were sold off to new private operators between 1938 and 1948.

Transit Windsor provides public transportation in the city of Windsor, Ontario, Canada as well as LaSalle, Essex, Kingsville, Amherstburg and Leamington and serves more than 6 million passengers each year, covering an area of 310 km2 (120 sq mi) and a population of 235,000. They operate a cross border service between the downtown areas of Windsor and Detroit, Michigan via the Tunnel Bus, and service to events at Detroit's Comerica Park, Little Caesars Arena, Huntington Place, and Ford Field. The Windsor International Transit Terminal neighbours with the Windsor International Aquatic and Training Centre.
The Elmira and Lake Ontario Railroad was a subsidiary of the Northern Central Railway and later the Pennsylvania Railroad, formed to give the Northern Central an outlet for coal traffic on Lake Ontario.

The International Railway Company (IRC) was a transportation company formed in a 1902 merger between several Buffalo-area interurban and street railways. The city railways that merged were the West Side Street Railway, the Crosstown Street Railway and the Buffalo Traction Company. The suburban railroads that merged included the Buffalo & Niagara Electric Street Railway, and its subsidiary the Buffalo, Lockport & Olcott Beach Railway; the Buffalo, Depew & Lancaster Railway; and the Niagara Falls Park & River Railway. Later the IRC acquired the Niagara Gorge Railroad (NGRR) as a subsidiary, which was sold in 1924 to the Niagara Falls Power Company. The NGRR also leased the Lewiston & Youngstown Frontier Railroad.

The Terre Haute, Indianapolis and Eastern Traction Company, or THI&E, was the second largest interurban electric railway in the U.S. state of Indiana during the height of the 1920s "interurban era." This system included over 400 miles (640 km) of track, with lines radiating from Indianapolis to the east, northwest, west and southwest as well as streetcar lines in several major cities. The THI&E was formed in 1907 by the Schoepf-McGowan Syndicate as a combination of several predecessor interurban and street car companies and was operated independently until incorporation into the Indiana Railroad in 1931. The THI&E served a wide range of territory, including farmlands in central Indiana, the mining region around Brazil, and numerous urban centers. Eventually, it slowly succumbed like all the other central Indiana interurban lines, to competition from automobiles, trucks, and improved paralleling highways.
Michigan United Railways (MUR) was an interurban which owned and leased numerous lines in the state of Michigan during the early twentieth century.

The New York Museum of Transportation (NYMT), founded in 1975, is a non-profit organization located at 6393 East River Road, in the Rochester suburb of Rush. A private rail line built by volunteers connects NYMT with the Rochester & Genesee Valley Railroad Museum, over a distance of two miles. This demonstration railway allows both museums to offer train rides with their collections of vintage railroad equipment. NYMT operates the only electric trolley ride in New York State, not to be confused with the similarly named Trolley Museum of New York located in Kingston, New York.

Originally, various track gauges were used in the United States. Some railways, primarily in the northeast, used standard gauge of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in ; others used gauges ranging from 2 ft to 6 ft. As a general rule, southern railroads were built to one or another broad gauge, mostly 5 ft, while northern railroads that were not standard-gauge tended to be narrow-gauge. The Pacific Railroad Acts of 1863 specified standard gauge.
The Beebe Syndicate was the name given to a group of electric streetcar and interurban railroads as well as construction and finance companies that shared common management based in Syracuse, New York. Founder Clifford D. Beebe (1866–1937) had returned to New York State after building up his career in the banking industry in Michigan. His first involvement with managing electric railways was presiding over the Syracuse and East Side Railway in 1894. After several years of involvement with various local streetcar lines, Beebe turned his attention to the development of electric interurban railways. Beginning in 1899, the Beebe Syndicate grew to control 28 individual companies at its height in 1915. By this time, many properties were placed in receivership due to overwhelming debt. Large parts of the Syndicate were sold into foreclosure in 1917, with the remaining lines reorganized independently. Beebe left the Syracuse area in 1919 and moved to New York City to pursue a career in real estate. He returned to Kalamazoo, Michigan, in 1935 and died of a sudden heart attack in 1937.
The Rochester Railway Company operated a streetcar transit system throughout the city of Rochester from 1890 until its acquisition by Rochester Transit Corp. in 1938. Formed by a group of Pittsburgh investors, the Rochester Railway Company purchased the Rochester City & Brighton Railroad in 1890, followed by a lease of the Rochester Electric Railway in 1894. The Rochester and Suburban Railway was leased in 1905, extending the system's reach to Irondequoit and Sea Breeze. Rochester Railways was acquired by the Mohawk Valley Company, a subsidiary of the New York Central Railroad set up to take control of electric railways in its territory. In 1909 the holdings of the Mohawk Valley Company were consolidated as the New York State Railways.
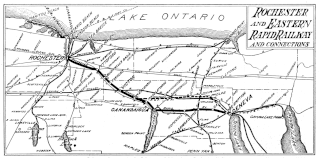
The Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway (R&ER) was an electric interurban railway in New York State, USA, connecting Rochester, Canandaigua, and Geneva.

The Rochester and Sodus Bay Railway was an electric interurban railway connecting Rochester with the shores of Lake Ontario at Sodus Point. The line was leased to the Rochester Railway Company in 1902 and later merged into New York State Railways in 1909. Ridership dropped off in the 1920s, and the railway east of Glen Haven was abandoned in 1929. The remaining local streetcar service ended in 1933.
The Rochester and Suburban Railway was a streetcar company that operated in the Rochester, New York area. The company was preceded by the Rochester and Lake Ontario Railway, which was formed in 1879 to construct a steam-powered railroad connecting Rochester at Portland Avenue with Sea Breeze on the shores of Lake Ontario. The line was operated with enclosed "dummy" steam locomotives. At the line's terminus, the railroad constructed a resort, which later became the modern Seabreeze amusement park. The railroad was leased by the Rochester and Irondequoit Railroad in 1893, which in turn built its own electric streetcar line along St. Paul Boulevard to the Summerville lakeside community in Irondequoit. The electric line only operated in the summer months, and connected to a ferry boat that transported passengers across the Genesee River to Charlotte. The opening of the Stutson Street Bridge in 1927 forced the termination of ferry service, and the railroads entered receivership soon after.
Connecticut Railway and Lighting Company was a streetcar and bus transit operator serving the region around Bridgeport, Norwalk, Derby, New Britain and Waterbury, Connecticut. It was formed in 1901 by United Gas Improvement Company of Philadelphia to manage the streetcar operations of the Connecticut Light and Power Company, which at the time included Central Railway and Electric Company, Norwalk Street Railway, and the Waterbury Traction Company. The newly formed Connecticut Railway and Lighting acquired Bridgeport Traction Company, Derby Street Railway, Milford Street Railway, Shelton Street Railway, Meriden, Southington and Compounce Tramway Company, and the Cheshire Street Railway. Connecticut Railway and Lighting was leased to the Consolidated Railway and in turn the Connecticut Company between 1906 and 1936. Streetcar operations were discontinued in 1937 when all lines were converted to bus. Transit operations continued until 1972, when all remaining bus operations were suspended and taken over by Connecticut Transit, except in Bridgeport- by the Greater Bridgeport Transit District in 1975.
The Newark and Marion Railway operated between Newark, New York, and Marion, New York. Chartered in 1900, it opened for business in 1906. The railroad was constructed by the Beebe Syndicate, a conglomeration of streetcar and interurban lines across New York State, though the Newark and Marion was never electrified. The company entered receivership in 1915, and control by the Beebe Syndicate ended. The railroad was reorganized as the Marion Railway Corporation in 1917. The Pennsylvania Railroad acquired the line in 1930. It continued to operate as a spur of the Elmira Branch through the Penn Central and Conrail eras. Operation passed to short line Ontario Midland Railroad in 1979. Dwindling freight traffic and deteriorating track conditions led to the line's closure in July 1984.
For over two decades in the early twentieth century, there existed a network of streetcars in Reno that served as the main mode of public transit in Reno, Nevada, United States. The system consisted of a streetcar network in the area of Reno and Sparks, Nevada, as well as an interurban line between Reno and the Moana Springs resort.
Fresno Traction Company operated electric trams in Fresno, California, from 1903 to 1939. Earlier horsecar tracks were improved and electrified under consolidated ownership which passed to Southern Pacific Transportation Company operation in 1910. A separate Fresno Interurban Railway shared some lines along Fresno city streets.
References
- ↑ Reifschneider, Felix E. (1947). Toonervilles of the Empire State. Orlando, Florida. p. 7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ King 1975, p. 1.
- ↑ King 1975, p. 51.
- ↑ Moodys Manual of Railroads and Corporation Securities. New York: Poor's Publishing Co. 1922. p. 533.
- ↑ King 1975, p. 52.