
At 824,292 km2 (318,261 sq mi), Namibia is the world's thirty-fourth largest country. After Mongolia, Namibia is the second least densely populated country in the world. Namibia got its name from the Namib desert that stretches along the coast of the Atlantic. It is also known for its wildlife.

South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian (eastern) coast. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers 1,390,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574 km (1,599 mi) river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

Malanje is the capital city of Malanje Province in Angola, with a population of 455,000, and a municipality, with a population of 506,847. Projected to be the thirteenth fastest growing city on the African continent between 2020 and 2025, with a 5.17% growth. It is located 380 kilometres (240 mi) east of Angola's capital Luanda. Near it are the spectacular Calandula waterfalls, the rock formations of Pungo Andongo, and the Capanda Dam. The climate is mainly humid, with average temperatures between 20 and 24 °C and rainfall 900 to 130 millimetres in the rainy season.

Malanje is a province of Angola. It has an area of 97,602 km2 and a 2014 census population of 986,363. Malanje is the provincial capital.

The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The Eastern Highlands extend north and south for about 300 kilometres (190 mi) through Zimbabwe's Manicaland Province and Mozambique's Manica Province.

Brachystegia is a genus of tree of the subfamily Detarioideae that is native to tropical Africa.

Augrabies Falls National Park is a national park located around the Augrabies Falls, about 120 km west of Upington in the Northern Cape Province, South Africa.

The wildlife of Zimbabwe occurs foremost in remote or rugged terrain, in national parks and private wildlife ranches, in miombo woodlands and thorny acacia or kopje. The prominent wild fauna includes African buffalo, African bush elephant, black rhinoceros, southern giraffe, African leopard, lion, plains zebra, and several antelope species.
Hyperolius vilhenai is a species of frog in the family Hyperoliidae. It is only known from its type locality, Cuílo, along the Luita River in northern Angola, although it is likely to occur in adjacent Democratic Republic of the Congo. Additional specimens from the Cangandala National Park have been provisionally assigned to this species. The specific name vilhenai honours Ernesto Jardim de Vilhena, a Portuguese naval officer, politician, and businessman. Common names Luita River reed frog and Vilhena's reed frog have been proposed for this frog.

The Angolan talapoin, also known as the southern talapoin, is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. Talapoins are the smallest species of Old-World monkeys.
Mavinga is a National Park in Kuando Kubango Province in south-eastern Angola. It covers an area of 46,076 square kilometres (17,790 sq mi). The Park was proclaimed in 2011 along with the neighbouring Luengue-Luiana National Park, which measures 22,610 square kilometres (8,730 sq mi). The two parks are contiguous and managed as a single unit. The parks were created to conserve the areas’ high ecological and biological value. Mavinga forms the western border of Africa's largest conservation area, the Kavango-Zambezi Trans-Frontier Conservation Area.

Angolan miombo woodlands cover most of central Angola and extend into the Democratic Republic of Congo. They are part of the larger miombo ecosystem that covers much of eastern and southern Africa.

The Kalahari Acacia-Baikiaea woodlands are an ecoregion located in Botswana, northern Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe.
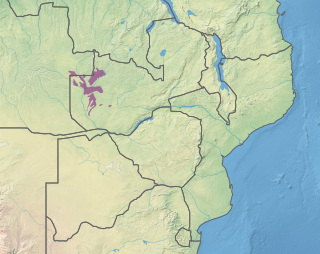
The Zambezian dry evergreen forest, also known as the Zambezian Cryptosepalum dry forest, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone.
Cangandala is a town and municipality in the province of Malanje (Malange) in Angola. It covers an area of 5,770 square kilometres (2,230 sq mi) and its population is 45,120.

The Chimanimani Mountains are a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The mountains are in the southern portion of the Eastern Highlands, or Manica Highlands, a belt of highlands that extend north and south along the international border, between the Zambezi and Save rivers.

The Magaliesberg Biosphere Reserve is located in South Africa between the cities of Pretoria and Johannesburg to the east and Rustenburg to the west. The reserve lies at the interface of two great African biomes — the Central Grassland Plateaux and the sub-Saharan savannah — and the remnants of a third biome, the Afro‐montane forest. The rich biodiversity includes floral species such as Aloe peglerae and Frithia pulchra, and faunal species such as the forest shrew, sable antelope and 443 bird species representing 46.6% of total bird species in the southern African sub-region.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
The Zambezian region is a large biogeographical region in Africa. The Zambezian region includes woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and thickets, extending from east to west in a broad belt across the continent. The Zambezian region lies south of the rainforests of the Guineo-Congolian region. The Zambezian region is bounded by deserts and xeric shrublands on the southwest, the Highveld grasslands of South Africa to the south, and the subtropical Maputaland forests on the southeast.
















