Related Research Articles

The RRS Discovery is a barque-rigged auxiliary steamship built in Dundee, Scotland for Antarctic research. Launched in 1901, she was the last traditional wooden three-masted ship to be built in the United Kingdom. Her first mission was the British National Antarctic Expedition, carrying Robert Falcon Scott and Ernest Shackleton on their first, and highly successful, journey to the Antarctic, known as the Discovery Expedition.
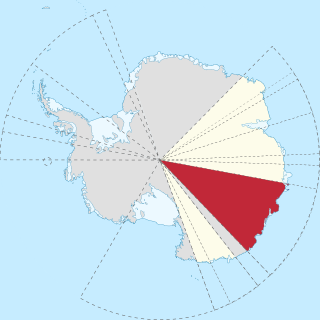
Wilkes Land is a large district of land in eastern Antarctica, formally claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory, though the validity of this claim has been placed for the period of the operation of the Antarctic Treaty, to which Australia is a signatory.
Bowman Island is a high ice-covered island, about 39 kilometres (24 mi) long and from 3 to 10 kilometres wide, shaped like a figure eight. Bowman Island is located at 65°16′48″S103°6′36″E. Bowman Island rises above the northeastern part of Shackleton Ice Shelf, which partially encloses the island, 40 kilometres (25 mi) northeast of Cape Elliott. Discovered on January 28, 1931, by British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson, who named it for Isaiah Bowman, then Director of the American Geographical Society.

The British Australian (and) New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) was a research expedition into Antarctica between 1929 and 1931, involving two voyages over consecutive Austral summers. It was a British Commonwealth initiative, driven more by geopolitics than science, and funded by the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand.

Mac. Robertson Land is the portion of Antarctica lying southward of the coast between William Scoresby Bay and Cape Darnley. It is located at 70°00′S65°00′E. In the east, Mac. Robertson Land includes the Prince Charles Mountains. It was named by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) (1929–1931), under Sir Douglas Mawson, after Sir Macpherson Robertson of Melbourne, a patron of the expedition.

Banzare Coast, part of Wilkes Land, is that portion of the coast of Antarctica lying between Cape Southard, at 122°05′E, and Cape Morse, at 130°10′E.
Cape Morse is a low, ice-covered cape which marks the east side of the entrance to Porpoise Bay and forms the division between Banzare Coast and Clarie Coast in Wilkes Land, Antarctica. It was delineated from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in 1946–47, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for William H. Morse, purser's steward on the brig Porpoise of the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–42) under Charles Wilkes.
Shirase Coast is the north segment of the relatively ill-defined coast along the east side of Ross Ice Shelf and Ross Sea, lying between the north end of Siple Coast and Cape Colbeck. Named by NZ-APC in 1961 after Lieutenant Nobu Shirase (1861-1946), leader of the Japanese expedition, whose ship Kainan Maru sailed near this coast in January 1912. Landings were made at Kainan Bay and at the Bay of Whales, the origin of a 160-mile journey southeast on Ross Ice Shelf. From 76°56′S155°55′W, another party landed for a sledge trip to the edge of the Queen Alexandra Range.
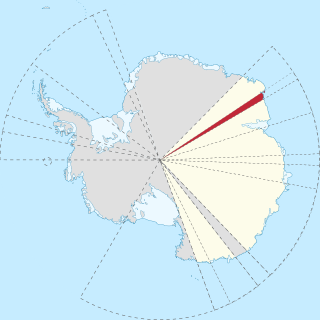
Kemp Land is a thin sliver of Antarctica including, and lying inland from, the Kemp Coast. Part of the Australian Antarctic claim it is defined as lying between 56° 25' E and 59° 34' E, and, as with other sectors of the Antarctic, is deemed being limited by the 60° S parallel. It is bounded in the east by Mac. Robertson Land and in the west by Enderby Land. Kemp Land includes one major group of islands, the Øygarden Group.

Cape Batterbee is a small, rocky point on the coast, the most northerly cape of Enderby Land. It is located 92 km north of Mount Elkins.
Conradi Peak is an isolated peak, 1,040 metres (3,410 ft) high, rising northward of the Napier Mountains and inland from the coast, some 19 nautical miles (35 km) southwest of Cape Borley. It was discovered in January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, who named it after a prominent member of the South African government who, in 1929, rendered much help to BANZARE during the stay of the Discovery at Cape Town.
Fold Island, also known as Foldøya is an offshore island north of Ives Tongue, 11 kilometres (6 nmi) long and 6 kilometres (3 nmi) wide, which, with smaller islands south, separate Stefansson Bay to the west from William Scoresby Bay to the east. This feature was seen by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel on the RSS William Scoresby in February 1936, who mapped it as part of the mainland. It was determined to be an island and named Foldøya by Norwegian cartographers who charted this area from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition (LCE) in January–February 1937.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.
Vogel Glacier is a glacier flowing into Flandres Bay 3 nautical miles (6 km) southeast of Cape Willems, on the west coast of Graham Land. The glacier appears on an Argentine government chart of 1952. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1960 for Hermann W. Vogel (1834–1898), German chemist who introduced the first orthochromatic emulsion for photographic plates in 1903.
Nilsen Bay is a small bay just west of Strahan Glacier, and 18 nautical miles (33 km) east-southeast of Cape Daly. Discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, who named it after the master of the Norwegian whaler Sir James Clark Ross which transported coal to Antarctic waters for the Discovery. On the map published in the Cape Daly and the Strahan Glacier is called Nielsen Bay. Recent examination of Mawson's notes shows that the bay was placed too far west and the name misspelled.
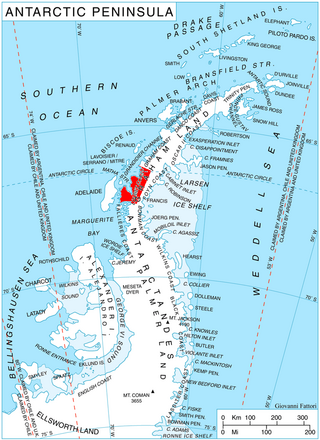
Darbel Bay is a bay 25 nautical miles (50 km) wide, indenting the west coast of Graham Land between Stresher Peninsula and Pernik Peninsula. Entered southwest of Cape Bellue and northeast of Cape Rey. The glaciers Widmark Ice Piedmont, Cardell, Erskine, Hopkins, Drummond, Widdowson, McCance, Solun, and Škorpil feed the bay.
Cape Davis is a rounded ice-covered cape along the north coast of Edward VIII Plateau, 17 kilometres (9 nmi) east of Magnet Bay. It was discovered on 12 January 1930 by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, who named it for Captain John King Davis, Director of Navigation under the Commonwealth Government and ship's captain and second in command of BANZARE.
Doyle Point is a point between Cape Batterbee and Cape Borley on the coast of Enderby Land. It was discovered on 12 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Mawson, who named it for Stuart Doyle, who assisted the expedition photographer with the film record.
Cape Moore is a cape at the east end of Tapsell Foreland which forms the north side of the entrance to Smith Inlet, on the north coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered in 1841 by Captain James C. Ross, who named it for Thomas E.L. Moore, mate on the Terror.

Kenneth Norman MacKenzie was an officer in the merchant fleet known for his role in the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition, for which he was awarded a Polar Medal.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Borley, Cape". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Borley, Cape". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.