
Cape Breton Island is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.

The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from Mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters.

Prince Edward Island is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. While it is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation". Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces.

Sydney is a former city and urban community on the east coast of Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada within the Cape Breton Regional Municipality. Sydney was founded in 1785 by the British, was incorporated as a city in 1904, and dissolved on 1 August 1995, when it was amalgamated into the regional municipality.

Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

Baddeck is a village in northeastern Nova Scotia, Canada. It is situated in the centre of Cape Breton, approximately 6 km east of where the Baddeck River empties into Bras d'Or Lake.

Cape Reinga, and officially Cape Reinga / Te Rerenga Wairua, is the northwesternmost tip of the Aupōuri Peninsula, at the northern end of the North Island of New Zealand. Cape Reinga is more than 100 km north of the nearest small town of Kaitaia.

Elephant Island is an ice-covered, mountainous island off the coast of Antarctica in the outer reaches of the South Shetland Islands, in the Southern Ocean. The island is situated 245 kilometres north-northeast of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, 1,253 kilometres west-southwest of South Georgia, 935 kilometres south of the Falkland Islands, and 885 kilometres southeast of Cape Horn. It is within the Antarctic claims of Argentina, Chile and the United Kingdom.

Devon Island is an island in Canada and the largest uninhabited island in the world. It is located in Baffin Bay, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the largest members of the Arctic Archipelago, the second-largest of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, Canada's sixth-largest island, and the 27th-largest island in the world. It has an area of 55,247 km2 (21,331 sq mi). The bedrock is Precambrian gneiss and Paleozoic siltstones and shales. The highest point is the Devon Ice Cap at 1,920 m (6,300 ft) which is part of the Arctic Cordillera. Devon Island contains several small mountain ranges, such as the Treuter Mountains, Haddington Range and the Cunningham Mountains. The notable similarity of its surface to that of Mars has attracted interest from scientists.

Kinngait, known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
Gordon Noel Humphreys (1883–1966) was a British born surveyor, pilot, botanist, explorer and doctor. Originally trained as a surveyor, Humphreys worked in both Mexico and Uganda. During World War I he served as a pilot with the Royal Flying Corps, was shot down and spent his internment training himself in botany.

Cape Jourimain is an area made of two islands and a section of mainland along the southwestern shore of the Northumberland Strait, three kilometres west of New Brunswick's easternmost point at Cape Tormentine. The two islands, Jourimain and Trenholm, have been connected to the mainland since 1966 by an artificial causeway. Cape Jourimain is the historic crossing point from New Brunswick (NB) to Prince Edward Island (PEI) and is host to the western end of the Confederation Bridge, Canada's longest fixed-link crossing. In 1980, the two islands, including a section of mainland, were designated as a National Wildlife Area (NWA) and in 2001 the Cape Jourimain Nature Centre, operated by a charitable nonprofit organization, was opened to the public.

Fort Chesterfield, known as Umiajuatnak by the Inuit, was a Hudson's Bay Company motor schooner which distributed supplies arriving in Chesterfield Inlet to isolated communities along Hudson Bay, including Repulse Bay, Eskimo Point, Coral Harbour, Fullerton Harbour, Wager Bay, and the inland community of Baker Lake, during the 1920s. It established a transportation and communications network for the entire region.
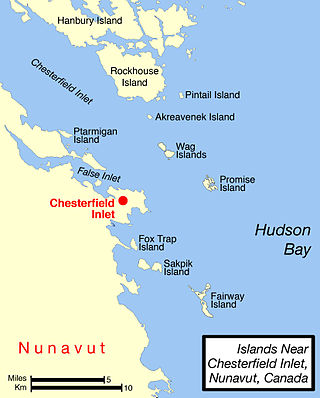
Pitsiulartok or Pituilaktok is a small, uninhabited island located at 63°15'N, 90°33'W in Hudson Bay, about 13 km from the community of Chesterfield Inlet, Nunavut, Canada. The narrow island is about 3.5 km in length and barely 1 km wide at its widest point. Traditionally it was a walrus-hunting ground for the local Inuit, and a landmark for southern whalers. It is part of a loose chain of small islands running along the coast, including Sakpik Island and Promise Island.
The Bjorne Peninsula is located on the western coast of Ellesmere Island, a part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It protrudes northwest into Norwegian Bay from the island's mainland. Goose Point, a narrow isthmus, is the furthest northwest landform. Other areas of the peninsula include Schei Point (north), Little Bear Cape (west), and Great Bear Cape (southwest). The peninsula's midsection is approximately 144 m (472 ft) above sea level.

Dorset Island, or Cape Dorset Island, is one of the Canadian Arctic islands located in Hudson Strait, Nunavut, Canada. It lies off the Foxe Peninsula area of southwestern Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region. It is serviced by an airport and a harbour.

Harry Potter and the Forbidden Journey is a motion-based dark ride located in The Wizarding World of Harry Potter-themed areas of Islands of Adventure in Orlando, Florida; Universal Studios Hollywood in Universal City, California; Universal Studios Japan in Osaka, Japan; and Universal Studios Beijing in Beijing, China. The ride takes guests through scenes and environments in and around Hogwarts Castle from the Harry Potter series of books and films. Mark Woodbury, president of Universal Creative, described the ride as an in-depth look at the world of Harry Potter, which utilizes never-before-seen technology which transforms "the theme park experience as you know it". The ride first opened at Islands of Adventure with The Wizarding World of Harry Potter on June 18, 2010; subsequent versions opened at Universal Studios Japan on July 15, 2014, at Universal Studios Hollywood on April 7, 2016, and at Universal Studios Beijing on September 20, 2021.

Suzette Mayr is a Canadian novelist who has written five critically acclaimed novels. Currently a professor at the University of Calgary's Faculty of Arts, Mayr's works have both won and been nominated for several literary awards.
Eetookashoo Bay is a waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located at the northern end of Axel Heiberg Island between Cape Thomas Hubbard and Cape Stallworthy. The bay is named in honor of Eetookashoo (Itukassuk), one of the Inuit who had traveled with Frederick Cook and Donald Baxter MacMillan.
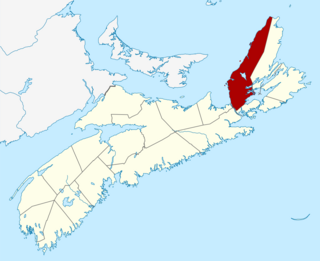
The Municipality of the County of Inverness is a county municipality on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It provides local government to about 17,000 residents of the historical county of the same name, except for the incorporated town of Port Hawkesbury and the Whycocomagh 2 Miꞌkmaq reserve, both of which are enclaves. Public services are provided in the areas of recreation, tourism, administration, finance, and public works.
















