In biology, regeneration is the process of renewal, restoration, and growth that makes genomes, cells, organisms, and ecosystems resilient to natural fluctuations or events that cause disturbance or damage. Every species is capable of regeneration, from bacteria to humans. Regeneration can either be complete where the new tissue is the same as the lost tissue, or incomplete where after the necrotic tissue comes fibrosis. At its most elementary level, regeneration is mediated by the molecular processes of gene regulation. Regeneration in biology, however, mainly refers to the morphogenic processes that characterize the phenotypic plasticity of traits allowing multi-cellular organisms to repair and maintain the integrity of their physiological and morphological states. Above the genetic level, regeneration is fundamentally regulated by asexual cellular processes. Regeneration is different from reproduction. For example, hydra perform regeneration but reproduce by the method of budding.

Crassula is a genus of succulent plants containing about 200 accepted species, including the popular jade plant. They are native to many parts of the globe, but cultivated varieties originate almost exclusively from species from the Eastern Cape of South Africa.

The Prodoxidae are a family of moths, generally small in size and nondescript in appearance. They include species of moderate pest status, such as the currant shoot borer, and others of considerable ecological and evolutionary interest, such as various species of "yucca moths".

Baffin Bay is a bay in South Texas, an inlet of the larger Laguna Madre. Located near the Gulf of Mexico, Baffin Bay forms part of the boundary between Kenedy County and Kleberg County.

The fauna of Connecticut comprise a variety of animal species.

Neuropsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPN5 gene. It is a photoreceptor protein sensitive to ultraviolet (UV) light. The OPN5 gene was discovered in mouse and human genomes and its mRNA expression was also found in neural tissues. Neuropsin is bistable at 0 °C and activates a UV-sensitive, heterotrimeric G protein Gi-mediated pathway in mammalian and avian tissues.
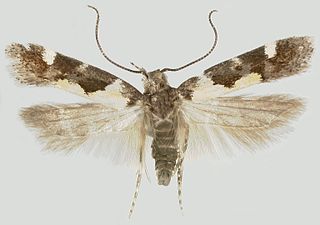
Stegasta is a genus of moth in the family Gelechiidae.

Antocha is a genus of crane flies in the family Limoniidae. It was first described by Baron Carl Robert Osten-Sacken in 1860.
Atarba is a genus of crane fly in the family Limoniidae.

The currant shoot borer moth is a species of moth of the family Prodoxidae. It is found in most of central, northern and eastern Europe. It is also found in North America.

Lampronia is a genus of moths of the family Prodoxidae.

Crassula capitella, is a perennial succulent plant native to southern Africa.
Pialea is a genus of small-headed flies. It is known from South America.
Epimorphosis is defined as the regeneration of a specific part of an organism in a way that involves extensive cell proliferation of somatic stem cells, dedifferentiation, and reformation, as well as blastema formation. Epimorphosis can be considered a simple model for development, though it only occurs in tissues surrounding the site of injury rather than occurring system-wide. Epimorphosis restores the anatomy of the organism and the original polarity that existed before the destruction of the tissue and/or a structure of the organism.
Cheryl A. Zimmer is a North American evolutionary biologist whose research interests are focused marine population ecology, specifically the role of hydrodynamics as a driving force in the evolution of marine life. She is a professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of California, Los Angeles. There she runs the Zimmer Lab, in collaboration with her husband and colleague Richard Zimmer.
Stegasta capitella, the teaweed moth, is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1794. It is found in West Indies and the south-eastern United States, where it has been recorded from Florida, Georgia and Texas.

MirGeneDB is a database of microRNA genes that have been validated and annotated as described in Fromm et al. 2015. The initial version contained 1'434 microRNA genes for human, mouse, chicken and zebrafish. Version 2.0 will contain more than 7'500 genes from 32 organisms representing nearly every metazoan group, and these microRNAs can be browsed, searched and downloaded. Planned release data for 2.0 is December 2017.