
Gegharkunik, is a province (marz) of Armenia. Its capital and largest city is the town of Gavar.

Sevan, is a town and urban municipal community, as well as one of the most and popular resorts in Armenia, located in the Gegharkunik Province on the northwestern shores of Lake Sevan. The town is built at a height of more than 1,925 metres above sea level, 65 km (40 mi) northeast of the capital Yerevan, and 35 km (22 mi) north of the provincial centre Gavar.

The Wolf River is a 225 mi (362 km) long tributary of the Fox River in northeastern Wisconsin in the Great Lakes region of the United States. The river is one of the two National Scenic Rivers in Wisconsin, along with the St. Croix River. The scenic portion is 24 miles (39 km) long. The river and its parent the Fox River and associated lakes are renown for their sturgeon which spawn every spring upstream on the lower river until blocked by the Shawano Dam. The river flows through mostly undeveloped forestland southerly from central Forest County in the north to Lake Poygan in the south. The lake is part of the Winnebago Pool of lakes fed by both the Fox and Wolf Rivers. The Fox-Wolf basin is usually considered to be a single unified basin and the rivers themselves may be referred to as the Fox-Wolf River system.

Sockeye salmon, also called red salmon, kokanee salmon, or blueback salmon, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it. This species is a Pacific salmon that is primarily red in hue during spawning. They can grow up to 84 cm in length and weigh 2.3 to 7 kg (5–15 lb). Juveniles remain in freshwater until they are ready to migrate to the ocean, over distances of up to 1,600 km (1,000 mi). Their diet consists primarily of zooplankton. Sockeye salmon are semelparous, dying after they spawn. Some populations, referred to as kokanee, do not migrate to the ocean and live their entire lives in freshwater.

The Hrazdan River is a major river and the second largest in Armenia. It originates at the northwest extremity of Lake Sevan and flows south through the Kotayk Province and Armenia's capital, Yerevan; the lake in turn is fed by several streams. In the Ararat plain it joins the Aras River along the border with Turkey. A series of hydro-electric plants have been constructed on the river. Its waters are in demand to irrigate crops.
The lake sturgeon, also known as the rock sturgeon, is a North American temperate freshwater fish, one of about 25 species of sturgeon. Like other sturgeons, this species is an evolutionarily ancient bottom feeder with a partly cartilaginous skeleton, an overall streamlined shape and skin bearing rows of bony plates on its sides and back, resembling an armored torpedo. The fish uses its elongated, spade-like snout to stir up the substrate and sediments on the beds of rivers and lakes while feeding. The lake sturgeon has four purely sensory organs that dangle near its mouth. These organs, called barbels, help the sturgeon to locate bottom-dwelling prey. Lake sturgeons can grow to a relatively large size, topping 7.25 ft long and weighing over 240 lb (108 kg).

Gavar, is a town and urban municipal community in Armenia serving as the administrative centre of Gegharkunik Province. It is situated among the high mountains of Gegham range to the west of Lake Sevan, with an average height of 1982 meters above sea level. Located 98 kilometers east of the capital Yerevan, the town had a population of 20,765 as per the 2011 census. As per the 2016 official estimate, the population of Gavar is 19,500.
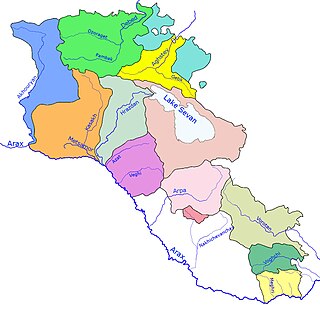
The Rivers and lakes in Armenia are mainly powered by fresh water. Throughout history Armenia has been called Nairi by the Assyrians meaning the "Land of the lakes and rivers". Armenia is home to many rivers and lakes.

Sevan National Park, is one of the 4 protected national parks of the Republic of Armenia, founded in 1978 to protect Lake Sevan and the surrounding areas. It is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Nature Protection and includes a research center, which monitors the ecosystems, and undertakes various conservation measures. Licensed fishing on the lake is also regulated.

The wildlife of Armenia includes wild boars, porcupines, various lizards, snakes and numerous species of birds. Endangered species living in Armenia are the Caucasian bear, Caucasian bearded goat, the Armenian mouflon (sheep) and the leopard.

Tsapatagh, is a small resort-village in the Gegharkunik Province of Armenia, on the north-eastern shore of Lake Sevan.
Capoeta baliki, also known as the fourbarbel scraper or Sakarya barb, is a species of cyprinid fish endemic to Turkey. It inhabits slowly flowing rivers, lakes and reservoirs.
Capoeta banarescui. the Colchic scraper or Banarescu’s barb, is a species of cyprinid fish known from Turkey. It inhabits swiftly flowing water with cobbles and pebbles bottom.
Capoeta caelestis, the Taurus scraper, is a species of freshwater cyprinid fish endemic to southern Anatolia, Turkey. It is less than 20 cm long.
Capoeta tinca, or the Anatolian khramulya or western fourbarbel scraper, is a species of cyprinid fish endemic to Turkey, inhabiting swiftly flowing rivers.

The Peipsi whitefish is a freshwater whitefish of the family Salmonidae that naturally occurs in Lake Peipus on the border of Estonia and Russia, from where it also ascends to Lake Võrtsjärv to spawn. It has been introduced in Lake Burtnieks (Latvia), Gulf of Riga, many lakes of northern Russia, Poland, Germany, Netherlands, Japan, Lake Sevan (Armenia) and Balkash (Kazakhstan). It is a benthopelagic fish up to 60 cm long.














