Related Research Articles

The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 association countries of the IEA represent 75% of global energy demand.

The hydrogen economy is an umbrella term for the roles hydrogen can play alongside low-carbon electricity to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. The aim is to reduce emissions where cheaper and more energy-efficient clean solutions are not available. In this context, hydrogen economy encompasses the production of hydrogen and the use of hydrogen in ways that contribute to phasing-out fossil fuels and limiting climate change.

Energy is sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Definitions of sustainable energy usually look at its effects on the environment, the economy, and society. These impacts range from greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution to energy poverty and toxic waste. Renewable energy sources such as wind, hydro, solar, and geothermal energy can cause environmental damage, but are generally far more sustainable than fossil fuel sources.

Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions are primarily caused by people burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Phasing out fossil fuel use can happen by conserving energy and replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources such as wind, hydro, solar, and nuclear power. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Governments have pledged to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but actions to date are insufficient to avoid dangerous levels of climate change.

Climate Group is a nonprofit organisation with a mission to drive climate action, fast, and achieve a world of net zero carbon emissions by 2050, with greater prosperity for all. The organisation builds influential networks of business and governments to unlock the power of collective action and scale. With its partners, Climate Group drives demand for net zero solutions, moving whole systems such as energy, transport, the built environment, industry and food towards a cleaner future. The organisation and its members are helping to shift global markets and policies towards faster reductions in carbon emissions.
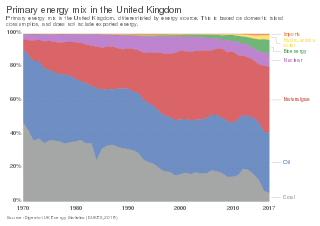
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.

A low-carbon economy (LCE) is an economy which absorbs as much greenhouse gas as it emits. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. There are many proven approaches for moving to a low-carbon economy, such as encouraging renewable energy transition, energy conservation, electrification of transportation, and carbon capture and storage. An example are zero-carbon cities.
The Climate Change Committee (CCC), originally named the Committee on Climate Change, is an independent non-departmental public body, formed under the Climate Change Act (2008) to advise the United Kingdom and devolved Governments and Parliaments on tackling and preparing for climate change. The Committee provides advice on setting carbon budgets, and reports regularly to the Parliaments and Assemblies on the progress made in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Notably, in 2019 the CCC recommended the adoption of a target of net zero greenhouse gas emissions by the United Kingdom by 2050. On 27 June 2019 the British Parliament amended the Climate Change Act (2008) to include a commitment to net zero emissions by 2050. The CCC also advises and comments on the UK's progress on climate change adaptation through updates to Parliament.

Fossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels to zero, to reduce deaths and illness from air pollution, limit climate change, and strengthen energy independence. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition, but is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies.

Despite abundant natural resources and a relatively small population, New Zealand is a net importer of energy, in the form of petroleum products. The ratio of non-renewable and renewable energy sources was fairly consistent from 1975 to 2008, with about 70 per cent of primary energy supply coming from hydrocarbon fuels. This ratio decreased to about 60 per cent in 2018. The proportion of non-renewable energy varies annually, depending on water flows into hydro-electricity lakes and demand for energy. In 2018, approximately 60% of primary energy was from non-renewable hydrocarbon fuels and 40% was from renewable sources. In 2007 energy consumption per capita was 120 gigajoules. Per capita energy consumption had increased 8 per cent since 1998. New Zealand uses more energy per capita than 17 of 30 OECD countries. New Zealand is one of 13 OECD countries that does not operate nuclear power stations.

Climate change is having major effects on the Chinese economy, society and the environment. China is the largest emitter of carbon dioxide, through an energy infrastructure heavily focused on coal. Other industries, such as a burgeoning construction industry and industrial manufacturing, contribute heavily to carbon emissions. However, like other developing countries, on a per-capita basis, China's carbon emissions are considerably less than countries like the United States. It has also been noted that higher-income countries have outsourced emissions-intensive industries to China. On the basis of cumulative CO2 emissions measured from 1751 through to 2017, China is responsible for 13% globally and about half of the United States' cumulative emissions. China is now the world's largest polluter and in 2023 recorded its hottest year on record with an average temperature of 10.7 C.

A zero-carbon city is a goal of city planners that can be variously defined. In a narrower sense of energy production and use, a zero-carbon city is one that generates as much or more carbon-free sustainable energy as it uses. In a broader sense of managing greenhouse gas emissions, a zero-carbon city is one that reduces its carbon footprint to a minimum by using renewable energy sources; reducing all types of carbon emissions through efficient urban design, technology use and lifestyle changes; and balancing any remaining emissions through carbon sequestration. Since the supply chains of a city stretch far beyond its borders, Princeton University's High Meadows Environmental Institute suggests using a transboundary definition of a net-zero carbon city as "one that has net-zero carbon infrastructure and food provisioning systems".

The Energiewende is the ongoing energy transition by Germany to a low carbon, environmentally sound, reliable, and affordable energy supply. The new system intends to rely heavily on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and energy demand management.

An energy transition is a major structural change to energy supply and consumption in an energy system. Currently, a transition to sustainable energy is underway to limit climate change. As much sustainable energy is renewable it is also known as the renewable energy transition. The current transition aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from energy quickly and sustainably, mostly by phasing-down fossil fuels and changing as many processes as possible to operate on low carbon electricity. A previous energy transition perhaps took place during the Industrial Revolution from 1760 onwards, from wood and other biomass to coal, followed by oil and later natural gas.

The Council on Energy, Environment and Water, commonly known as CEEW, is a Not-For profit Think Tank and policy institution based in New Delhi, India. CEEW was formed to provide independent research-based insights to policymakers for building a sustainable India. The Council also has an office in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh. It has multiple research projects running across 22 Indian states and other parts of the world.

Climate change is leading to long-term impacts on agriculture in Germany, more intense heatwaves and coldwaves, flash and coastal flooding, and reduced water availability. Debates over how to address these long-term challenges caused by climate change have also sparked changes in the energy sector and in mitigation strategies. Germany's energiewende has been a significant political issue in German politics that has made coalition talks difficult for Angela Merkel's CDU.

The San Diego Climate Action Plan was adopted by the city of San Diego in December 2015. It is a local climate action plan whose rules are defined by the California global warming Solutions Act of 2006, with the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Through this plan, the city initially set goals of eliminating half of all greenhouse emissions and sourcing all energy from renewable sources by the year 2035. With a coalition of business owners, environmental advocates, and community leaders, Mayor Kevin Faulconer approved the Climate Action Plan. The Climate Action Plan consists of several policies to ensure the economic and environmental growth of the city of San Diego. It was referred to in The San Diego Union-Tribune as "the most aggressive climate action plan in California."

Coal, cars and lorries vent more than a third of Turkey's six hundred million tonnes of annual greenhouse gas emissions, which are mostly carbon dioxide and part of the cause of climate change in Turkey. The nation's coal-fired power stations emit the most carbon dioxide, and other significant sources are road vehicles running on petrol or diesel. After coal and oil the third most polluting fuel is fossil gas; which is burnt in Turkey's gas-fired power stations, homes and workplaces. Much methane is belched by livestock; cows alone produce half of the greenhouse gas from agriculture in Turkey.

India is ranked seventh among the list of countries most affected by climate change in 2019. India emits about 3 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases each year; about two and a half tons per person, which is less than the world average. The country emits 7% of global emissions, despite having 17% of the world population. Temperature rises on the Tibetan Plateau are causing Himalayan glaciers to retreat, threatening the flow rate of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Yamuna and other major rivers. A 2007 World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) report states that the Indus River may run dry for the same reason. Heat waves' frequency and intensity are increasing in India because of climate change. Severe landslides and floods are projected to become increasingly common in such states as Assam. The climate change performance index of India ranks eighth among 63 countries which account for 92% of all GHG emissions in the year 2021.
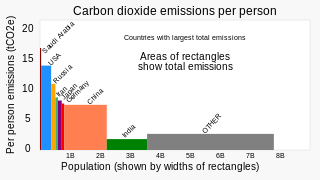
China's greenhouse gas emissions are the largest of any country in the world both in production and consumption terms, and stem mainly from coal burning, including coal power, coal mining, and blast furnaces producing iron and steel. When measuring production-based emissions, China emitted over 14 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases in 2019, 27% of the world total. When measuring in consumption-based terms, which adds emissions associated with imported goods and extracts those associated with exported goods, China accounts for 13 gigatonnes (Gt) or 25% of global emissions. According to the Carbon Majors Database, Chinese state coal production alone accounts for 14% of historic global emissions.
References
- ↑ "COP26: India PM Narendra Modi pledges net zero by 2070". BBC News. 1 November 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ↑ "India's Intended Nationally Determined Contributions" (PDF). Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change .
- ↑ "India: Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022, Allowing for a Carbon Credit Trading System, Comes into Force". Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "The Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill, 2022". prsindia.org. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "Cabinet approves India's Updated Nationally Determined Contribution to be communicated to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change". pib.gov.in. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "India Updates its Nationally Determined Contribution to Tackle Climate Change". The Wire. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "India's long-term low-carbon development strategy" (PDF). Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change .
- ↑ "India Outlines a Long-Term Decarbonization Strategy at COP 27". www.globaldata.com. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ Dickie, Gloria (14 November 2022). "COP27: India lays out plan for long-term decarbonization". Reuters. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "India's Long-Term Low-Carbon Development Strategy" (PDF). unfccc.int. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "Draft: National Energy Policy - NITI Aayog" (PDF). NITI Aayog .
- ↑ Kumar. J, Charles Rajesh; Majid, M. A. (7 January 2020). "Renewable energy for sustainable development in India: current status, future prospects, challenges, employment, and investment opportunities". Energy, Sustainability and Society. 10 (1): 2. doi: 10.1186/s13705-019-0232-1 . ISSN 2192-0567.
- ↑ "National Electric Mobility Mission Plan | BEE | Department of Heavy Industry (DHI)". evyatra.beeindia.gov.in. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020 – Policies". IEA. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ↑ "National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020 | ESCAP Policy Documents Management". policy.asiapacificenergy.org. Retrieved 28 August 2023.