
Ophrys apifera, known in Europe as the bee orchid, is a perennial herbaceous plant of the genus Ophrys, in the family of Orchidaceae. It serves as an example of sexually deceptive pollination and floral mimicry, a highly selective and highly evolved plant–pollinator relationship.

Anacamptis pyramidalis, the pyramidal orchid, is a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the genus Anacamptis of the family Orchidaceae. The scientific name Anacamptis derives from Greek ανακάμτειν 'anakamptein' meaning 'bend forward', while the Latin name pyramidalis refers to the pyramidal form of the inflorescence.

Dactylorhiza fuchsii, the common spotted orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae.

The genus Ophrys is a large group of orchids from the alliance Orchis in the subtribe Orchidinae. They are widespread across much of Europe, North Africa, Caucasus, the Canary Islands, and the Middle East as far east as Turkmenistan.

Friedrich Richard Rudolf Schlechter was a German taxonomist, botanist, and author of several works on orchids.

Cephalanthera longifolia, the narrow-leaved helleborine, sword-leaved helleborine or long-leaved helleborine, is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant in the family Orchidaceae. It is native to light woodland, and widespread across Europe, Asia and North Africa from Ireland and Morocco to China. This includes the United Kingdom, Iran, Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkey, Algeria, India, Pakistan, Germany, Italy, France, Spain, Portugal and many other countries.

Epipactis atrorubens, the dark-red helleborine or royal helleborine, is an herbaceous plant in the orchid family, Orchidaceae.

Orchis simia, commonly known as the monkey orchid, is a greyish pink to reddish species of the genus Orchis. It gets its common name from its lobed lip which mimics the general shape of a monkey's body.

Dactylorhiza incarnata, the early marsh-orchid, is a perennial, temperate-climate species of orchid generally found growing in wet meadows, and generally on base-rich soils, up to about 2100m asl. The species occurs widely in Europe and Asia from Portugal and Ireland east to Siberia and Xinjiang.

Dactylorhiza maculata, known as the heath spotted-orchid or moorland spotted orchid, is an herbaceous perennial plant of the family Orchidaceae. It is widespread in mountainous regions across much of Europe from Portugal and Iceland east to Russia. It is also found in Algeria, Morocco, and western Siberia.

Epipactis helleborine, the broad-leaved helleborine, is a terrestrial species of orchid with a broad distribution. It is a long lived herb which varies morphologically with ability to self-pollinate.

Epipactis palustris, the marsh helleborine, is a species of orchid native to Europe and Asia.

Epipactis microphylla, the small-leaved helleborine, is a species of orchid. It is native to much of Europe and to Southwest Asia as far east as Iran though noticeably absent from the British Isles and from Scandinavia. It has also been found in North Africa, in the Babor mountains in Little Kabylia, Algeria.
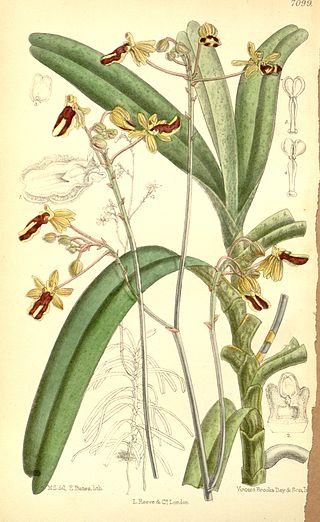
Cottonia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae: the only known species is Cottonia peduncularis. It is native to India and Sri Lanka. The genus was erected by Robert Wight and named after Major Frederick Cotton, an amateur botanist who served in the Madras Engineer Group and collected the species from Tellichery. A coloured illustration of the plant had been sent to Wight by Thomas C. Jerdon.

Heinrich (Harry) Wilhelm Eduard van Bruggen was a Dutch amateur botanist.

Epipactis dunensis, commonly known as dune helleborine, is a species of plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to Great Britain and Ireland. It typically grows to a height of 20–50 cm (7.9–19.7 in) and the upper half of the flowering stalk is hairy. The plant has a long, fleshy rootstock and three to ten yellowish green, oval to lance-shaped leaves arranged in opposite rows along the flowering stem with up to 35 flowers. The three sepals are greenish, the two petals paler, the lower part of the labellum is boat-shaped and dark, chocolate brown with a transparent, whitish rim and the epichile is heart-shaped with a pointed tip. Flowering occurs from late June to mid-August, the flowers are mainly self-pollinated, and the fruit is a capsule, from which light, microscopic seeds are spread by the wind.

In evolutionary biology, mimicry in plants is where a plant organism evolves to resemble another organism physically or chemically, increasing the mimic's Darwinian fitness. Mimicry in plants has been studied far less than mimicry in animals, with fewer documented cases and peer-reviewed studies. However, it may provide protection against herbivory, or may deceptively encourage mutualists, like pollinators, to provide a service without offering a reward in return.
Leslie Andrew Garay, born Garay László András, was an American botanist. He was the curator of the Oakes Ames Orchid Herbarium at Harvard University, where he succeeded Charles Schweinfurth in 1958. In 1957 he was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship.

Ophrys holosericea, the late spider orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the family Orchidaceae, native to western and central Europe and the Mediterranean region. There has been considerable confusion about the identity of this species and the correct spelling of its name.


















