
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea lasting a few days. Vomiting and muscle cramps may also occur. Diarrhea can be so severe that it leads within hours to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. This may result in sunken eyes, cold skin, decreased skin elasticity, and wrinkling of the hands and feet. Dehydration can cause the skin to turn bluish. Symptoms start two hours to five days after exposure.
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal.

Bornholm disease, also known as epidemic pleurodynia, is a condition characterized by myositis of the abdomen or chest caused by the Coxsackie B virus or other viruses. The myositis manifests as an intermittent stabbing pain in the musculature that is seen primarily in children and young adults.

Shigellosis is an infection of the intestines caused by Shigella bacteria. Symptoms generally start one to two days after exposure and include diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, and feeling the need to pass stools even when the bowels are empty. The diarrhea may be bloody. Symptoms typically last five to seven days and it may take several months before bowel habits return entirely to normal. Complications can include reactive arthritis, sepsis, seizures, and hemolytic uremic syndrome.
El Tor is a particular strain of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera. Also known as V. cholerae biotype eltor, it has been the dominant strain in the seventh global cholera pandemic. It is distinguished from the classic strain at a genetic level, although both are in the serogroup O1 and both contain Inaba, Ogawa and Hikojima serotypes. It is also distinguished from classic biotypes by the production of hemolysins.

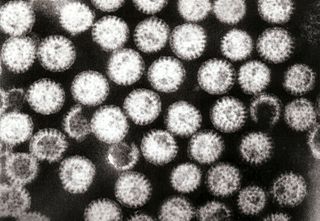
Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the Picornaviridae family of nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus Enterovirus, which also includes poliovirus and echovirus. Enteroviruses are among the most common and important human pathogens, and ordinarily its members are transmitted by the fecal–oral route. Coxsackieviruses share many characteristics with poliovirus. With control of poliovirus infections in much of the world, more attention has been focused on understanding the nonpolio enteroviruses such as coxsackievirus.
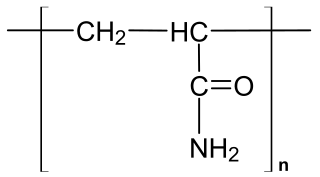
Polyacrylamide (abbreviated as PAM or pAAM) is a polymer with the formula (-CH2CHCONH2-). It has a linear-chain structure. PAM is highly water-absorbent, forming a soft gel when hydrated. In 2008, an estimated 750,000,000 kg were produced, mainly for water treatment and the paper and mineral industries.

Fecal occult blood (FOB) refers to blood in the feces that is not visibly apparent. A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) checks for hidden (occult) blood in the stool (feces).

An asymptomatic carrier is a person or other organism that has become infected with a pathogen, but shows no signs or symptoms.

Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydration may also occur. This typically lasts less than two weeks. Although it is not related to influenza, in the U.S. and U.K., it is sometimes called the "stomach flu".

Travelers' diarrhea (TD) is a stomach and intestinal infection. TD is defined as the passage of unformed stool while traveling. It may be accompanied by abdominal cramps, nausea, fever, headache and bloating. Occasionally dysentery may occur. Most travelers recover within three to four days with little or no treatment. About 12% of people may have symptoms for a week.

Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium. Oral rehydration therapy can also be given by a nasogastric tube. Therapy can include the use of zinc supplements to reduce the duration of diarrhea in infants and children under the age of 5. Use of oral rehydration therapy has been estimated to decrease the risk of death from diarrhea by up to 93%.
Bacillary dysentery is a type of dysentery, and is a severe form of shigellosis. It is associated with species of bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. The term is usually restricted to Shigella infections.

Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), also known as a stool transplant, is the process of transferring fecal bacteria and other microbes from a healthy individual into another individual. FMT is an effective treatment for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI). For recurrent CDI, FMT is more effective than vancomycin alone, and may improve the outcome after the first index infection.
Dientamoebiasis is a medical condition caused by infection with Dientamoeba fragilis, a single-cell parasite that infects the lower gastrointestinal tract of humans. It is an important cause of traveler's diarrhea, chronic abdominal pain, chronic fatigue, and failure to thrive in children.

Atracurium besilate, also known as atracurium besylate, is a medication used in addition to other medications to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It can also be used to help with endotracheal intubation but suxamethonium (succinylcholine) is generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour.
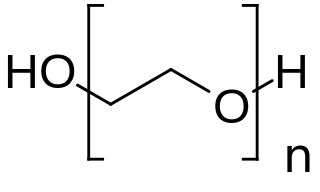
Macrogol, also called polyethylene glycol (PEG), is used as a laxative to treat constipation in children and adults. It is taken by mouth. Benefits usually occur within three days. Generally it is only recommended for up to two weeks. It is also used as an excipient. It is also used to clear the bowels before a colonoscopy, when the onset of the laxative effect is more rapid, typically within an hour.

The seventh cholera pandemic is the seventh major outbreak of cholera beginning in 1961 and continuing to the present. Cholera has become endemic in many countries. In 2017, WHO announced a global strategy aiming to end the pandemic by 2030.

Sabouraud agar or Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) is a type of agar growth medium containing peptones. It is used to cultivate dermatophytes and other types of fungi, and can also grow filamentous bacteria such as Nocardia. It has utility for research and clinical care.
Middlebrook 7H11 agar is identical to Middlebrook 7H10 agar, with an addition of pancreatic digest of casein to facilitate the growth of fastidious cultures of M. tuberculosis.













