
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses are as treatments for congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias; however, their relative toxicity prevents them from being widely used. Most commonly found as secondary metabolites in several plants such as foxglove plants, these compounds nevertheless have a diverse range of biochemical effects regarding cardiac cell function and have also been suggested for use in cancer treatment.

Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body.

Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles.
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as medications to decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension. CCBs are particularly effective against large vessel stiffness, one of the common causes of elevated systolic blood pressure in elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers are also frequently used to alter heart rate, to prevent peripheral and cerebral vasospasm, and to reduce chest pain caused by angina pectoris.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalaemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia.

Biofeedback is the technique of gaining greater awareness of many physiological functions of one's own body by using electronic or other instruments, and with a goal of being able to manipulate the body's systems at will. Humans conduct biofeedback naturally all the time, at varied levels of consciousness and intentionality. Biofeedback and the biofeedback loop can also be thought of as self-regulation. Some of the processes that can be controlled include brainwaves, muscle tone, skin conductance, heart rate and pain perception.

The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.

Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy may be used to treat a variety of tissue lesions. The most prominent use of the term refers to the surgical treatment, specifically known as cryosurgery or cryoablation. Cryosurgery is the application of extremely low temperatures to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue and is used most commonly to treat skin conditions.
An atonic seizure is a type of seizure that consists of partial or complete loss of muscle tone that is caused by temporary alterations in brain function. These seizures are brief – usually less than fifteen seconds. They usually begin in childhood and may persist into adulthood. The seizure itself causes no physical injury, but the loss of control, predominantly in trunk muscles, can result in direct injury from falling. Electroencephalography can be used to confirm diagnosis. It is rare and can be indicative of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome . Atonic seizures can occur while standing, walking, or sitting, and are often noticeable by a head drop. Fall injuries may result in impact to the face or head. As with common epileptic occurrences, no first aid is needed post-seizure, except in the instances where falling injuries have occurred. In some cases, a person may become temporarily paralyzed in part of his or her body. This usually does not last longer than 3 minutes.
Hemiballismus or hemiballism is a basal ganglia syndrome resulting from damage to the subthalamic nucleus in the basal ganglia. Hemiballismus is a rare hyperkinetic movement disorder, that is characterized by violent involuntary limb movements, on one side of the body, and can cause significant disability. Ballismus affects both sides of the body and is much rarer. Symptoms can decrease during sleep.

Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
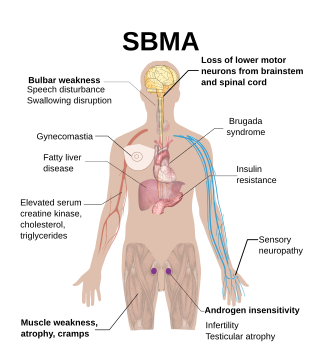
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), popularly known as Kennedy's disease, is a rare, adult-onset, X-linked recessive lower motor neuron disease caused by trinucleotide CAG repeat expansions in exon 1 of the androgen receptor (AR) gene, which results in both loss of AR function and toxic gain of function.
Sarcopenia is a type of muscle loss that occurs with aging and/or immobility. It is characterized by the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass, quality, and strength. The rate of muscle loss is dependent on exercise level, co-morbidities, nutrition and other factors. The muscle loss is related to changes in muscle synthesis signalling pathways. It is distinct from cachexia, in which muscle is degraded through cytokine-mediated degradation, although the two conditions may co-exist. Sarcopenia is considered a component of frailty syndrome. Sarcopenia can lead to reduced quality of life, falls, fracture, and disability.
Hypertonia is a term sometimes used synonymously with spasticity and rigidity in the literature surrounding damage to the central nervous system, namely upper motor neuron lesions. Impaired ability of damaged motor neurons to regulate descending pathways gives rise to disordered spinal reflexes, increased excitability of muscle spindles, and decreased synaptic inhibition. These consequences result in abnormally increased muscle tone of symptomatic muscles. Some authors suggest that the current definition for spasticity, the velocity-dependent over-activity of the stretch reflex, is not sufficient as it fails to take into account patients exhibiting increased muscle tone in the absence of stretch reflex over-activity. They instead suggest that "reversible hypertonia" is more appropriate and represents a treatable condition that is responsive to various therapy modalities like drug or physical therapy.

Penbutolol is a medication in the class of beta blockers, used in the treatment of high blood pressure. Penbutolol is able to bind to both beta-1 adrenergic receptors and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, thus making it a non-selective β blocker. Penbutolol is a sympathomimetic drug with properties allowing it to act as a partial agonist at β adrenergic receptors.

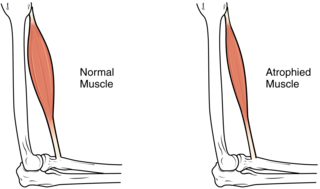
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakness and causes disability.
Thyrotoxic myopathy (TM) is a neuromuscular disorder that develops due to the overproduction of the thyroid hormone thyroxine. Also known as hyperthyroid myopathy, TM is one of many myopathies that lead to muscle weakness and muscle tissue breakdown. Evidence indicates the onset may be caused by hyperthyroidism. Physical symptoms of TM may include muscle weakness, the breakdown of muscle tissue, fatigue, and heat intolerance. Physical acts such as lifting objects and climbing stairs may become increasingly difficult. If untreated, TM can be an extremely debilitating disorder that can, in extreme rare cases, lead to death. If diagnosed and treated properly the effects can be controlled and in most cases reversed leaving no lasting effects.

Enobosarm, also formerly known as ostarine and by the developmental code names GTx-024, MK-2866, and S-22, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of androgen receptor-positive breast cancer in women and for improvement of body composition in people taking GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide. It was also under development for a variety of other indications, including treatment of cachexia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, muscle atrophy or sarcopenia, and stress urinary incontinence, but development for all other uses has been discontinued. Enobosarm was evaluated for the treatment of muscle wasting related to cancer in late-stage clinical trials, and the drug improved lean body mass in these trials, but it was not effective in improving muscle strength. As a result, enobosarm was not approved and development for this use was terminated. Enobosarm is taken by mouth.

Levamlodipine (INN), also known as levoamlodipine or S-amlodipine is a pharmacologically active enantiomer of amlodipine. Amlodipine belongs to the dihydropyridine group of calcium channel blocker used as an antihypertensive and antianginal agent. It was approved by the U.S. FDA in December 2019 and is currently marketed under the brand name Conjupri.













