Related Research Articles

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the United States Geological Survey and the Geological Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' physiographic regions. The U.S. uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands; the Appalachian Mountains are not synonymous with the Appalachian Plateau, which is one of the provinces of the Appalachian Highlands.

The Appalachian Trail, also called the A.T., is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost 2,200 miles (3,540 km) between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states. The Appalachian Trail Conservancy claims the Appalachian Trail to be the world's longest hiking-only trail. More than three million people hike segments of it each year.

McDowell County is a county located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 44,578. Its county seat is Marion.

The Shenandoah Valley is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia in the United States. The Valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, to the north by the Potomac River, to the south by the James River, and to the Southwest by the New River Valley. The cultural region covers a larger area that includes all of the Valley plus the Virginia Highlands to the west and the Roanoke Valley to the south. It is physiographically located within the Ridge and Valley Province and is a portion of the Great Appalachian Valley.

The Great Appalachian Valley, also called The Great Valley or Great Valley Region, is one of the major landform features of eastern North America. It is a gigantic trough, including a chain of valley lowlands, and the central feature of the Appalachian Mountains system. The trough stretches about 1,200 miles (1,900 km) from Quebec in the north to Alabama in the south and has been an important north–south route of travel since prehistoric times.

Appalachia is a geographic region located in the central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountains of New York, continuing south through the Blue Ridge Mountains and Great Smoky Mountains into northern Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi, with West Virginia near the center, being the only state entirely within the boundaries of Appalachia. In 2021, the region was home to an estimated 26.3 million people.
Trans-Appalachia is an area in the United States bounded to the east by the Appalachian Mountains and extending west roughly to the Mississippi River. It spans from the Midwest to the Upper South. The term is used most frequently when referring to the area as a frontier in the 17th, 18th and 19th century. During this period, the region gained its own identity, defined by its isolation and separation from the rest of the United States to the east. It included much of Ohio Country and at least the northern and eastern parts of the Old Southwest. It was never an organized territory or other political unit. Most of what was referred to by this name became the states of western Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee and western Virginia. It is still a vague and little used place name today.

The Allegheny Mountain Range — also spelled Alleghany or Allegany, less formally the Alleghenies — is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada. Historically it represented a significant barrier to westward land travel and development. The Alleghenies have a northeast–southwest orientation, running for about 300 miles (480 km) from north-central Pennsylvania southward, through western Maryland and eastern West Virginia.

The Eastern Continental Divide, Eastern Divide or Appalachian Divide is a hydrological divide in eastern North America that separates the easterly Atlantic Seaboard watershed from the westerly Gulf of Mexico watershed. It is one of six continental hydrological divides of North America which define several drainage basins, each of which drains to a particular body of water.

The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands division. The physiographic province is divided into three sections: the Hudson Valley, the Central, and the Tennessee.

The Kittanning Path was a major east-west Native American trail that crossed the Allegheny Mountains barrier ridge connecting the Susquehanna River valleys in the center of Pennsylvania to the highlands of the Appalachian Plateau and thence to the western lands beyond drained by the Ohio River. Kittanning Village was the first major Delaware (Lenape) Indian settlement along the descent from the Allegheny Plateau.

The Catawba, also known as Issa, Essa or Iswä but most commonly Iswa, are a federally recognized tribe of Native Americans, known as the Catawba Indian Nation. Their current lands are in South Carolina, on the Catawba River, near the city of Rock Hill. Their territory once extended into North Carolina, as well, and they still have legal claim to some parcels of land in that state. They were once considered one of the most powerful Southeastern tribes in the Carolina Piedmont, as well as one of the most powerful tribes in the South as a whole, with other, smaller tribes merging into the Catawba as their post-contact numbers dwindled due to the effects of colonization on the region.
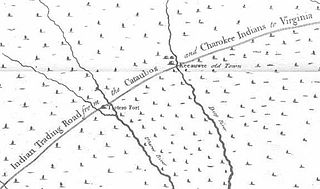
The Trading Path was a corridor of roads and trails between the Tsenacommacah or Chesapeake Bay region and the Cherokee, Catawba, and other Native-American countries in the Piedmont region of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. Indigenous folks had used and maintained much of the path for their expansive trading network for centuries prior to its use by Europeans and/or European-Americans. Native and later European/European-American settlements occupied key points along the path. That section of the Trading Path through the Carolina piedmont was also known as the Upper Road, and a portion between North Carolina and Georgia was called the Lower Cherokee Traders Path.
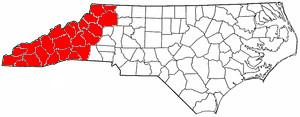
Western North Carolina is the region of North Carolina which includes the Appalachian Mountains; it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It contains the highest mountains in the Eastern United States, with 125 peaks rising to over 5,000 feet in elevation. Mount Mitchell at 6,684 feet, is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains and mainland eastern North America. The population of the 23 most commonly associated counties for the region, as measured by the 2020 U.S. Census, is 1,149,405. The region accounts for approximately 11% of North Carolina's total population.
The Appalachian National Scenic Trail spans 14 U.S. states over its roughly 2,200 miles (3,500 km): Georgia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine. The southern end is at Springer Mountain, Georgia, and it follows the ridgeline of the Appalachian Mountains, crossing many of its highest peaks and running almost continuously through wilderness before reaching the northern end at Mount Katahdin, Maine.

The Great Indian Warpath (GIW)—also known as the Great Indian War and Trading Path, or the Seneca Trail—was that part of the network of trails in eastern North America developed and used by Native Americans which ran through the Great Appalachian Valley. The system of footpaths extended from what is now upper New York to deep within Alabama. Various Native peoples traded and made war along the trails, including the Catawba, numerous Algonquian tribes, the Cherokee, and the Iroquois Confederacy. The British traders' name for the route was derived from combining its name among the northeastern Algonquian tribes, Mishimayagat or "Great Trail", with that of the Shawnee and Delaware, Athawominee or "Path where they go armed".
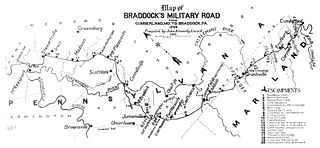
Nemacolin's Trail, or less often Nemacolin's Path, was an ancient Native American trail that crossed the great barrier of the Allegheny Mountains via the Cumberland Narrows Mountain pass, connecting the watersheds of the Potomac River and the Monongahela River in the present-day United States of America. Nemacolin's Trail connected what are now Cumberland, Maryland and Brownsville, Pennsylvania.

The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, and settlement patterns.

The Appalachian region has always had to allocate much resources and time into transportation due to the region's notable and unique geography. Mountainous terrain and commonly occurring adverse weather effects such as heavy fog and snowfall made roads hazardous and taxing on the traveling vehicles. Initially, European settlers found gaps in the mountains, among them the Cumberland Gap and the Wilderness Road. Another notable challenge of Appalachian travel is the political elements of constructing transportation routes. Most travel systems are funded by municipalities, but since The Appalachian area has several different states it can be difficult for the various governments to agree on how to work on transportation. The most influential forms of travel in the Appalachian region are based on water trading routes, roads and railroads.

The gaps of the Allegheny, meaning gaps in the Allegheny Ridge in west-central Pennsylvania, is a series of escarpment eroding water gaps along the saddle between two higher barrier ridge-lines in the eastern face atop the Allegheny Ridge or Allegheny Front escarpment. The front extends south through Western Maryland and forms much of the border between Virginia and West Virginia, in part explaining the difference in cultures between those two post-Civil War states. While not totally impenetrable to daring and energetic travelers on foot, passing the front outside of the water gaps with even sure footed mules was nearly impossible without navigating terrain where climbing was necessary on slopes even burros would find extremely difficult.
References
- Donehoo, G.P. (2019). A History of the Indian Villages and Place Names in Pennsylvania. Papamoa Press. ISBN 978-1-78912-305-0 . Retrieved 2021-05-02.