
Neurology is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system.
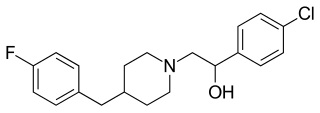
Eliprodil is an NMDA antagonist drug candidate which selectively inhibits the NR2B (GLUN2B) subtype NMDA receptor at submicromolar concentrations. Eliprodil failed a Phase III clinical trial for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in 1996, sponsored by Synthélabo Recherche.

Steven Laureys is a Belgian neurologist. He is principally known as a clinician and researcher in the field of neurology of consciousness.

Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis is a type of brain inflammation caused by antibodies. Early symptoms may include fever, headache, and feeling tired. This is then typically followed by psychosis which presents with false beliefs (delusions) and seeing or hearing things that others do not see or hear (hallucinations). People are also often agitated or confused. Over time, seizures, decreased breathing, and blood pressure and heart rate variability typically occur. In some cases, patients may develop catatonia.
Clinical neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that focuses on the scientific study of fundamental mechanisms that underlie diseases and disorders of the brain and central nervous system. It seeks to develop new ways of conceptualizing and diagnosing such disorders and ultimately of developing novel treatments.
The trigeminovascular system (TVS) refers to neurons and their axonal projections within the trigeminal nerve that project to the cranial meninges and meningeal blood vessels residing on the brain's surface. The term, introduced in 1983 denotes also the neuropeptides contained within axons that are released into the meninges to target vessels and surrounding cells.

Autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) is a type of encephalitis, and one of the most common causes of noninfectious encephalitis. It can be triggered by tumors, infections, or it may be cryptogenic. The neurological manifestations can be either acute or subacute and usually develop within six weeks. The clinical manifestations include behavioral and psychiatric symptoms, autonomic disturbances, movement disorders, and seizures.
Maiken Nedergaard is a Danish neuroscientist most well known for discovering the glymphatic system. She is a jointly appointed professor in the Departments of Neuroscience and Neurology at the University of Rochester Medical Center. She holds a part-time appointment in the Department of Neurosurgery within the University of Rochester Center for Translational Neuromedicine, where she is the principal investigator of the Division of Glial Disease and Therapeutics laboratory. She is also Professor of Glial Cell Biology at the University of Copenhagen, Center for Translational Neuromedicine.
Julie Bernhardt is an Australian physiotherapist and clinician scientist, known for her work in the field of stroke recovery. She has been a principal research fellow and an NHMRC senior research fellow and clinical head of the Stroke Division at the Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, University of Melbourne.

Vladimir Hachinski is a Canadian clinical neuroscientist and researcher based at the Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry at Western University. He is also a Senior Scientist at London's Robarts Research Institute. His research pertains in the greatest part to stroke and dementia, the interactions between them and their joint prevention through holistic brain health promotion. He and John W. Norris helped to establish the world's first successful stroke unit at Sunnybrook Hospital in Toronto, and, by extension, helped cement stroke units as the standard of care for stroke patients everywhere. He discovered that the control of the heart by the brain is asymmetric, the fight/flight (sympathetic) response being controlled by the right hemisphere and the rest and digest (parasympathetic) response being controlled by the left hemisphere and damage to one key component can lead to heart irregularities and sudden death. This discovery has added fundamental knowledge to how the brain controls the heart and blood pressure and lays the foundation for helping prevent sudden death.

Sarah Joanna Tabrizi FMedSci FRS is a British neurologist and neuroscientist in the field of neurodegeneration, particularly Huntington's disease. She is a Professor and Joint Head of the Department of Neurodegenerative Diseases at the UCL Institute of Neurology; the founder and Director of the UCL Huntington's Disease Centre; a Principal Investigator at the UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL; and an Honorary Consultant Neurologist at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London, where she established the Multidisciplinary Huntington's Disease Clinic. The UCL Huntington’s Disease Centre was officially opened on 1 March 2017 by UCL President and Provost Professor Michael Arthur.
Merit Cudkowicz is an American neurologist and neuroscientist who studies amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Cudkowicz is Julieanne Dorn Professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School, director of the ALS clinic and the Neurological Clinical Research Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), and chair of the Department of Neurology at MGH. Cudkowicz has led several large-scale collaborations and clinical trials to test novel treatments for ALS and as of 2020, researching ways to detect early biomarkers of ALS to improve diagnosis.
Susanne A. Schneider is a German neurologist at the Ludwig Maximilians-Universität in Munich, Germany who is known for her work in movement disorders.

Friedhelm Christoph Hummel is a German neuroscientist and neurologist. A full professor at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, he is the Defitech Chair of Clinical Neuroengineering, and the head of the Hummel Laboratory at EPFL's School of Life Sciences. He also is an associate professor of clinical neuroscience at the University of Geneva.

Ava Easton is a health scientist and researcher who specialises in encephalitis, acquired brain injury and narrative medicine, and is considered a world expert in her field of Encephalitis patient outcomes and quality of life. She is the current Chief Executive of The Encephalitis Society, a non-profit organisation which provides support and resources for those affected by the neurological disease of Encephalitis, and collaborates with various organisations on research into the disease.
Lynda D. Lisabeth is an American epidemiologist who is Professor and Senior Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs in the School of Public Health at the University of Michigan. Her research considers the epidemiology of stroke in the United States, and she has worked with the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke on the advancement of stroke research.
David John Werring is a British physician, neurologist, and academic specialising in stroke. He is professor of Neurology at the UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and current head of Stroke Research Centre and the department of Brain Repair & Rehabilitation at UCL.

Rita V. Krishnamurthi is a New Zealand academic, and since 2023 is a full professor at the Auckland University of Technology, specialising in the epidemiology of stroke and dementia.
Annemarei Ranta is a New Zealand academic neurologist, and is a full professor at the University of Otago, specialising in stroke care.

Louise Frances Basford Nicholson is a New Zealand neuroscientist, and is professor emerita at the University of Auckland, specialising in molecular mechanisms common to neurodegenerative diseases. In 2021, Nicholson was appointed a Companion of the New Zealand Order of Merit for services to neuroscience and education.










