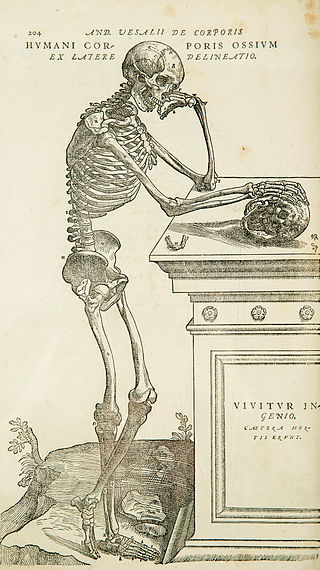
Anatomy is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology.

The human body is the entire structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organs and then organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.

Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes.

Gray's Anatomy is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter and first published in London in 1858. It has had multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd, remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible".

The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate.

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.
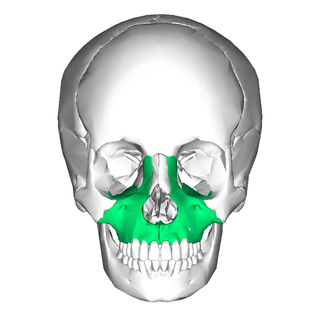
In vertebrates, the maxilla is the upper fixed bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible, which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw.

Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny.
Grey's Anatomy is an American medical drama television series focusing on the personal and professional lives of surgical interns, residents, and attendings at the fictional Seattle Grace Hospital, later named the Grey Sloan Memorial Hospital. The series premiered on March 27, 2005, on ABC as a mid-season replacement. The show's title is an allusion to Gray's Anatomy, a classic human anatomy textbook. Writer Shonda Rhimes developed the pilot and served as showrunner, head writer, and executive producer until stepping down in 2015. Set in Seattle, Washington, the series is filmed primarily in Los Angeles, California, and Vancouver, British Columbia.

Ellen Kathleen Pompeo is an American actress. One of the world's highest-paid actors since 2017, she has made multiple appearances on Forbes' year-end lists. Her accolades include a Screen Actors Guild Award and a Golden Globe Award nomination.
The Foundational Model of Anatomy Ontology (FMA) is a reference ontology for the domain of human anatomy. It is a symbolic representation of the canonical, phenotypic structure of an organism; a spatial-structural ontology of anatomical entities and relations which form the physical organization of an organism at all salient levels of granularity.
Private Practice is an American medical drama television series that aired on ABC from September 26, 2007, to January 22, 2013. A spin-off of Grey's Anatomy, the series takes place at Seaside Health & Wellness Center and chronicles the life of Dr. Addison Montgomery, played by Kate Walsh, as she leaves Seattle Grace Hospital in order to join a private practice, located in Los Angeles. Private Practice also revolves around Addison's co-workers at Oceanside Wellness Center, and how they deal with patients and the practice while still finding time to live their everyday lives.

A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body. Cadavers are used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Students in medical school study and dissect cadavers as a part of their education. Others who study cadavers include archaeologists and arts students. In addition, a cadaver may be used in the development and evaluation of surgical instruments.
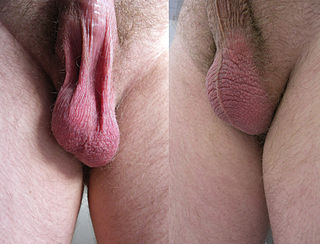
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures.

Katherine Heigl is an American actress. She played Izzie Stevens on the ABC television medical drama Grey's Anatomy from 2005 to 2010, a role that brought her recognition and accolades, including the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Drama Series in 2007.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.

Station 19 is an American action-drama television series created by Stacy McKee for ABC that premiered on March 22, 2018. It is the second spin-off of Grey's Anatomy. Set in Seattle, the series focuses on the lives of the men and women at Seattle Fire Station 19. It stars Jaina Lee Ortiz, Jason George, Grey Damon, Barrett Doss, Alberto Frezza, Jay Hayden, Okieriete Onaodowan, Danielle Savre, Miguel Sandoval, Boris Kodjoe, Stefania Spampinato, Carlos Miranda, Josh Randall, Merle Dandridge, and Pat Healy.

The seventeenth season of the American medical drama television series Grey's Anatomy was ordered in May 2019, by the American Broadcasting Company (ABC), as part of a double renewal with the sixteenth season. Shortly after, Krista Vernoff signed an agreement to continue serving as the showrunner of the series. Filming on the series began in September 2020 while the season did not premiere until November 12, 2020, both dates being delayed as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, for the 2020–2021 broadcast television season. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on television only allowed seventeen episodes to be produced, the fewest of any season since the fourth season. Numerous safety protocols were also implemented across various areas of production to prevent COVID-19 transmission.
















