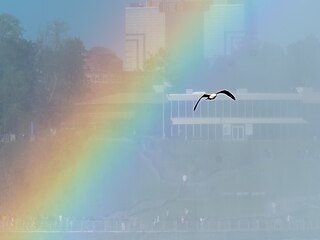In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases.

Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a scene file containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output.

Global illumination (GI), or indirect illumination, is a group of algorithms used in 3D computer graphics that are meant to add more realistic lighting to 3D scenes. Such algorithms take into account not only the light that comes directly from a light source, but also subsequent cases in which light rays from the same source are reflected by other surfaces in the scene, whether reflective or not.

In 3-D computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for modeling light transport for use in a wide variety of rendering algorithms for generating digital images.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.
In computer graphics, photon mapping is a two-pass global illumination rendering algorithm developed by Henrik Wann Jensen between 1995 and 2001 that approximately solves the rendering equation for integrating light radiance at a given point in space. Rays from the light source and rays from the camera are traced independently until some termination criterion is met, then they are connected in a second step to produce a radiance value. The algorithm is used to realistically simulate the interaction of light with different types of objects. Specifically, it is capable of simulating the refraction of light through a transparent substance such as glass or water, diffuse interreflection between illuminated objects, the subsurface scattering of light in translucent materials, and some of the effects caused by particulate matter such as smoke or water vapor. Photon mapping can also be extended to more accurate simulations of light, such as spectral rendering. Progressive photon mapping (PPM) starts with ray tracing and then adds more and more photon mapping passes to provide a progressively more accurate render.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
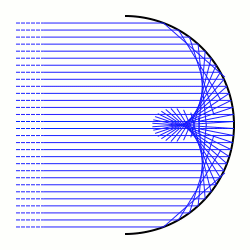
In differential geometry, a caustic is the envelope of rays either reflected or refracted by a manifold. It is related to the concept of caustics in geometric optics. The ray's source may be a point or parallel rays from a point at infinity, in which case a direction vector of the rays must be specified.
Brazil Rendering System was a proprietary commercial plugin for 3D Studio Max, Autodesk VIZ and Rhinoceros 3D. Steve Blackmon and Scott Kirvan started developing Brazil R/S while working as the R&D team of Blur Studio, and formed the company SplutterFish to sell and market Brazil. It was capable of photorealistic rendering using fast ray tracing and global illumination.

Sodium aluminate is an inorganic chemical that is used as an effective source of aluminium hydroxide for many industrial and technical applications. Pure sodium aluminate (anhydrous) is a white crystalline solid having a formula variously given as NaAlO2, NaAl(OH)4 (hydrated), Na2O·Al2O3, or Na2Al2O4. Commercial sodium aluminate is available as a solution or a solid.
Other related compounds, sometimes called sodium aluminate, prepared by reaction of Na2O and Al2O3 are Na5AlO4 which contains discrete AlO45− anions, Na7Al3O8 and Na17Al5O16 which contain complex polymeric anions, and NaAl11O17, once mistakenly believed to be β-alumina, a phase of aluminium oxide.

In optics, a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. Rays are used to model the propagation of light through an optical system, by dividing the real light field up into discrete rays that can be computationally propagated through the system by the techniques of ray tracing. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction, which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model.

Ray-tracing hardware is special-purpose computer hardware designed for accelerating ray tracing calculations.

In optics, a caustic or caustic network is the envelope of light rays which have been reflected or refracted by a curved surface or object, or the projection of that envelope of rays on another surface. The caustic is a curve or surface to which each of the light rays is tangent, defining a boundary of an envelope of rays as a curve of concentrated light. Therefore, in the photo to the right, caustics can be seen as patches of light or their bright edges. These shapes often have cusp singularities.
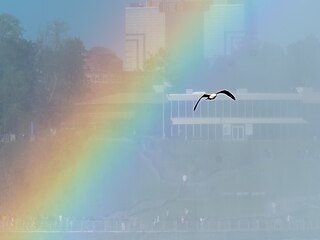
A rainbow is an optical phenomenon caused by refraction, internal reflection and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a continuous spectrum of light appearing in the sky. The rainbow takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the Sun. Rainbows can be caused by many forms of airborne water. These include not only rain, but also mist, spray, and airborne dew.

3D rendering is the 3D computer graphics process of converting 3D models into 2D images on a computer. 3D renders may include photorealistic effects or non-photorealistic styles.
Computer graphics lighting is the collection of techniques used to simulate light in computer graphics scenes. While lighting techniques offer flexibility in the level of detail and functionality available, they also operate at different levels of computational demand and complexity. Graphics artists can choose from a variety of light sources, models, shading techniques, and effects to suit the needs of each application.

A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.

Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter.
The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as optical, acoustic, microwave, and X-ray. In the figure below, the line representing a ray makes an angle θ with the normal. The angle of incidence at which light is first totally internally reflected is known as the critical angle. The angle of reflection and angle of refraction are other angles related to beams.
Caustic Graphics was a computer graphics and fabless semiconductor company that developed technologies to bring real-time ray-traced computer graphics to the mass market.