
Dayton is the sixth-largest city in the state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2018 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 140,640, while Greater Dayton was estimated to be at 803,416 residents. This makes Dayton the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Ohio and 63rd in the United States. Dayton is within Ohio's Miami Valley region, just north of Greater Cincinnati.

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering, and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological tissues. Tissue engineering involves the use of a tissue scaffold for the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own.

The University of Dayton (UD) is a private Roman Catholic research university in Dayton, Ohio. Founded in 1850 by the Society of Mary (Marianists), it is one of three Marianist universities in the nation and the second-largest private university in Ohio. The university's campus is in the city's southern portion and spans 388 acres on both sides of the Great Miami River. The campus is noted for the Immaculate Conception Chapel and the University of Dayton Arena.

Robert Samuel Langer, Jr. FREng is an American chemical engineer, scientist, entrepreneur, inventor and one of the twelve Institute Professors at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
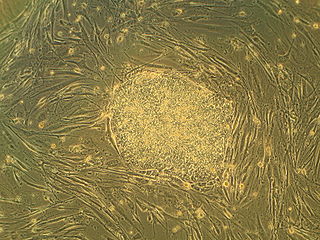
Regenerative medicine is a branch of translational research in tissue engineering and molecular biology which deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.
Neural engineering is a discipline within biomedical engineering that uses engineering techniques to understand, repair, replace, or enhance neural systems. Neural engineers are uniquely qualified to solve design problems at the interface of living neural tissue and non-living constructs.
Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition.

Anthony Atala, M.D., is the W.H. Boyce professor of urology and director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and chair of the Department of Urology at Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina. Regenerative medicine is "a practice that aims to refurbish diseased or damaged tissue using the body's own healthy cells".
Downtown Dayton is the central business district of Dayton, Ohio. Major reinvestment in the downtown area began heavily in the mid-1990s, and continues today with $2 billion in residential, commercial, health, and transportation developments that has or is taking place in the downtown area.
The National Center for Regenerative Medicine (NCRM) was founded in 2004 and specializes in regenerative medical research, while acting as the coordinating organization for other associated institutions.
Dr Nick Rhodes, Ph.D., is a Reader in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine at the University of Liverpool, in the U.K. Tissue Engineering can be described as the use of engineering techniques, including engineering materials and processes, in order to grow living tissues. Regenerative Medicine can be described as the treatment of defective tissues using the regenerative capacity of the body's healthy tissues. Combined, Dr Nick Rhodes describes the discipline as "aiming to repair tissue defects by driving regeneration of healthy tissues using engineered materials and processes."
ThePartnership in Education is a non-profit multidisciplinary health literacy and informal science education project based at Duquesne University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The Partnership in Education produces planetarium shows and other multimedia that focus on topics in health and biology.
Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic is a Serbian American biomedical engineer. She is a university professor at Columbia University, as well as a Mikati Foundation professor of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Sciences. She also heads the laboratory for Stem Cells and Tissue Engineering at Columbia University. She is part of the faculty at the Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Center for Human Development, both found at Columbia University. She is also an honorary professor at the Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy at the University of Belgrade, an honorary professor at the University of Novi Sad, and an adjunct professor at the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Tufts University.
The Morgridge Institute for Research is a private, nonprofit biomedical research institute in Madison, Wis., affiliated with the University of Wisconsin–Madison. The institute works to improve human health by conducting, enabling and translating interdisciplinary biomedical research. Research in regenerative biology, virology, medical devices and core computational technology is currently underway.
Ohio is a major research and development center, home to many institutions.

The Ohio bioscience sector strength was ranked #4 among USA states in 2008 by Business Facilities magazine.

Rui Luís Reis is a Portuguese scientist known for his research in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, biomaterials, biomimetics, stem cells, and biodegradable polymers. Reis is Professor of tissue engineering, regenerative medicine and stem cells at the Department of Polymer Engineering, School of Engineering of the University of Minho, in Braga and Guimarães. He is the Director of the 3B's Research Group, part of the Research Institute on Biomaterials, Biodegradables and Biomimetics (I3Bs) of UMinho (www.i3bs.uminho.pt), which specializes in the areas of regenerative Medicine, tissue engineering, stem cells and biomaterials. He is also the Director of the ICVS/3B's Associate Laboratory of UMinho. He is also the CEO of the European Institute of Excellence on Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Rui L. Reis is also, since 2013, the Vice-Rector (Vice-President) for research and innovation of UMinho. Since 2007 he is also editor-in-chief of the Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. He is since 2016 and until 2018 the Global (World) President of the Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine International Society (TERMIS). He is the responsible and PI of the EU funded project for the creation of the new center of Excellence, with headquarters in AvePark in Caldas das Taipas - Guimarães, the Discoveries Center for Regenerative and Precision Medicine in a Teaming process between University of Minho, University College London, University of Porto, University of Aveiro, University of Lisbon, University NOVA Lisbon.

Anthony Steven Weiss PhD AM FRSC FTSE FRSN FRACI, FTERM, FBSE is a university researcher, company founder and entrepreneur. He is the leading scientist in human tropoelastin research and synthetic human elastin. He holds the McCaughey Chair in Biochemistry, heads the Charles Perkins Centre Node in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, and is Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biotechnology at the University of Sydney. His discoveries are on human elastic materials that accelerate the healing and repair of arteries, skin and 3D human tissue components. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry. Weiss is on the editorial boards of the American Chemical Society Biomaterials Science and Engineering, Applied Materials Today (Elsevier), Biomaterials, Biomedical Materials, BioNanoScience (Springer) and Tissue Engineering. He is a biotechnology company founder, promoter of national and international technology development, and has received national and international awards, including the Order of Australia.

McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine is a medical research institute which is a partnership between the University of Pittsburgh and the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and is located in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States.

Jennifer Hartt Elisseeff is a professor of biomedical engineering, orthopedic surgery and ophthalmology at the Whiting School of Engineering and Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. Elisseeff's research is in the fields of regenerative medicine and immunoengineering. She was elected to the National Academy of Engineering in 2018 for "development and commercial translation of injectable biomaterials for regenerative therapies." In 2018 she was also elected to the National Academy of Medicine. Her research has been cited over cited over 17,000 and she has an h-index over 65.











