This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(November 2016) |
Cerasa is a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(November 2016) |

Cerasa is a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
It goes back a former diocese in the Roman province of Asia and Lydia in western Turkey. It belonged to the ecclesiastical province of Sardis.
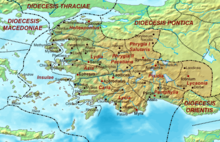
Cerasa, identifiable with Eliesler in modern Turkey, is an ancient episcopal see of the Roman province of Lydia in the civil Diocese of Asia. It was part of the Patriarchate of Constantinople and was suffragan of the Archdiocese of Sardis.
The lists of participants in the ecumenical councils have handed the names of four bishops of this ancient episcopal:
Cerasa survives today as titular bishop but has been vacant since May 2, 2001.

Tripolis on the Meander – also Neapolis, Apollonia, and Antoniopolis – was an ancient city on the borders of Phrygia, Caria and Lydia, on the northern bank of the upper course of the Maeander, and on the road leading from Sardes by Philadelphia to Laodicea ad Lycum. It was situated 20 km to the northwest of Hierapolis.
Palaeopolis (in Asia) was a city in ancient Lydia that was included in the late Roman province of Asia Prima. Its bishopric was thus a suffragan of Ephesus, the metropolitan see of that province.
Bageis, Bagis (Βάγις), or Bage (Βάγη) was an ancient Greek city in the province of Lydia in Asia Minor.
Hierocaesarea or Hierokaisareia, from the Greek for 'sacred' and the Latin for 'Caesar's', also known as Hieracome or Hierakome, was a town and bishopric in the late Roman province of Lydia, the metropolitan see of which was Sardis. It was inhabited during Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine times.

Hypaepa or Hypaipa was an Ancient city and (arch)bishopric in ancient Lydia, near the north bank of the Cayster River, and 42 miles from Ephesus, Ephesus and remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Harpasa was a city and bishopric in ancient Caria in Roman Asia Minor, which only remains a Latin Catholic titular see.

The See of Sardis or Sardes was an episcopal see in the city of that name. It was one of the Seven Churches of the Apocalypse, held by metropolitan bishops since the middle to late 1st century, with jurisdiction over the province of Lydia, when this was formed in 295. After 1369 it became a titular see both for the Greek Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church.

Nyssa was a town and bishopric in Cappadocia, Asia Minor. It is important in the history of Christianity due to being the see of the prominent 4th century bishop Gregory of Nyssa. Today, its name continues to be used as a titular see in the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church.

Silandus or Silandos was an episcopal city in the late Roman province of Lydia. It was near and gave its name to the present town of Selendi in Manisa Province, Turkey.
Aureliopolis in Lydia is a city in the Roman province of Lydia, previously called Tmolus or in Greek Τμῶλος (Tmolos). It issued coinage under each of these names, and one coin combines both names. In the Synecdemus it appears as Auliou Kome. The name "Aureliopolis" was given in honour of the emperor Marcus Aurelius.

The city of Blaundus was the seat of a bishopric in the Roman and Byzantine era. It was a suffragan of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Sardes, also in Lydia. It was part of the Patriarchate of Constantinople and was suffragan of Archdiocese of Sardis.
Coela or Cœla was a Roman city and bishopric in the province of Europa and is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
Daldis, was a town on the borders of ancient Lydia and Phrygia, a former bishopric, and is now a Latin Catholic titular see. It also minted coins in antiquity with the legend Δαλδιανων. It also bore the name Flaviocaesaria or Phlabiokaisareia, which is not attested among ancient authors but is reconstructed from epigraphic and other evidence.

Tracula is a former Ancient city and bishopric in Asia Minor, which remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Anineta, also known as Aninetum or Anineton, was a town of ancient Lydia or of Caria, and later of the Roman, and Byzantine empires, located in modern Turkey, the site of an ancient bishopric in and was an important site early in christianity. Anineta remains today a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church in the ecclesiastical province of Ephesus. In addition it minted coins bearing the legend Ἀνινησίων.

Satala or Satala in Lydia was a Roman era city and Bishopric in ancient Lydia.
Acrassus or Akrassos was an ancient Roman and Byzantine-era city in Lydia. in the Roman province of Asia and Lydia. Apparently, it is the same place that Ptolemy calls Nacrasa or Nakrasa, placed on the road from Thyatira to Pergamum.

Mostene (Μοστήνη), also called Mosteni or Mostenoi (Μοστηνοί), or Mostina (Μόστινα), or Mustene or Moustene (Μουστήνη), is a Roman and Byzantine era city in the Hyrcanian plain of ancient Lydia. The town minted its own coin of which many examples exist today. In 17 CE the city was hit by an earthquake and was assisted with relief from Tiberius.

Sala or Salena was a town of ancient Lydia, and is a suppressed, vacant and titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
It is located 9 km. northeast of Ödemiş/İzmir.(ref: Tmolos’ta saklı kutsal bir kent Dioshieron, Hüseyin Üreten, Journal of International Social Research, Vol 9, Issue 44: 562-578) Dios Hieron was a town of ancient Lydia, in the upper valley of the Cayster River. The city became part of the Roman Republic and the Roman province of Asia with the annexation of the Attalid kingdom. It also bore the name Diospolis (Διόσπολις), and was cited by the sixth century Byzantine geographer Stephanus of Byzantium under that name. It was renamed to Christopolis or Christoupolis in the 7th century and was known as Pyrgium or Pyrgion (Πυργίον) from the 12th century on. Pyrgion fell to the Turks in 1307, and became the capital of the beylik of Aydin. The town minted coins in antiquity, often with the inscription "Διοσιερειτων".