
Artillery are ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower.

A machine gun (MG) is a fully automatic and rifled firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles are typically designed more for firing short bursts rather than continuous firepower and are not considered true machine guns. Submachine guns fire handgun cartridges rather than rifle cartridges, therefore they are not considered machine guns, while automatic firearms of 20 mm (0.79 in) caliber or more are classified as autocannons rather than machine guns.

A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting and higher stopping power, with a barrel that has a helical or spiralling pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with both hands and braced firmly against the shooter's shoulder via a buttstock for stability during shooting. Rifles have been used in warfare, law enforcement, hunting and target shooting sports.

A kinetic energy penetrator (KEP), also known as long-rod penetrator (LRP), is a type of ammunition designed to penetrate vehicle armour using a flechette-like, high-sectional density projectile. Like a bullet or kinetic energy weapon, this type of ammunition does not contain explosive payloads and uses purely kinetic energy to penetrate the target. Modern KEP munitions are typically of the armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) type.

A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constructions, including specialized functions such as hunting, target shooting, training, and combat. Bullets are often tapered, making them more aerodynamic. Bullet size is expressed by weight and diameter in both imperial and metric measurement systems. Bullets do not normally contain explosives but strike or damage the intended target by transferring kinetic energy upon impact and penetration.
Tubes and primers are used to ignite the propellant in projectile weapons.
A muzzleloader is any firearm in which the user loads the projectile and the propellant charge into the muzzle end of the gun. This is distinct from the modern designs of breech-loading firearms, in which user loads the ammunition into the breech end of the barrel. The term "muzzleloader" applies to both rifled and smoothbore type muzzleloaders, and may also refer to the marksman who specializes in the shooting of such firearms. The firing methods, paraphernalia and mechanism further divide both categories as do caliber.

A shell, in a modern military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, contrasting with solid shells used for early rifled artillery, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. A shell can hold a tracer.

A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition from the breech end of the barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, in which the user loads the ammunition from the (muzzle) end of the barrel.
A rifled breech loader (RBL) is an artillery piece which, unlike the smoothbore cannon and rifled muzzle loader which preceded it, has rifling in the barrel and is loaded from the breech at the rear of the gun.

Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for more specialized roles in surface warfare such as naval gunfire support (NGFS) and anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) engagements. The term generally refers to powder-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines.

Field artillery in the American Civil War refers to the artillery weapons, equipment, and practices used by the artillery branch to support infantry and cavalry forces in the field. It does not include siege artillery, use of artillery in fixed fortifications, coastal or naval artillery. It also does not include smaller, specialized artillery pieces classified as infantry guns.

The M1819 Hall rifle was a single-shot breech-loading rifle designed by John Hancock Hall, patented on May 21, 1811, and adopted by the U.S. Army in 1819. It was preceded by the Harpers Ferry M1803. It used a pivoting chamber breech design and was made with either flintlock or percussion cap ignition systems. The years of production were from the 1820s to the 1840s at the Harpers Ferry Arsenal. This was the first breech-loading rifle to be adopted in large numbers by any nation's army, but not the first breech-loading military rifle – the Ferguson rifle was used briefly by the British Army in the American Revolutionary War. The Hall rifle remained overshadowed by common muskets and muzzleloading rifles which were still prevalent until the Civil War. The early flintlocks were mostly converted to percussion ignition.
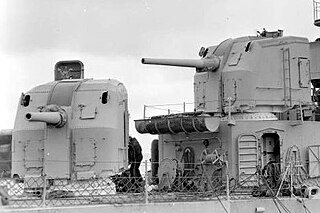
The Mark 12 5"/38-caliber gun was a United States dual-purpose naval gun, but also installed in single-purpose mounts on a handful of ships. The 38-caliber barrel was a mid-length compromise between the previous United States standard 5"/51 low-angle gun and 5"/25 anti-aircraft gun. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 38 calibers long. The increased barrel length provided greatly improved performance in both anti-aircraft and anti-surface roles compared to the 5"/25 gun. However, except for the barrel length and the use of semi-fixed ammunition, the 5"/38 gun was derived from the 5"/25 gun. Both weapons had power ramming, which enabled rapid fire at high angles against aircraft. The 5"/38 entered service on USS Farragut, commissioned in 1934, the first new destroyer design since the last Clemson was built in 1922. The base ring mount, which improved the effective rate of fire, entered service on USS Porter, commissioned in 1936.

The Armstrong RBL 7-inch gun, also known as the 110-pounder, was a heavy caliber Armstrong gun, an early type of rifled breechloader.
A muzzle-loading rifle is a muzzle-loaded small arm that has a rifled barrel rather than a smoothbore, and is loaded from the muzzle of the barrel rather than the breech. Historically they were developed when rifled barrels were introduced by the 1740ies, which offered higher accuracy than the earlier smoothbores. The American longrifle evolved from the German "Jäger" rifle; a popularly recognizable form of the "muzzleloader" was the Kentucky Rifle. Although by definition they must be reloaded after each shot in a time-consuming fashion, they are still produced for hunting.
Naval artillery in the Age of Sail encompasses the period of roughly 1571–1862: when large, sail-powered wooden naval warships dominated the high seas, mounting a large variety of types and sizes of cannon as their main armament. By modern standards, these cannon were extremely inefficient, difficult to load, and short ranged. These characteristics, along with the handling and seamanship of the ships that mounted them, defined the environment in which the naval tactics in the Age of Sail developed.

An Armstrong gun was a uniquely designed type of rifled breech-loading field and heavy gun designed by Sir William Armstrong and manufactured in England beginning in 1855 by the Elswick Ordnance Company and the Royal Arsenal at Woolwich. Such guns involved a built-up gun construction system of a wrought-iron tube surrounded by a number of wrought-iron strengthening coils shrunk over the inner tube to keep it under compression.

The 68-pounder cannon was an artillery piece designed and used by the British Armed Forces in the mid-19th century. The cannon was a smoothbore muzzle-loading gun manufactured in several weights firing projectiles of 68 lb (31 kg). Colonel William Dundas designed the 112 cwt version in 1841 which was cast the following year. The most common variant, weighing 95 long cwt (4,800 kg), dates from 1846. It entered service with the Royal Artillery and the Royal Navy and saw active service with both arms during the Crimean War. Over 2,000 were made and it gained a reputation as the finest smoothbore cannon ever made.
















