
Hudson Strait links the Atlantic Ocean and Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Quebec and Resolution Island off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km long with an average width of 125 km, varying from 70 km at the eastern entrance to 240 km at Deception Bay.

Victoria Island is a large island in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,008 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,182 sq mi]). It contains the world's largest island within an island within an island. The western third of the island belongs to the Inuvik Region in the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region.

The Gulf of Saint Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the Saint Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semienclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is a group of islands north of the Canadian mainland.
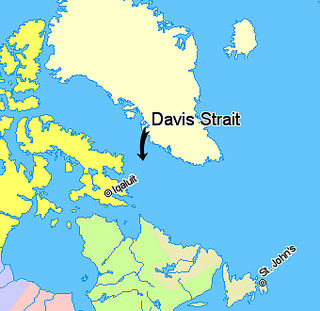
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Nunavut, Canada's Baffin Island. To the north is Baffin Bay. The strait was named for the English explorer John Davis (1550–1605), who explored the area while seeking a Northwest Passage. By the 1650s it was used for whale hunting.

Bransfield Strait is a body of water about 100 kilometres (60 mi) wide extending for 300 miles (500 km) in a general northeast – southwest direction between the South Shetland Islands and the Antarctic Peninsula.
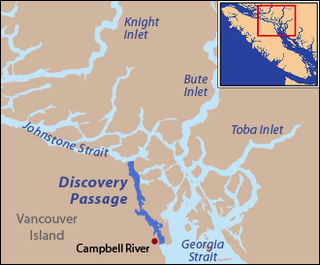
Discovery Passage is a channel that forms part of the Inside Passage between Vancouver Island and the Discovery Islands which lie off the British Columbia coast north of the Georgia Strait. It was named by Captain Vancouver for his ship, HMS Discovery. Most of the eastern shoreline of the passage is Quadra Island, with Sonora Island forming the shoreline at the northern end where Discovery Passage meets Johnstone Strait. The southern end of Discovery Passage enters the Strait of Georgia. It is 25 km (16 mi) in length and is typically about 2 km (1.2 mi) in width, less at Seymour Narrows which lies in the lower half of Discovery Passage.

Albone Glacier is a deeply entrenched narrow glacier on the east side of Wolseley Buttress flowing southward from Detroit Plateau on Nordenskjöld Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey from surveys (1960–61) and was named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Dan Albone, English designer of the Ivel tractor, the first successful tractor with an internal combustion engine.
Crozier Strait is a natural waterway in Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It separates Bathurst Island's Gregory Peninsula to the west from Milne Island and Little Cornwallis Island to the east. The strait, an arm of the Arctic Ocean, connects Queens Channel to the north with the McDougall Sound to the south. Kalvik Island is located within the strait, as is Karluk Island, an archaeological site.

Morton Strait is the 9 km (4.9 nmi)-long and 6.2 km (3.3 nmi)-wide strait between Snow Island on the southwest and Rugged Island and Livingston Island on the northeast, in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The Aim Rocks and Long Rock lie in the strait.

Bozhinov Glacier is the 5 km long and 2.5 km wide glacier on Danco Coast in Graham Land on the Antarctic Peninsula situated north of Krebs Glacier and south of Nobile Glacier. Flowing westwards to enter Gerlache Strait at Kapisturia Cove in Charlotte Bay.

Cape Conway is the rounded low and ice-free tipped cape forming the south extremity of Snow Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is a south entrance point for Boyd Strait. Tooth Rock rising to 85 m (279 ft) and lying 1.94 km (1.21 mi) to the south is the largest in a group of rocks extending 2.7 km (1.7 mi) from the cape. The area was visited by 19th century sealers.

Poduene Glacier is the 3.3 km long and 2.4 km wide glacier on Pefaur (Ventimiglia) Peninsula, Danco Coast on the west side of Antarctic Peninsula, situated west of Agalina Glacier. It drains the north slopes of Mount Zeppelin, and flows northwestwards into Gerlache Strait east of Eckener Point.
Nomad Rock is an isolated rock in Bransfield Strait, 5 nautical miles (9 km) off the north coast of Trinity Peninsula and 9 nautical miles (17 km) northeast of Cape Legoupil. So named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) because of confusion about the identity of geographic points along this coast, and because of the wandering of features and names on charts of this vicinity.
Croker Passage is a passage lying between the Christiania Islands and Two Hummock Island to the east, and Hoseason Island and Liège Island to the west, in the Palmer Archipelago. The northern entrance of this passage was very roughly charted and named "Croker Inlet" by Henry Foster in 1829, for John W. Croker (1780–1857), Secretary to the Admiralty at that time. The name has since been applied to the whole of this deep water passage, which provides an alternative entrance to the northern end of Gerlache Strait.
Diamonen Island is an island lying north of Moreno Rock in Gerlache Strait, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was charted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache, 1897–99. The island was called "Big Diamonen Island" by Captain Skidsmo of the Graham in 1921–22. The name was shortened by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960.
Eielson Peninsula is a rugged, mainly snow-covered peninsula, 37 kilometres (20 nmi) long in an east–west direction and averaging 19 kilometres (10 nmi) wide, lying between Smith Inlet and Lehrke Inlet on the east coast of Palmer Land. The rocky north wall of this peninsula is probably the feature which, on his flight of December 20, 1928, Sir Hubert Wilkins sighted and named "Cape Eielson" from a position above Stefansson Strait. This rock wall is conspicuous in the aerial photographs of the peninsula taken by members of the United States Antarctic Service in 1940 from an aerial position at the north side of Stefansson Strait. The peninsula is named for Carl B. Eielson, the pilot on Wilkins' flight of 1928.
Moreno Rock is a rock lying in Gerlache Strait, 7 nautical miles (13 km) west-southwest of Cape Sterneck, Antarctic Peninsula. It was named by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition (1897–99) under Lieutenant Adrien de Gerlache for Argentine scientist and statesman Francisco P. Moreno.
















