
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta borders British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada, with Saskatchewan being the other. The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds.

British Columbia is the westernmost province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east; the territories of Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north; the U.S. states of Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south, and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.6 million as of 2024, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada, with the 2021 census recording 2.6 million people in Metro Vancouver. British Columbia is Canada's third-largest province in terms of total area, after Quebec and Ontario.

North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.

Nova Scotia is a province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime provinces.

The prime minister of Canada is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the confidence of a majority of the elected House of Commons; as such, the prime minister typically sits as a member of Parliament (MP) and leads the largest party or a coalition of parties. As first minister, the prime minister selects ministers to form the Cabinet.

Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 15th prime minister of Canada from 1968 to 1979 and from 1980 to 1984. Between his non-consecutive terms as prime minister, he served as the leader of the Opposition from 1979 to 1980.

Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Metro Vancouver area had a population of 2.6 million in 2021, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 inhabitants per square kilometre (15,000/sq mi), and the fourth highest in North America.

The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is a Canadian public broadcaster and television network for both radio and television. It is a Crown corporation that serves as the national public broadcaster, with its English-language and French-language service units known as CBC and Radio-Canada, respectively.
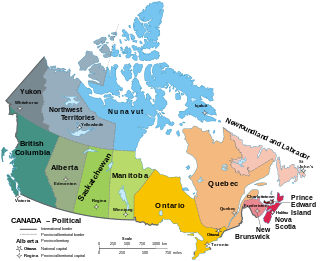
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.

The Liberal Party of Canada is a federal political party in Canada. The party espouses the principles of liberalism, and generally sits at the centre to centre-left of the Canadian political spectrum, with their main rival, the Conservative Party, positioned to their right and the New Democratic Party positioned to their left. The party is described as "big tent", practising "brokerage politics", attracting support from a broad spectrum of voters. The Liberal Party is the longest-serving and oldest active federal political party in the country, and has dominated federal politics of Canada for much of its history, holding power for almost 70 years of the 20th century. As a result, it has sometimes been referred to as Canada's "natural governing party".

The Order of Canada is a Canadian state order and the second-highest honour for merit in the system of orders, decorations, and medals of Canada, after the Order of Merit.

The Canadian Armed Forces are the unified military forces of Canada, including land, sea, and air commands referred to as the Canadian Army, Royal Canadian Navy and the Royal Canadian Air Force. The CAF also operates several other commands, including the Canadian Forces Intelligence Command, the Canadian Joint Operations Command, and the Canadian Special Operations Forces Command. Personnel may belong to either the Regular Force or the Reserve Force, which has four sub-components: the Primary Reserve, Supplementary Reserve, Cadet Organizations Administration and Training Service, and the Canadian Rangers. Under the National Defence Act, the Canadian Armed Forces are an entity separate and distinct from the Department of National Defence, which also exists as the civilian support system for the forces.
The Conservative Party of Canada, colloquially known as the Tories or simply the Conservatives, is a federal political party in Canada. It was formed in 2003 by the merger of the two main right-leaning parties, the Progressive Conservative Party and the Canadian Alliance, the latter being the successor of the Western Canadian–based Reform Party. The party sits at the centre-right to the right of the Canadian political spectrum, with their federal rival, the centre-left Liberal Party of Canada, positioned to their left. The Conservatives are defined as a "big tent" party, practising "brokerage politics" and welcoming a broad variety of members, including "Red Tories" and "Blue Tories".

Justin Pierre James Trudeau is a Canadian politician who has been serving as the 23rd prime minister of Canada since 2015 and the leader of the Liberal Party since 2013.

The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico.

Canadian nationality law details the conditions by which a person is a national of Canada. The primary law governing these regulations is the Citizenship Act, which came into force on February 15, 1977 and is applicable to all provinces and territories of Canada.

Halifax is the capital and most populous municipality of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the most populous municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of 2023, it is estimated that the population of the Halifax CMA was 518,711, with 348,634 people in its urban area. The regional municipality consists of four former municipalities that were amalgamated in 1996: Halifax, Dartmouth, Bedford, and Halifax County.

Nunavut is the largest, easternmost, and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for self-government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Montreal is the largest city in the province of Quebec, the second-largest in Canada, and the ninth-largest in North America. Founded in 1642 as Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary", it is now named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked mountain around which the early settlement was built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal and a few, much smaller, peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is 196 km (122 mi) east of the national capital, Ottawa, and 258 km (160 mi) southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City.
The New Democratic Party is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic, the party sits at the centre-left to left-wing of the Canadian political spectrum, with the party generally sitting to the left of the Liberal Party. The party was founded in 1961 by the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) and the Canadian Labour Congress (CLC).
















