In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
Circuit reliability (CiR) is the percentage of time an electronic circuit was available for use in a specified period of scheduled availability. Circuit reliability is given by where To is the circuit total outage time, Ts is the circuit total scheduled time, and Ta is the circuit total available time.
In telecommunication, data signaling rate (DSR), also known as gross bit rate, is the aggregate rate at which data passes a point in the transmission path of a data transmission system.
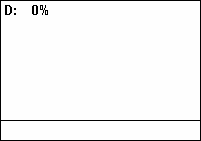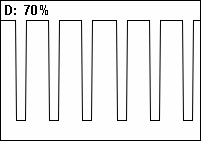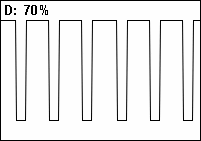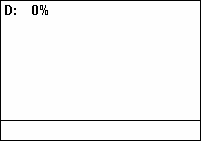
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as:
In telecommunication, an equivalent noise resistance is a quantitative representation in resistance units of the spectral density of a noise-voltage generator, given by where is the spectral density, is the Boltzmann constant, is the standard noise temperature, so .
In a system the mean time between outages (MTBO) is the mean time between equipment failures that result in loss of system continuity or unacceptable degradation.
Noise figure (NF) and noise factor (F) are figures of merit that indicate degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is caused by components in a signal chain. These figures of merit are used to evaluate the performance of an amplifier or a radio receiver, with lower values indicating better performance.
In telecommunications and fiber optics, ovality or noncircularity is the degree of deviation from perfect circularity of the cross section of the core or cladding of the fiber.
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system during normal system operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system. The term is used for repairable systems while mean time to failure (MTTF) denotes the expected time to failure for a non-repairable system.

Image response is a measure of performance of a radio receiver that operates on the superheterodyne principle.
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratios or, equivalently, as percentages with respect to a given reference value. In analog electronics and digital electronics, these percentages are commonly the 10% and 90% of the output step height: however, other values are commonly used. For applications in control theory, according to Levine, rise time is defined as "the time required for the response to rise from x% to y% of its final value", with 0% to 100% rise time common for overdamped second order systems, 5% to 95% for critically damped and 10% to 90% for underdamped ones. According to Orwiler, the term "rise time" applies to either positive or negative step response, even if a displayed negative excursion is popularly termed fall time.
Digital Signal 1 is a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs. DS1 is the primary digital telephone standard used in the United States, Canada and Japan and is able to transmit up to 24 multiplexed voice and data calls over telephone lines. E-carrier is used in place of T-carrier outside the United States, Canada, Japan, and South Korea. DS1 is the logical bit pattern used over a physical T1 line; in practice, the terms DS1 and T1 are often used interchangeably.
Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed in failures per unit of time. It is usually denoted by the Greek letter λ (lambda) and is often used in reliability engineering.
In sports, a winning percentage or Copeland score is the fraction of games or matches a team or individual has won. The statistic is commonly used in standings or rankings to compare teams or individuals. It is defined as wins divided by the total number of matches played. A draw counts as a 1⁄2 win.
In telecommunications, the carrier-to-noise ratio, often written CNR or C/N, is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a modulated signal. The term is used to distinguish the CNR of the radio frequency passband signal from the SNR of an analog base band message signal after demodulation. For example, with FM radio, the strength of the 100 MHz carrier with modulations would be considered for CNR, whereas the audio frequency analogue message signal would be for SNR; in each case, compared to the apparent noise. If this distinction is not necessary, the term SNR is often used instead of CNR, with the same definition.
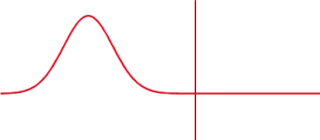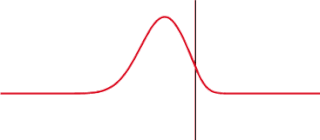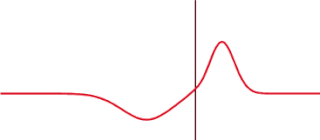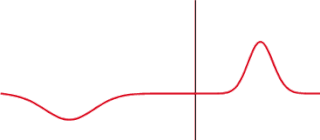
The transmission coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A transmission coefficient describes the amplitude, intensity, or total power of a transmitted wave relative to an incident wave.
In computing, computer performance is the amount of useful work accomplished by a computer system. Outside of specific contexts, computer performance is estimated in terms of accuracy, efficiency and speed of executing computer program instructions. When it comes to high computer performance, one or more of the following factors might be involved:
Availability is the probability that a system will work as required when required during the period of a mission. The mission could be the 18-hour span of an aircraft flight. The mission period could also be the 3 to 15-month span of a military deployment. Availability includes non-operational periods associated with reliability, maintenance, and logistics.
Operational availability in systems engineering is a measurement of how long a system has been available to use when compared with how long it should have been available to be used.
Time Slotted Channel Hopping or Time Synchronized Channel Hopping (TSCH) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks.



