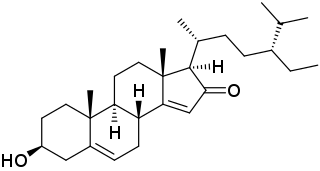
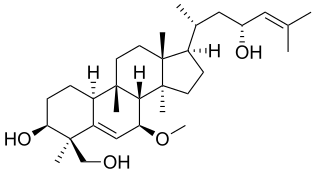
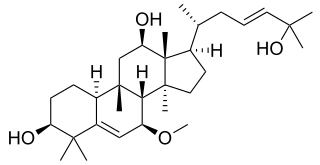
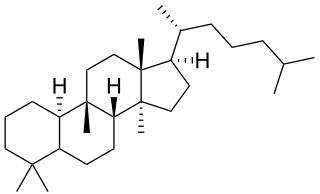
Charantoside is any of several related cucurbitane triterpenoid glycosides found in the fruits bitter melon vine (Momordica charantia). [1] They include:

In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of Heliconius butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body.
- charantoside I, (19R,23E)-5β,19-Epoxy-19-methoxycucurbita-6,23,25-trien-3β-ol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: amorphous solid.
- charantoside II, (19R,23R)-5β,19-Epoxy-19,23-dimethoxycucurbita-6,24-dien-3β-ol 3-O-β-D-allopyranoside: amorphous solid.
- charantoside III, (23E)-5β,19-Epoxycucurbita-6,23,25-trien-3β-ol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: amorphous solid.
- charantoside IV, (23E)-5β,19-Epoxycucurbita-6,23,25-trien-3β-ol 3-O-β-D-allopyranoside: colorless needles, melting at 256–260 °C.
- charantoside V, (23R)-5β,19-Epoxy-23-methoxycucurbita-6,24-dien-3β-ol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: colorless needles, melting at 235–240 °C.
- charantoside VI, (23S)-5β,19-Epoxy-23-methoxycucurbita-6,24-dien-3β-ol 3-O-β-D-allopyranoside: amorphous solid.
- charantoside VII, (23E)-3β-Hydroxycucurbita-6,23,25-trien-5β,19-olide 3-O-β-Dglucopyranoside: colorless needles, melting at 258–262 °C
- charantoside VIII, (23E)-3β-Hydroxy-7β,25-dimethoxycucurbita-5,23-dien-19-al 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: amorphous solid.
Charantosides I through VIII can be extracted from the fresh fruit with methanol and ethyl acetate. [1]
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol among others, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated MeOH). Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH
3–COO–CH
2–CH
3, simplified to C
4H
8O
2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, decaffeinating tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tonnes. In 2004, an estimated 1.3 million tonnes were produced worldwide.