Related Research Articles
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.

A limited liability company (LLC) is the United States-specific form of a private limited company. It is a business structure that can combine the pass-through taxation of a partnership or sole proprietorship with the limited liability of a corporation. An LLC is not a corporation under the laws of every state; it is a legal form of a company that provides limited liability to its owners in many jurisdictions. LLCs are well known for the flexibility that they provide to business owners; depending on the situation, an LLC may elect to use corporate tax rules instead of being treated as a partnership, and, under certain circumstances, LLCs may be organized as not-for-profit. In certain U.S. states, businesses that provide professional services requiring a state professional license, such as legal or medical services, may not be allowed to form an LLC but may be required to form a similar entity called a professional limited liability company (PLLC).
A creditor or lender is a party that has a claim on the services of a second party. It is a person or institution to whom money is owed. The first party, in general, has provided some property or service to the second party under the assumption that the second party will return an equivalent property and service. The second party is frequently called a debtor or borrower. The first party is called the creditor, which is the lender of property, service, or money.
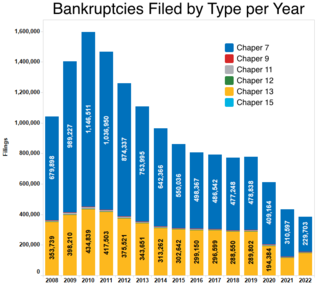
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).

A limited partnership (LP) is a type of partnership with general partners who have a right to manage the business and limited partners who have no right to manage the business but have only limited liability for its debts. Limited partnerships are distinct from limited liability partnerships, in which all partners have limited liability.

A general partnership, the basic form of partnership under common law, is in most countries an association of persons or an unincorporated company with the following major features:
In finance, a floating charge is a security interest over a fund of changing assets of a company or other legal person. Unlike a fixed charge, which is created over ascertained and definite property, a floating charge is created over property of an ambulatory and shifting nature, such as receivables and stock.

Salomon v A Salomon & Co Ltd[1896] UKHL 1, [1897] AC 22 is a landmark UK company law case. The effect of the House of Lords' unanimous ruling was to uphold firmly the doctrine of corporate personality, as set out in the Companies Act 1862, so that creditors of an insolvent company could not sue the company's shareholders for payment of outstanding debts.
In finance, a security interest is a legal right granted by a debtor to a creditor over the debtor's property which enables the creditor to have recourse to the property if the debtor defaults in making payment or otherwise performing the secured obligations. One of the most common examples of a security interest is a mortgage: a person borrows money from the bank to buy a house, and they grant a mortgage over the house so that if they default in repaying the loan, the bank can sell the house and apply the proceeds to the outstanding loan.

The Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act is one of the statutes that regulates the law on bankruptcy and insolvency in Canada. It governs bankruptcies, consumer and commercial proposals, and receiverships in Canada.

A series limited liability company, commonly known as a series LLC, protected cell company, segregated account company, or segregated portfolio company, and sometimes abbreviated as SLLC, is a form of a limited liability company that provides liability protection across multiple "series" each of which is theoretically protected from liabilities arising from the other series. In overall structure, the series LLC has been described as a master LLC that has separate divisions, which is similar to an S corporation with Q-subs.
Asset protection is a set of legal techniques and a body of statutory and common law dealing with protecting assets of individuals and business entities from civil money judgments. The goal of asset protection planning is to insulate assets from claims of creditors without perjury or tax evasion.

United Kingdom insolvency law regulates companies in the United Kingdom which are unable to repay their debts. While UK bankruptcy law concerns the rules for natural persons, the term insolvency is generally used for companies formed under the Companies Act 2006. Insolvency means being unable to pay debts. Since the Cork Report of 1982, the modern policy of UK insolvency law has been to attempt to rescue a company that is in difficulty, to minimise losses and fairly distribute the burdens between the community, employees, creditors and other stakeholders that result from enterprise failure. If a company cannot be saved it is liquidated, meaning that the assets are sold off to repay creditors according to their priority. The main sources of law include the Insolvency Act 1986, the Insolvency Rules 1986, the Company Directors Disqualification Act 1986, the Employment Rights Act 1996 Part XII, the EU Insolvency Regulation, and case law. Numerous other Acts, statutory instruments and cases relating to labour, banking, property and conflicts of laws also shape the subject.
Bankruptcy in Irish Law is a legal process, supervised by the High Court whereby the assets of a personal debtor are realised and distributed amongst his or her creditors in cases where the debtor is unable or unwilling to pay his debts.

Commercial insolvency in Canada has options and procedures that are distinct from those available in consumer insolvency proceedings. It is governed by the following statutes:

The Companies' Creditors Arrangement Act is a statute of the Parliament of Canada that allows insolvent corporations owing their creditors in excess of $5 million to restructure their businesses and financial affairs.
Insolvency in South African law refers to a status of diminished legal capacity imposed by the courts on persons who are unable to pay their debts, or whose liabilities exceed their assets. The insolvent's diminished legal capacity entails deprivation of certain of his important legal capacities and rights, in the interests of protecting other persons, primarily the general body of existing creditors, but also prospective creditors. Insolvency is also of benefit to the insolvent, in that it grants him relief in certain respects.

British Virgin Islands bankruptcy law is principally codified in the Insolvency Act, 2003, and to a lesser degree in the Insolvency Rules, 2005. Most of the emphasis of bankruptcy law in the British Virgin Islands relates to corporate insolvency rather than personal bankruptcy. As an offshore financial centre, the British Virgin Islands has many times more resident companies than citizens, and accordingly the courts spend more time dealing with corporate insolvency and reorganisation.

Cayman Islands company law is primarily codified in the Companies Law and the Limited Liability Companies Law, 2016, and to a lesser extent in the Securities and Investment Business Law. The Cayman Islands is a leading offshore financial centre, and financial services form a significant part of the economy of the Cayman Islands. Accordingly company law forms a much more prominent part of the law of the Cayman Islands than might otherwise be expected.
Anguillan company law is primarily codified in three principal statutes:
- the International Business Companies Act ;
- the Companies Act ; and
- the Limited Liability Companies Act.
References
- 1 2 3 4 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Charging Order". Encyclopædia Britannica . Vol. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 859.
- ↑ Brown, Janson & Co. v. A. Hutchinson & Co., 1 Q.B. 737, 2 (Eng. C.A. 1895) (Lindley, J.).
- ↑ "Evans v. Galardi, 16 Cal. 3d 300 (Cal. 1976)". Stanford University . Retrieved March 9, 2012.
- ↑ Charles, James (20 March 2008). "Creditors want your money or your home". The Times. London. Retrieved 28 April 2010.[ dead link ]
- ↑ Alistair Darling pledges to help homeowners – Sunday Mirror [ permanent dead link ]