
Charles Boutell (1 August 1812 – 31 July 1877) [1] was an English archaeologist, antiquary and clergyman, publishing books on brasses, arms and armour and heraldry, often illustrated by his own drawings. [2]

Charles Boutell (1 August 1812 – 31 July 1877) [1] was an English archaeologist, antiquary and clergyman, publishing books on brasses, arms and armour and heraldry, often illustrated by his own drawings. [2]
Boutell was born at Pulham St Mary, Norfolk, the son of the Rev. Charles Boutell. He entered St John's College, Cambridge, and graduated BA in 1834. In 1836 he took his MA at Trinity College, Oxford. Having served briefly as curate of Hemsby, Norfolk, and then curate of St Leonard's Church, Sandridge, Hertfordshire (1837–46), during which period, in 1839, he was ordained priest. He was subsequently rector of Downham Market (1847–1850) and vicar of Wiggenhall St Mary Magdalen, Norfolk (1847–55). After moving to London in 1855 he held various positions, including reader at St Luke's, Lower Norwood, Surrey (1860–67). [3]
He was secretary of the St Albans Architectural Society, founded in 1845; and was one of the founders in 1855 of the London and Middlesex Archaeological Society. During the first forty years of the Surrey Archaeological Society, Boutell appeared regularly as lecturer at the Society's annual excursions.
Among Boutell's several publications, A Manual of Heraldry, Historical and Popular (1863) was particularly successful. A second edition was called for in two months (published under the revised title, Heraldry, Historical and Popular), and a third edition appeared in 1864. Boutell also published a shorter companion work, English Heraldry (1867), which appeared in a second edition in 1871, and in several later editions including those revised by S.T. Aveling in 1892 and by A.C. Fox-Davies in 1907. The two works had become standard popular heraldic handbooks, and in 1931 a book entitled Boutell's Manual of Heraldry was published, edited by V. Wheeler-Holohan, which drew on both Boutell's originals. Later revisions, now simply entitled Boutell's Heraldry, were edited by C.W. Scott-Giles (1950, 1954, 1958, 1963 and 1966) and J.P. Brooke-Little (1963, 1966, 1970, 1973, 1978 and 1983).
Boutell served as Honorary Secretary of the London and Middlesex Archaeological Society from 23 July to 27 November 1857, but was dismissed for what was termed "improper" bookkeeping, involving the amount of £56 15s received in subscription fees. [4] [5] According to Charles Roach Smith, he subsequently suffered from a "similar lapse" in relation to the Surrey Archaeological Society. [6] In 1868 he was imprisoned for debt, and in December of that year was declared bankrupt. [3]
Boutell died of a ruptured heart on 31 July 1877, following two years of declining health. He was buried at Paddington Old Cemetery, Kilburn. [3]
He married Mary Chevallier (1809–1885), daughter of John Chevallier and Caroline Hepburn.
Their children were:
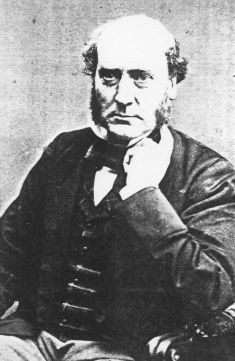
Sir George Gilbert Scott, largely known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he started his career as a leading designer of workhouses. Over 800 buildings were designed or altered by him.

Thomas Wright was an English antiquarian and writer. He is chiefly remembered as an editor of medieval texts.

Edward William Fitzalan-Howard, 18th Duke of Norfolk,, styled Earl of Arundel between 1975 and 2002, is a British peer who holds the hereditary office of Earl Marshal and, as Duke of Norfolk, is the most senior peer in the peerage of England. He is also the titular head of the House of Howard.

James Robinson Planché was a British dramatist, antiquary and officer of arms. Over a period of approximately 60 years he wrote, adapted, or collaborated on 176 plays in a wide range of genres including extravaganza, farce, comedy, burletta, melodrama and opera. Planché was responsible for introducing historically accurate costume into nineteenth century British theatre, and subsequently became an acknowledged expert on historical costume, publishing a number of works on the topic.

Sir Arthur William Blomfield was an English architect. He became president of the Architectural Association in 1861; a Fellow of the Royal Institute of British Architects in 1867 and vice-president of the RIBA in 1886. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he studied Architecture.

A monumental brass is a type of engraved sepulchral memorial once found through Western Europe, which in the 13th century began to partially take the place of three-dimensional monuments and effigies carved in stone or wood. Made of hard latten or sheet brass, let into the pavement, and thus forming no obstruction in the space required for the services of the church, they speedily came into general use, and continued to be a favourite style of sepulchral memorial for three centuries.

Temple Chevallier FRAS was a British clergyman, astronomer, and mathematician. Between 1847 and 1849, he made important observations regarding sunspots. Chevallier has been called "a remarkable Victorian polymath". Not only did he write many papers on astronomy and physics, he also published a translation of the Apostolic Fathers that went into a second edition, and translated the works of Clement of Rome, Polycarp and Ignatius of Antioch.

Thomas Spencer Cobbold FRS was an English biologist.

The Chevalliers of Aspall Hall are a family in Britain that has lived and farmed at Aspall Hall since 1702. Descendants of the family still exist, and are involved in the production of Aspall Cider.

Richard Cobbold was a British writer.

Arthur Charles Fox-Davies was a British expert on heraldry. His Complete Guide to Heraldry, published in 1909, has become a standard work on heraldry in England. A barrister by profession, Fox-Davies worked on several notable cases involving the peerage, and also worked as a journalist and novelist.

The cross moline is a Christian cross, constituting a kind of heraldic cross.

A church monument is an architectural or sculptural memorial to a deceased person or persons, located within a Christian church. It can take various forms ranging from a simple commemorative plaque or mural tablet affixed to a wall, to a large and elaborate structure, on the ground or as a mural monument, which may include an effigy of the deceased person and other figures of familial, heraldic or symbolic nature. It is usually placed immediately above or close to the actual burial vault or grave, although very occasionally the tomb is constructed within it. Sometimes the monument is a cenotaph, commemorating a person buried at another location.

John Gough Nichols (1806–1873) was an English painter and antiquary, the third generation in a family publishing business with strong connection to learned antiquarianism.

English heraldry is the form of coats of arms and other heraldic bearings and insignia used in England. It lies within the so-called Gallo-British tradition. Coats of arms in England are regulated and granted to individuals by the English kings of arms of the College of Arms. An individual's arms may also be borne 'by courtesy' by members of the holder's nuclear family, subject to a system of cadency marks, to differentiate those displays from the arms of the original holder. The English heraldic style is exemplified in the arms of British royalty, and is reflected in the civic arms of cities and towns, as well as the noble arms of individuals in England. Royal orders in England, such as the Order of the Garter, also maintain notable heraldic bearings.
William Henry Overall (1829–1888) was an English librarian and antiquary.

Sir William Henry St John Hope (1854–1919) was an English antiquary.

The London and Middlesex Archaeological Society (LAMAS) is a society founded in 1855 for the study of the archaeology and local history of the City of London and the historic county of Middlesex. It also takes an interest in districts that were historically in Surrey, Kent, Essex and Hertfordshire, but that now lie within Greater London. The Society receives support from the Museum of London, and works in close association both with the Museum and with Museum of London Archaeology. It acts to some extent as an umbrella organisation to support smaller archaeological and local history societies in the Greater London area. It hosts an Annual Conference of London Archaeologists and an annual Local History Conference.

Sir Francis Hepburn Chevallier-Boutell F.R.G.S (1851-1937) was a British engineer and sports manager, who served as President of the Argentine Association Football League between 1900 and 1906.

Charles Alban Buckler (1825–1905) was an English author, topographer, architect, artist and officer of arms. According to Historic England, he "became one of the most distinguished of the early to mid-Victorian Catholic architects." In the field of heraldry he was the Surrey Herald Extraordinary.