Related Research Articles

The Black Hawk War was a conflict between the United States and Native Americans led by Black Hawk, a Sauk leader. The war erupted after Black Hawk and a group of Sauks, Meskwakis (Fox), and Kickapoos, known as the "British Band", crossed the Mississippi River, into the U.S. state of Illinois, from Iowa Indian Territory in April 1832. Black Hawk's motives were ambiguous, but he was apparently hoping to reclaim land sold to the United States in the disputed 1804 Treaty of St. Louis.

Keokuk was a leader of the Sauk tribe in central North America, and for decades was one of the most recognized Native American leaders and noted for his accommodation with the U.S. government. Keokuk moved his tribe several times and always acted as an ardent friend of the Americans. His policies were contrary to fellow Sauk leader Black Hawk, who led part of their band to defeat in the Black Hawk War, was later returned by U.S. forces to Keokuk's custody, and who died a decade before Keokuk.

Black Hawk, born Ma-ka-tai-me-she-kia-kiak, was a Sauk leader and warrior who lived in what is now the Midwestern United States. Although he had inherited an important historic sacred bundle from his father, he was not a hereditary civil chief. Black Hawk earned his status as a war chief or captain by his actions: leading raiding and war parties as a young man and then a band of Sauk warriors during the Black Hawk War of 1832.

The Bad Axe Massacre was a massacre of Sauk (Sac) and Fox Indians by United States Army regulars and militia that occurred on August 1–2, 1832. This final scene of the Black Hawk War took place near present-day Victory, Wisconsin in the United States. It marked the end of the war between white settlers and militia in Illinois and Michigan Territory, and the Sauk and Fox tribes under warrior Black Hawk.

The Battle of Stillman's Run, also known as the Battle of Sycamore Creek or the Battle of Old Man's Creek, occurred in Illinois on May 14, 1832. The battle was named for the panicked retreat by Major Isaiah Stillman and his detachment of 275 Illinois militia after being attacked by an unknown number of Sauk warriors of Black Hawk's British Band. The numbers of warriors has been estimated at as few as fifty but as many as two hundred participated in the attack. However, reports found in Whitney's Black Hawk War indicated that large numbers of Indians were on the move throughout the region, and it appeared that widespread frontier warfare was underway. The engagement was the first battle of the Black Hawk War (1832), which developed after Black Hawk crossed the Mississippi River from Iowa into Illinois with his band of Sauk and Fox warriors along with women, children, and elders to try to resettle in Illinois. The militia had pursued a small group of Sauk scouts to the main British Band camp following a failed attempt by Black Hawk's emissaries to negotiate a truce.

The Indian Creek Massacre occurred on May 21, 1832 with the attack by a party of Native Americans on a group of United States settlers in LaSalle County, Illinois following a dispute about a settler-constructed dam that prevented fish from reaching a nearby Potawatomi village. The incident coincided with the Black Hawk War, but it was not a direct action of the Sauk leader Black Hawk and conflict with the United States. The removal of the dam was asked, was rejected by the settlers and between 40 and 80 Potawatomis and three Sauks attacked and killed fifteen settlers, including women and children. Two young women kidnapped by the Indians were ransomed and released unharmed about two weeks later.

The Battle of Kellogg's Grove is either of two minor battles, or skirmishes, fought during the Black Hawk War in the U.S. state of Illinois, in present-day Stephenson County at and near Kellogg's Grove. In the first skirmish, also known as the Battle of Burr Oak Grove, on June 16, 1832, Illinois militia forces fought against a band of at least 80 Native Americans. During the battle, three militia men under the command of Adam W. Snyder were killed in action. The second battle occurred nine days later when a larger Sauk and Fox band, under the command of Black Hawk, attacked Major John Dement's detachment and killed five militia men.
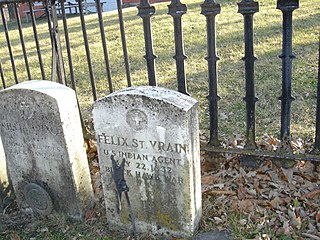
The St. Vrain massacre was an incident in the Black Hawk War. It occurred near present-day Pearl City, Illinois, in Kellogg's Grove, on May 24, 1832. The massacre was most likely committed by Ho-Chunk warriors who were unaffiliated with Black Hawk's band of warriors. It is also unlikely that the group of Ho-Chunk had the sanction of their nation. Killed in the massacre were United States Indian Agent Felix St. Vrain and three of his companions. Some accounts reported that St. Vrain's body was mutilated.

Stillman's Run Battle Site is a site in Stillman Valley, Illinois. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and has been since December 1983. The Battle of Stillman's Run was an 1832 clash between the Illinois militia and Black Hawk and his Sauk Indian Band. The battle took place in 1832 as part of the Black Hawk War. During the engagement 12 militia men were killed while making a stand on a small hill. The rest of the militia fled back to Dixon's Ferry where they spread news of a terrible slaughter at Stillman's Run.

The Battle of Wisconsin Heights was the penultimate engagement of the 1832 Black Hawk War, fought between the United States state militia and allies, and the Sauk and Fox tribes, led by Black Hawk. The battle took place in what is now Dane County, near present-day Sauk City, Wisconsin. Despite being vastly outnumbered and sustaining heavy casualties, Black Hawk's warriors managed to delay the combined government forces long enough to allow the majority of the Sauk and Fox civilians in the group to escape across the Wisconsin River. This reprieve was temporary; when the militia finally caught up with the fleeing band it resulted in the Bad Axe massacre at the mouth of the Bad Axe River.

The Battle of Waddams Grove, also known as the Battle of Yellow Creek was part of the Black Hawk War. It took place in present-day Stephenson County, Illinois on June 18, 1832. After several incidents of Sauk Indian raids on settlers along the Apple River, Captain James W. Stephenson left Galena with a group of volunteer militia in pursuit of the Native party. The group clashed on June 18, 1832 near Yellow Creek and the ensuing battle descended into a bayonet and knife fight in which several Sauk and three militia men were killed. Stephenson was severely wounded by a musketball to the chest during the fighting. The dead were eventually interred in a memorial cemetery in Kellogg's Grove, Illinois where a stone monument was erected in memory of those killed during the war.

The attacks at Fort Blue Mounds were two separate incidents which occurred on June 6 and 20, 1832, as part of the Black Hawk War. In the first incident, area residents attributed the killing of a miner to a band of Ho-Chunk warriors, and concluded that more Ho-Chunk planned to join Black Hawk in his war against white settlers. The second incident occurred east of the fort as a Sauk raiding party, estimated by eyewitnesses to be as large as 100 warriors, attacked two militiamen who were investigating noises heard the night before. Two members of the militia stationed at Blue Mounds were killed in the attack, and both their bodies were badly mutilated.
The Sinsinawa Mound raid occurred on June 29, 1832, near the Sinsinawa mining settlement in Michigan Territory. This incident, part of the Black Hawk War, resulted in the deaths of two men; a third man survived by seeking cover in a nearby blockhouse. In the aftermath of the raid, Captain James W. Stephenson set out to pursue the attackers—a straggling band of Sauk Native Americans—but lost their trail at the Mississippi River. The attack occurred in the same week as other skirmishes and raids, and as a result helped contribute to the growing fear in the region. The raid caused the residents of nearby Platteville to consider fleeing their settlement.
The Plum River raid was a bloodless skirmish that occurred at present-day Savanna, Illinois, on May 21, 1832, as part of the Black Hawk War. Most of the settlement's inhabitants, except for a few defenders, had fled for Galena, Illinois, before the raid happened. A small band of Native Americans, either Sauk or Fox, attacked the settlement while only three of the six defenders were present. The men who were present fell back to the blockhouse and a firefight ensued for about one hour, after which the attackers withdrew. No one was killed or injured during the attack, but in its aftermath Colonel James M. Strode dispatched a detachment of militia to Savanna. They returned to Galena without incident and the settlement at Savanna was temporarily abandoned.

Wabokieshiek was a Native American army commander of the Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) and Sauk tribes in 19th century Illinois, playing a key role in the Black Hawk War of 1832. Known as a medicine man and prophet, he is sometimes called the Winnebago Prophet.

The British Band was a mixed-nation group of Native Americans commanded by the Sauk leader Black Hawk, which fought against Illinois and Michigan Territory militias during the 1832 Black Hawk War. The band was composed of about 1,500 men, women, and children from the Sauk, Meskwaki, Fox, Kickapoo, Potawatomi, Ho-Chunk, and Ottawa nations; about 500 of that number were warriors. Black Hawk had an alliance with the British that dated from the War of 1812, giving them their colloquial name. The band crossed the Mississippi River from Iowa into Illinois in an attempt to reclaim their homeland and in violation of several treaties. Subsequently, both the Illinois and Michigan Territory militia were called up and the Black Hawk War ensued.

Warrior was a privately owned and constructed steamboat that was pressed into service by the U.S. government during the Black Hawk War to assist with military operations. Warrior was constructed and launched in 1832 at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania by Joseph Throckmorton who also served as the vessel's captain. Once constructed the vessel traveled to St. Louis and into the war zone. Warrior played a key role in the decisive Battle of Bad Axe. Following the war the steamboat continued its service under Throckmorton along the Upper Mississippi River.

Joseph Throckmorton was an American steamboat builder and captain during the 19th century. He was born in Monmouth County, New Jersey and first worked in a mercantile business. His first steamboat was Red Rover, purchased on the Ohio River around 1830. In 1832 he built and skippered the steamboat Warrior. The vessel and Captain Throckmorton played a key role in the decisive battle of the 1832 Black Hawk War. Following the war, he built and owned several more steamboats, and worked for a short time as an insurance representative in St. Louis. Throckmorton died in December 1872 while employed by the United States government.
Pamisseu was a Sauk chief aligned with Black Hawk's British Band during the 1832 Black Hawk War.
Towaunonne was a Sauk chief aligned with Black Hawk's British Band during the 1832 Black Hawk War.
References
- ↑ Jung, Patrick J. The Black Hawk War of 1832, (Google Books), University of Oklahoma Press, 2008, p. 74, ( ISBN 0806139943).