Alexander Posey (c. 1794-?) was an American militia officer who served as a brigadier general under General Henry Atkinson during the Black Hawk War, specifically in the later stages of the second campaign as one of the commanders present at the Battle of Bad Axe.
Born in Orange County, Virginia to Revolutionary War General Thomas Posey and Mary Alexander, Alexander Posey was a physician in Gallatin County, Illinois when he was elected brigadier general by the volunteers gathered at Dixon's Ferry on June 13, 1832, possibly due to being the brother-in-law of U.S. Indian Agent Joseph Street. Assigned to command one of three brigades under General Henry Atkinson two days later, Posey was sent to Fort Hamilton accompanied by two companies of regulars under Hugh Brady on June 20.
On June 25, a detachment of soldiers from his command under Major John Dement were involved in a large skirmish with a Sauk war party under Neapope and Weesheet while encamped at Burr Oak Grove. Posey attempted to relieve Dement setting out from nearby Buffalo Grove, however the Sauk had retreated only two hours before his arrival. Five soldiers and twenty horses had been killed while nine Sauk were observed on the field. He briefly searched north for the raiding party then returned to Kellogg's Grove to await wait for the baggage-wagons before continuing on to Fort Hamilton where he made camp along the Pecatonica River on June 28.
Shortly after the Spafford Farm massacre, Dodge and Colonel William S. Hamilton arrived at Posey's encampment to take over Posey's command. Posey had previously received a letter from Atkinson on June 28 which stated "You will report and receive the orders of Genl. Dodge as practicable, who is an officer of great experience & merit & is aquatinted with the country." However, Posey refused to turn over his command to Dodge outright. Dodge agreed not to take his command by force and instead suggested they put the decision to the Illinois militiamen, with whom Dodge had considerable support. Of those most outspoken included Major Demet who had told his men "would lead them on to victory and retrieve the honor which a short time before they had lost in an Indian fight under Posey."
This statement accurately reflected the resentment against Posey for his refusal to use his main force against the raiding party which had attacked Demet's men. The Illinois Herald, a local Springfield newspaper, also campaigned for his removal in favor of Dodge citing cowardice and lack of aggressive leadership.
However, due in part to a personal appeal to his men as well as "a matter of state pride", Posey retained his command by a small majority. This caused some distention in the ranks as Demet reportedly tore up his commission, threw the shredded paper on the ground and spat on them, before resigning his command of his battalion.
Meeting up with Major Henry Dodge's battalion from Galena, Illinois, the two eventually rejoined General Atkinson, accompanied General Milton Alexander and General James D. Henry, at the White River or Whitewater on July 6. During the match, he and Dodge encountered White Crow and thirty Winnebagos. Offering to lead Posey and Dodge to Black Hawk's camp, they followed White Crow and his warriors through near impassable wilderness and swampland for several days. The party were reportedly only a short distance from Black Hawk's camp when they received a direct order from Atkinson to join him at his encampment on Bark River, part of eastern Lake Koshkonong.
As Atkinson's forces began to run low on provisions, Posey sent his 2nd Regiment under Colonel Ewing to accompany Alexander, Henry and Dodge to Fort Winnebago for supplies while he was sent back to Fort Hamilton to guard the mining country left exposed by Dodge's absence.
In late-July, Posey moved out from Fort Hamilton to join Atkinson's expedition at Fort Blue Mounds preparing for the final confrontation with Black Hawk's band at the Battle of Bad Axe where, during August 1–2, he and Alexander would command the ring flank in support of the main center force of regulars under Dodge.

The Black Hawk War was a conflict between the United States and Native Americans led by Black Hawk, a Sauk leader. The war erupted after Black Hawk and a group of Sauks, Meskwakis (Fox), and Kickapoos, known as the "British Band", crossed the Mississippi River, to the U.S. state of Illinois, from Iowa Indian Territory in April 1832. Black Hawk's motives were ambiguous, but he was apparently hoping to reclaim land that was taken over by the United States in the disputed 1804 Treaty of St. Louis.

The Bad Axe Massacre was a massacre of Sauk (Sac) and Fox Indians by United States Army regulars and militia that occurred on August 1–2, 1832. This final scene of the Black Hawk War took place near present-day Victory, Wisconsin, in the United States. It marked the end of the war between white settlers and militia in Illinois and Michigan Territory, and the Sauk and Fox tribes under warrior Black Hawk.

The Battle of Kellogg's Grove is either of two minor battles, or skirmishes, fought during the Black Hawk War in the U.S. state of Illinois, in present-day Stephenson County at and near Kellogg's Grove. In the first skirmish, also known as the Battle of Burr Oak Grove, on June 16, 1832, Illinois militia forces fought against a band of at least 80 Native Americans. During the battle, three militia men under the command of Adam W. Snyder were killed in action. The second battle occurred nine days later when a larger Sauk and Fox band, under the command of Black Hawk, attacked Major John Dement's detachment and killed five militia men.

The Battle of Horseshoe Bend, also referred to as the Battle of Pecatonica and the Battle of Bloody Lake, was fought on June 16, 1832 in present-day Wisconsin at an oxbow lake known as "Horseshoe Bend", which was formed by a change in course of the Pecatonica River. The battle was a major turning point in the Black Hawk War, despite being of only minor military significance. The small victory won by the U.S. militia at Horseshoe Bend helped restore public confidence in the volunteer force following an embarrassing defeat at Stillman's Run. The Battle of Horseshoe Bend ended with three militia men killed in action and a party of eleven Kickapoo warriors dead.

The Spafford Farm massacre, also referred to as the Wayne massacre, was an attack upon U.S. militia and civilians that occurred as part of the Black Hawk War near present-day South Wayne, Wisconsin. Spafford Farm was settled in 1830 by Omri Spafford and his partner Francis Spencer.
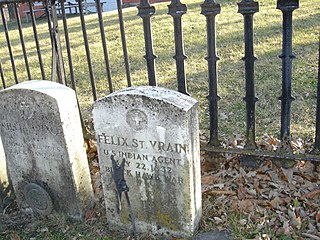
The St. Vrain massacre was an incident in the Black Hawk War. It occurred near present-day Pearl City, Illinois, in Kellogg's Grove, on May 24, 1832. The massacre was most likely committed by Ho-Chunk warriors who were unaffiliated with Black Hawk's band of warriors. It is also unlikely that the group of Ho-Chunk had the sanction of their nation. Killed in the massacre were United States Indian Agent Felix St. Vrain and three of his companions. Some accounts reported that St. Vrain's body was mutilated.

Felix St. Vrain, born Felix August Antoine St. Vrain, was an American United States Indian agent who was killed by Native Americans during the Black Hawk War. St. Vrain died along with three companions while on a mission to deliver dispatches from Dixon's Ferry to Fort Armstrong, both in Illinois. The incident has become known as the St. Vrain massacre.
The Sinsinawa Mound raid occurred on June 29, 1832, near the Sinsinawa mining settlement in Michigan Territory. This incident, part of the Black Hawk War, resulted in the deaths of two men; a third man survived by seeking cover in a nearby blockhouse. In the aftermath of the raid, Captain James W. Stephenson set out to pursue the attackers—a straggling band of Sauk Native Americans—but lost their trail at the Mississippi River. The attack occurred in the same week as other skirmishes and raids, and as a result helped contribute to the growing fear in the region. The raid caused the residents of nearby Platteville to consider fleeing their settlement.
James D. Henry was a militia officer from the U.S. state of Illinois who rose to the rank of general during the Black Hawk War. Henry was born in Pennsylvania in 1797, and moved to Edwardsville, Illinois in 1822. In 1825, while living in Edwardsville, he was indicted with two other men for the murder of an acquaintance, though he never went to trial. One defendant was tried but found not guilty, and following the trial Henry moved to Springfield, Illinois, where he was elected sheriff. When the Winnebago War broke out in 1827 Henry acted as adjutant for four companies of volunteers.

John Dement was an American politician and militia commander from the U.S. state of Illinois.

The British Band was a mixed-nation group of Native Americans commanded by the Sauk leader Black Hawk, which fought against Illinois and Michigan Territory militias during the 1832 Black Hawk War. The band was composed of about 1,500 men, women, and children from the Sauk, Meskwaki, Fox, Kickapoo, Potawatomi, Ho-Chunk, and Ottawa nations; about 500 of that number were warriors. Black Hawk had an alliance with the British that dated from the War of 1812, giving them their colloquial name. The band crossed the Mississippi River from Iowa into Illinois in an attempt to reclaim their homeland and in violation of several treaties. Subsequently, both the Illinois and Michigan Territory militia were called up and the Black Hawk War ensued.

William Stephen Hamilton, a son of Alexander Hamilton and Elizabeth Schuyler Hamilton, was an American politician and miner who lived much of his life in the U.S. state of Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory. Hamilton was born in New York, where he attended the United States Military Academy before he resigned and moved to Illinois in 1817. In Illinois, he lived in Springfield and Peoria and eventually migrated to the lead-mining region of southern Wisconsin and established Hamilton's Diggings at present-day Wiota, Wisconsin. Hamilton served in various political offices and as a commander in two Midwest Indian Wars. In 1849, he moved to California during the California Gold Rush. He died in Sacramento, most likely of cholera, in October 1850.
After the outbreak of the Black Hawk War, at the Battle of Stillman's Run in May 1832, there were minor attacks and skirmishes throughout the duration of the conflict. The war was fought between white settlers in Illinois and present-day Wisconsin and Sauk Chief Black Hawk. The relatively minor attacks of the war were widely dispersed and often carried out by bands of Native Americans that were unaffiliated with Black Hawk's British Band.

Hugh Brady was an American general from Pennsylvania. He served in the Northwest Indian War under General Anthony Wayne, and during the War of 1812. Following the War of 1812, Brady remained in the military, eventually rising to the rank of major general and taking command of the garrison at Detroit. He also marginally participated in the 1832 Black Hawk War. Hugh Brady died an accidental death in 1851 when he was thrown from a horse-drawn carriage.

Colonel Henry Gratiot was a French-American pioneer, farmer, and mill owner. During the Winnebago and Black Hawk Wars, he acted as both an intermediary and early U.S. Indian agent to the Winnebagos throughout the early 19th century. He and his brother Jean Pierre were among the first pioneers to settle in Wisconsin, operating a successful lead mining and lead smelting business, during the 1820s and 1830s. Both, the present-day village of Gratiot, Wisconsin and the town of Gratiot (town), Wisconsin are named in his honor.

David Bailey (1801–1854) was an American militia officer and abolitionist in the Illinois Militia who was a key participant in the Black Hawk War. Most notably, he served at the Battle of Stillman's Run, where he and Lt. Col. Major Isaiah Stillman were defeated by Black Hawk's British Band at Stillman Creek in present-day Ogle County, Illinois, on May 14, 1832.

Milton King Alexander was an American politician and militia officer who served during the War of 1812, the Seminole Wars and, most notably, as a brigadier general during the Black Hawk War.

General Joseph Montfort Street was a 19th-century American pioneer, trader and US Army officer. During the 1820s and 1830s, he was also a U.S. Indian Agent to the Winnebago and later to the Sauk and Fox tribes after the Black Hawk War. His eldest son was Joseph H. D. Street, the first appointed registrar of the Council Bluffs Land Office in western Iowa.

Abraham Lincoln served as a volunteer in the Illinois Militia April 21, 1832 – July 10, 1832, during the Black Hawk War. Lincoln never saw combat during his tour but was elected captain of his first company. He was also present in the aftermath of two of the war's battles, where he helped to bury the militia dead. He was mustered in and out of service during the war, going from captain to private and finishing his service in an independent spy company commanded by Captain Jacob Early.

Satterlee Clark was an American attorney, Democratic politician, and Wisconsin pioneer. He served ten years in the Wisconsin State Senate (1862–1872), representing eastern Dodge County, and also served two years in the Wisconsin State Assembly. He wrote a historical essay of his memories of Fort Winnebago and the Black Hawk War in pre-statehood Wisconsin. In his lifetime, he was widely known by the nickname Sat Clark.