Multituberculata is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and reached a peak diversity during the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene. They eventually declined from the mid-Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene. They are the most diverse order of Mesozoic mammals with more than 200 species known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals—Theria, including placentals and marsupials, and Monotremata—but usually as closer to Theria than to monotremes. They are considered to be closely related to Euharamiyida and Gondwanatheria as part of Allotheria.

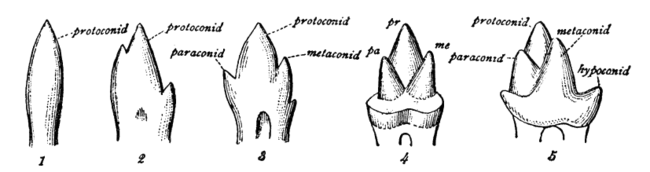
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology of the teeth of an animal.

The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name molar derives from Latin, molaris dens, meaning "millstone tooth", from mola, millstone and dens, tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial.

Catopsbaatar is a genus of multituberculate, an extinct order of rodent-like mammals. It lived in what is now Mongolia during the late Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 72 million years ago. The first fossils were collected in the early 1970s, and the animal was named as a new species of the genus Djadochtatherium in 1974, D. catopsaloides. The specific name refers to the animal's similarity to the genus Catopsalis. The species was moved to the genus Catopsalis in 1979, and received its own genus in 1994. Five skulls, one molar, and one skeleton with a skull are known; the last is the genus' most complete specimen. Catopsbaatar was a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae.
Ferugliotheriidae is one of three known families in the order Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic group of extinct mammals. Gondwanatheres have been classified as a group of uncertain affinities or as members of Multituberculata, a major extinct mammalian order. The best-known representative of Ferugliotheriidae is the genus Ferugliotherium from the Late Cretaceous epoch in Argentina. A second genus, Trapalcotherium, is known from a single tooth, a first lower molariform, from a different Late Cretaceous Argentinean locality. Another genus known from a single tooth, Argentodites, was first described as an unrelated multituberculate, but later identified as possibly related to Ferugliotherium. Finally, a single tooth from the Paleogene of Peru, LACM 149371, perhaps a last upper molariform, and a recent specimen from Mexico, may represent related animals.

Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified fourth upper premolar and the first lower molar. These teeth are also referred to as sectorial teeth.
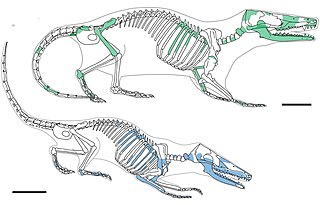
Docodonta is an order of extinct Mesozoic mammaliaforms. They were among the most common mammaliaforms of their time, persisting from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous across the continent of Laurasia. They are distinguished from other early mammaliaforms by their relatively complex molar teeth. Docodont teeth have been described as "pseudotribosphenic": a cusp on the inner half of the upper molar grinds into a basin on the front half of the lower molar, like a mortar-and-pestle. This is a case of convergent evolution with the tribosphenic teeth of therian mammals. There is much uncertainty for how docodont teeth developed from their simpler ancestors. Their closest relatives may have been certain Triassic "symmetrodonts", namely Woutersia, and Delsatia. The shuotheriids, another group of Jurassic mammaliaforms, also shared some dental characteristics with docodonts. One study has suggested that shuotheriids are closely related to docodonts, though others consider shuotheriids to be true mammals, perhaps related to monotremes.

A cusp is a pointed, projecting, or elevated feature. In animals, it is usually used to refer to raised points on the crowns of teeth. The concept is also used with regard to the leaflets of the four heart valves. The mitral valve, which has two cusps, is also known as the bicuspid valve, and the tricuspid valve has three cusps.

The evolution of mammals has passed through many stages since the first appearance of their synapsid ancestors in the Pennsylvanian sub-period of the late Carboniferous period. By the mid-Triassic, there were many synapsid species that looked like mammals. The lineage leading to today's mammals split up in the Jurassic; synapsids from this period include Dryolestes, more closely related to extant placentals and marsupials than to monotremes, as well as Ambondro, more closely related to monotremes. Later on, the eutherian and metatherian lineages separated; the metatherians are the animals more closely related to the marsupials, while the eutherians are those more closely related to the placentals. Since Juramaia, the earliest known eutherian, lived 160 million years ago in the Jurassic, this divergence must have occurred in the same period.

Post-canine megadontia is a relative enlargement of the molars and premolars compared to the size of the incisors and canines. This phenomenon is seen in some early hominid ancestors such as Paranthropus aethiopicus.

Morganucodonta is an extinct order of basal Mammaliaformes, a group including crown-group mammals (Mammalia) and their close relatives. Their remains have been found in Southern Africa, Western Europe, North America, India and China. The morganucodontans were probably insectivorous and nocturnal, though like eutriconodonts some species attained large sizes and were carnivorous. Nocturnality is believed to have evolved in the earliest mammals in the Triassic as a specialisation that allowed them to exploit a safer, night-time niche, while most larger predators were likely to have been active during the day.

Kuehneotherium is an early mammaliaform genus, previously considered a holothere, that lived during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Epochs and is characterized by reversed-triangle pattern of molar cusps. Although many fossils have been found, the fossils are limited to teeth, dental fragments, and mandible fragments. The genus includes Kuehneotherium praecursoris and all related species. It was first named and described by Doris M. Kermack, K. A. Kermack, and Frances Mussett in November 1967. The family Kuehneotheriidae and the genus Kuehneotherium were created to house the single species Kuehneotherium praecursoris. Modeling based upon a comparison of the Kuehneotherium jaw with other mammaliaforms indicates it was about the size of a modern-day shrew between 4 and 5.5 g at adulthood.

Ambondro mahabo is a mammal from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) Isalo III Formation of Madagascar. The only described species of the genus Ambondro, it is known from a fragmentary lower jaw with three teeth, interpreted as the last premolar and the first two molars. The premolar consists of a central cusp with one or two smaller cusps and a cingulum (shelf) on the inner, or lingual, side of the tooth. The molars also have such a lingual cingulum. They consist of two groups of cusps: a trigonid of three cusps at the front and a talonid with a main cusp, a smaller cusp, and a crest at the back. Features of the talonid suggest that Ambondro had tribosphenic molars, the basic arrangement of molar features also present in marsupial and placental mammals. It is the oldest known mammal with putatively tribosphenic teeth; at the time of its discovery it antedated the second oldest example by about 25 million years.

A tooth is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm.
Several mammals are known from the Mesozoic of Madagascar. The Bathonian Ambondro, known from a piece of jaw with three teeth, is the earliest known mammal with molars showing the modern, tribosphenic pattern that is characteristic of marsupial and placental mammals. Interpretations of its affinities have differed; one proposal places it in a group known as Australosphenida with other Mesozoic tribosphenic mammals from the southern continents (Gondwana) as well as the monotremes, while others favor closer affinities with northern (Laurasian) tribosphenic mammals or specifically with placentals. At least five species are known from the Maastrichtian, including a yet undescribed species known from a nearly complete skeleton that may represent a completely new group of mammals. The gondwanathere Lavanify, known from two teeth, is most closely related to other gondwanatheres found in India and Argentina. Two other teeth may represent another gondwanathere or a different kind of mammal. One molar fragment is one of the few known remains of a multituberculate mammal from Gondwana and another has been interpreted as either a marsupial or a placental.

Teeth are common to most vertebrates, but mammalian teeth are distinctive in having a variety of shapes and functions. This feature first arose among early therapsids during the Permian, and has continued to the present day. All therapsid groups with the exception of the mammals are now extinct, but each of these groups possessed different tooth patterns, which aids with the classification of fossils.
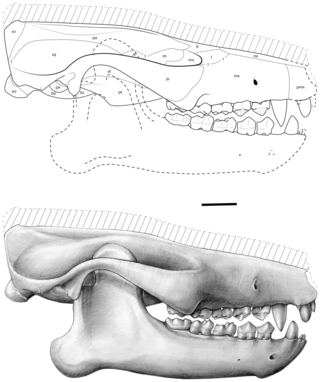
Ocepeia is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is O. daouiensis from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, O. grandis, is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and 10 kg (22 lb), respectively, and are believed to have been specialized leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of Ocepeia are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa.

Anatoliadelphys maasae is an extinct genus of predatory metatherian mammal from the Eocene of Anatolia. It was an arboreal, cat-sized animal, with powerful crushing jaws similar to those of the modern Tasmanian devil. Although most mammalian predators of the northern hemisphere in this time period were placentals, Europe was an archipelago, and the island landmass now forming Turkey might have been devoid of competing mammalian predators, though this may not matter since other carnivorous metatherians are also known from the Cenozoic in the Northern Hemisphere. Nonetheless, it stands as a reminder that mammalian faunas in the Paleogene of the Northern Hemisphere were more complex than previously thought, and metatherians did not immediately lose their hold as major predators after their success in the Cretaceous.

Gypsonictops is an extinct genus of leptictidan mammals of the family Gypsonictopidae, which was described in 1927 by George Gaylord Simpson. Species in this genus were small mammals and the first representatives of the order Leptictida, that appeared during the Upper Cretaceous.
Chaoyangodens is an extinct genus of eutriconodont mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Chaoyangodens lii, known from a single complete skeleton recovered from the Dawangzhangzi bed of the Yixian Formation, part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. Chaoyangodens was a moderate-sized Mesozoic mammal. The generic name refers to Chaoyang Prefecture while the specific name honors the collector of the fossil, Hai-Jun Li. Chaoyangodens is intermediate in age between Liaoconodon and a diverse fauna of eutriconodonts from older beds of the Yixian Formation. Like Liaoconodon, it is not easily equated with other eutriconodonts, since it bears distinctive dental traits relative to recognized eutriconodont subgroups.