Related Research Articles

Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram. In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate.

In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid H
3PO
4.

Lombardy is one of the twenty administrative regions of Italy. It has an extent of 23,844 km2 (9,206 sq mi) in the northern-central part of the country, and a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of the population of Italy. Over a fifth of the Italian gross domestic product is produced in the region.

Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of OH−, F− and Cl− ions, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of the three most common endmembers is written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH,F,Cl)2, and the crystal unit cell formulae of the individual minerals are written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, Ca10(PO4)6F2 and Ca10(PO4)6Cl2.

Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. Phosphoric acid is a colorless solid. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formulae, wherein the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side with a plus sign between the entities in both the reactants and the products and an arrow that points towards the products, and shows the direction of the reaction. The coefficients next to the symbols and formulae of entities are the absolute values of the stoichiometric numbers. The first chemical equation was diagrammed by Jean Beguin in 1615.
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white solids of nutritious value and are found in many living organisms, e.g., bone mineral and tooth enamel. In milk, it exists in a colloidal form in micelles bound to casein protein with magnesium, zinc, and citrate–collectively referred to as colloidal calcium phosphate (CCP). Various calcium phosphate minerals are used in the production of phosphoric acid and fertilizers. Overuse of certain forms of calcium phosphate can lead to nutrient-containing surface runoff and subsequent adverse effects upon receiving waters such as algal blooms and eutrophication (over-enrichment with nutrients and minerals).

Alkalinity is the capacity of water to resist acidification. It should not be confused with basicity, which is an absolute measurement on the pH scale.

Calcium nitrate, also called Norgessalpeter (Norwegian salpeter), is an inorganic compound with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhydrous and hydrated forms are colourless salts. Calcium nitrate is mainly used as a component in fertilizers, but it has other applications. Nitrocalcite is the name for a mineral which is a hydrated calcium nitrate that forms as an efflorescence where manure contacts concrete or limestone in a dry environment as in stables or caverns. A variety of related salts are known including calcium ammonium nitrate decahydrate and calcium potassium nitrate decahydrate.

Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. Hydroxyapatite is the hydroxyl endmember of the complex apatite group. The OH− ion can be replaced by fluoride, chloride or carbonate, producing fluorapatite or chlorapatite. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system. Pure hydroxyapatite powder is white. Naturally occurring apatites can, however, also have brown, yellow, or green colorations, comparable to the discolorations of dental fluorosis.

Phosphate minerals contain the tetrahedrally coordinated phosphate (PO43−) anion along sometimes with arsenate (AsO43−) and vanadate (VO43−) substitutions, and chloride (Cl−), fluoride (F−), and hydroxide (OH−) anions that also fit into the crystal structure.

Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Most commercial samples of "tricalcium phosphate" are in fact hydroxyapatite.

Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless solids. They are used mainly as superphosphate fertilizers and are also popular leavening agents.
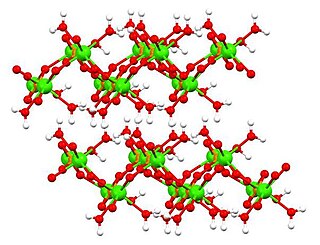
Dicalcium phosphate is the calcium phosphate with the formula CaHPO4 and its dihydrate. The "di" prefix in the common name arises because the formation of the HPO42– anion involves the removal of two protons from phosphoric acid, H3PO4. It is also known as dibasic calcium phosphate or calcium monohydrogen phosphate. Dicalcium phosphate is used as a food additive, it is found in some toothpastes as a polishing agent and is a biomaterial.

The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately 650 km (400 mi) in an east-west direction, with an area of 46,000 km2 including its Venetic extension not actually related to the Po river basin; it runs from the Western Alps to the Adriatic Sea. The flatlands of Veneto and Friuli are often considered apart since they do not drain into the Po, but they effectively combine into an unbroken plain, making it the largest in Southern Europe.

Fluorapatite, often with the alternate spelling of fluoroapatite, is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F (calcium fluorophosphate). Fluorapatite is a hard crystalline solid. Although samples can have various color (green, brown, blue, yellow, violet, or colorless), the pure mineral is colorless, as expected for a material lacking transition metals. Along with hydroxylapatite, it can be a component of tooth enamel, but for industrial use both minerals are mined in the form of phosphate rock, whose usual mineral composition is primarily fluorapatite but often with significant amounts of the other.
Kung Fu Panda is an American media franchise that originally started in 2008 with the release of the animated feature film of the same name, produced by DreamWorks Animation. Following the adventures of the titular Po Ping, a giant panda who is improbably chosen as the prophesied Dragon Warrior and becomes a master of kung fu, the franchise is set in a fantasy wuxia genre version of ancient China populated by anthropomorphic animals. Although his status is initially doubted, Po proves himself worthy as he strives to fulfill his destiny.
This list gives an overview of the classification of non-silicate minerals and includes mostly International Mineralogical Association (IMA) recognized minerals and its groupings. This list complements the List of minerals recognized by the International Mineralogical Association series of articles and List of minerals. Rocks, ores, mineral mixtures, not IMA approved minerals, not named minerals are mostly excluded. Mostly major groups only, or groupings used by New Dana Classification and Mindat.
Oxyphosphides are chemical compounds formally containing the group PO, with one phosphorus and one oxygen atom. The phosphorus and oxygen are not bound together as in phosphates or phosphine oxides, instead they are bound separately to the cations (metals), and could be considered as a mixed phosphide-oxide compound. So a compound with OmPn requires cations to balance a negative charge of 2m+3n. The cations will have charges of +2 or +3. The trications are often rare earth elements or actinides. They are in the category of oxy-pnictide compounds.