Related Research Articles

Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games such as xiangqi and shogi. The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as they are known today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, and is played by millions of people worldwide.

Computer chess includes both hardware and software capable of playing chess. Computer chess provides opportunities for players to practice even in the absence of human opponents, and also provides opportunities for analysis, entertainment and training. Computer chess applications that play at the level of a chess grandmaster or higher are available on hardware from supercomputers to smart phones. Standalone chess-playing machines are also available. Stockfish, Leela Chess Zero, GNU Chess, Fruit, and other free open source applications are available for various platforms.
This glossary of chess explains commonly used terms in chess, in alphabetical order. Some of these terms have their own pages, like fork and pin. For a list of unorthodox chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems; for a list of named opening lines, see List of chess openings; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants; for a list of terms general to board games, see Glossary of board games.

An evaluation function, also known as a heuristic evaluation function or static evaluation function, is a function used by game-playing computer programs to estimate the value or goodness of a position in a game tree. Most of the time, the value is either a real number or a quantized integer, often in nths of the value of a playing piece such as a stone in go or a pawn in chess, where n may be tenths, hundredths or other convenient fraction, but sometimes, the value is an array of three values in the unit interval, representing the win, draw, and loss percentages of the position.

XBoard is a graphical user interface chessboard for chess engines under the X Window System. It is developed and maintained as free software by the GNU project. WinBoard is a port of XBoard to run natively on Microsoft Windows.
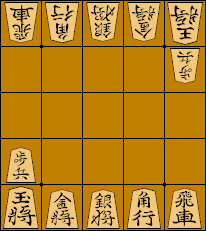
Minishogi is a modern variant of shogi. The game was invented around 1970 by Shigenobu Kusumoto of Osaka, Japan. The rules are nearly identical to those of standard shogi, with the exception that it is played on a 5x5 board with a reduced number of pieces, and each player's promotion zone consists only of the rank farthest from the player.
The Universal Chess Interface (UCI) is an open communication protocol that enables chess engines to communicate with user interfaces.
ChessBase is a German company that develops and sells chess software, maintains a chess news site, and operates an internet chess server for online chess. Founded in 1986, it maintains and sells large-scale databases containing the moves of recorded chess games. The databases contain data from prior games and provide engine analyses of games. Endgame tablebases are also provided by the company.

In computer chess, a chess engine is a computer program that analyzes chess or chess variant positions, and generates a move or list of moves that it regards as strongest.

Crafty is a chess program written by UAB professor Dr. Robert Hyatt, with continual development and assistance from Michael Byrne, Tracy Riegle, and Peter Skinner. It is directly derived from Cray Blitz, winner of the 1983 and 1986 World Computer Chess Championships. Tord Romstad, co-author of Stockfish, described Crafty as "arguably the most important and influential chess program ever".

Fritz is a German chess program originally developed for Chessbase by Frans Morsch based on his Quest program, ported to DOS, and then Windows by Mathias Feist. With version 13, Morsch retired, and his engine was first replaced by Gyula Horvath's Pandix, and then with Fritz 15, Vasik Rajlich's Rybka.
Shane's Chess Information Database (Scid) is a free and open source UNIX, Windows, Linux, and Mac application for viewing and maintaining large databases of chess games. It has features comparable to popular commercial chess software. Scid is written in Tcl/Tk and C++.
Computer shogi is a field of artificial intelligence concerned with the creation of computer programs which can play shogi. The research and development of shogi software has been carried out mainly by freelance programmers, university research groups and private companies. By 2017, the strongest programs were outperforming the strongest human players.
Shogi, like western chess, can be divided into the opening, middle game and endgame, each requiring a different strategy. The opening consists of arranging one's defenses and positioning for attack, the middle game consists of attempting to break through the opposing defenses while maintaining one's own, and the endgame starts when one side's defenses have been compromised.
ChessGenius is the name of a chess-playing computer program written by Richard Lang who has in the past written programs that have won the World Computer Chess Championship on 10 occasions.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to chess:
Computer Arimaa refers to the playing of the board game Arimaa by computer programs.
Elmo is a computer shogi evaluation function and book file (joseki) created by Makoto Takizawa (瀧澤誠). It is designed to be used with a third-party shogi alpha–beta search engine.

CuckooChess is an advanced free and open-source chess engine under the GNU General Public License written in Java by Peter Österlund. CuckooChess provides an own GUI, and optionally supports the Universal Chess Interface protocol for the use with external GUIs such as Arena. An Android port is available, where its GUI is also based on Peter Österlund's Stockfish port dubbed DroidFish.
References
- ↑ Jennings, Peter (January 1978). "The Second World Computer Chess Championships". BYTE. p. 108. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- ↑ "A Beginner's Guide to building an opening book". www.horizonchess.com. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ "Chess::Opening::Book::Polyglot - Read polyglot opening books - metacpan.org". metacpan.org. Retrieved 14 March 2023.