An author is the creator or originator of any written work such as a book or play, and is also considered a writer or poet. More broadly defined, an author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility for what was created.

Chess is a board game played between two players. It is sometimes called Western chess or international chess to distinguish it from related games such as xiangqi and shogi. The current form of the game emerged in Southern Europe during the second half of the 15th century after evolving from chaturanga, a similar but much older game of Indian origin. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide.

Robert's Rules of Order, often simply referred to as Robert's Rules, is a manual of parliamentary procedure by U.S. Army officer Henry Martyn Robert. It was first published in 1876 as an adaptation of the rules and practice of the United States Congress to the needs of non-legislative societies. Robert's Rules is the most widely used manual of parliamentary procedure in the United States. It governs the meetings of a diverse range of organizations—including church groups, county commissions, homeowners associations, nonprofit associations, professional societies, school boards, and trade unions—that have adopted it as their parliamentary authority. Robert published four editions of the manual before his death in 1923, the last being the thoroughly revised and expanded Fourth Edition published as Robert's Rules of Order Revised in May 1915.
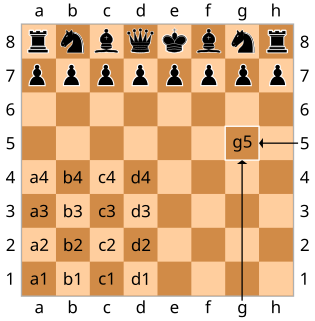
Algebraic notation is the standard method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is based on a system of coordinates to uniquely identify each square on the chessboard. It is used by most books, magazines, and newspapers. In English-speaking countries, the parallel method of descriptive notation was generally used in chess publications until about 1980. A few players still use descriptive notation, but it is no longer recognized by FIDE, the international chess governing body.

Fischer random chess, also known as Chess960, is a variation of the game of chess invented by the former World Chess Champion Bobby Fischer. Fischer announced this variation on June 19, 1996, in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Fischer random chess employs the same board and pieces as classical chess, but the starting position of the pieces on the players' home ranks is randomized, following certain rules. The random setup makes gaining an advantage through the memorization of openings impracticable; players instead must rely more on their skill and creativity over the board.
A chess opening or simply an opening is the initial stage of a chess game. It usually consists of established theory; the other phases are the middlegame and the endgame. Many opening sequences have standard names such as the "Sicilian Defense". The Oxford Companion to Chess lists 1,327 named openings and variants, and there are many others with varying degrees of common usage.

A citation is a reference to a source. More precisely, a citation is an abbreviated alphanumeric expression embedded in the body of an intellectual work that denotes an entry in the bibliographic references section of the work for the purpose of acknowledging the relevance of the works of others to the topic of discussion at the spot where the citation appears.
This glossary of chess explains commonly used terms in chess, in alphabetical order. Some of these terms have their own pages, like fork and pin. For a list of unorthodox chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems; for a list of named opening lines, see List of chess openings; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants.

A library catalog is a register of all bibliographic items found in a library or group of libraries, such as a network of libraries at several locations. A catalog for a group of libraries is also called a union catalog. A bibliographic item can be any information entity that is considered library material, or a group of library materials, or linked from the catalog as far as it is relevant to the catalog and to the users (patrons) of the library.

BibTeX is reference management software for formatting lists of references. The BibTeX tool is typically used together with the LaTeX document preparation system. Within the typesetting system, its name is styled as . The name is a portmanteau of the word bibliography and the name of the TeX typesetting software.
Alphabetical order is a system whereby character strings are placed in order based on the position of the characters in the conventional ordering of an alphabet. It is one of the methods of collation. In mathematics, a lexicographical order is the generalization of the alphabetical order to other data types, such as sequences of numbers or other ordered mathematical objects.

Book design is the art of incorporating the content, style, format, design, and sequence of the various components and elements of a book into a coherent unit. In the words of renowned typographer Jan Tschichold (1902–1974), book design, "though largely forgotten today, [relies upon] methods and rules upon which it is impossible to improve, [and which] have been developed over centuries. To produce perfect books, these rules have to be brought back to life and applied". Richard Hendel describes book design as "an arcane subject", and refers to the need for a context to understand what that means.
Parenthetical referencing, also known as Harvard referencing, is a citation style in which partial citations—for example, "(Smith 2010, p. 1)"—are enclosed within parentheses and embedded in the text, either within or after a sentence. They are accompanied by a full, alphabetized list of citations in an end section, usually titled "references", "reference list", "works cited", or "end-text citations". Parenthetical referencing can be used in lieu of footnote citations.

In library and information science, cataloging (US) or cataloguing (UK) is the process of creating metadata representing information resources, such as books, sound recordings, moving images, etc. Cataloging provides information such as creator names, titles, and subject terms that describe resources, typically through the creation of bibliographic records. The records serve as surrogates for the stored information resources. Since the 1970s these metadata are in machine-readable form and are indexed by information retrieval tools, such as bibliographic databases or search engines. While typically the cataloging process results in the production of library catalogs, it also produces other types of discovery tools for documents and collections.

Chess Informant is a publishing company from Belgrade that periodically produces a book entitled Chess Informant, as well as the Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings, Encyclopaedia of Chess Endings, Opening Monographs, other print publications, and software. Aleksandar Matanović and Milivoje Molerović founded the company in 1966 for the purpose of offering the rest of the world the sort of access to chess information enjoyed by Soviet players. The company has sold three million books in 150 countries, according to its website.

The game of chess is commonly divided into three phases: the opening, middlegame, and endgame. There is a large body of theory regarding how the game should be played in each of these phases, especially the opening and endgame. Those who write about chess theory, who are often also eminent players, are referred to as "theorists" or "theoreticians".

A list of poems by Robert E. Howard (1906–1936), an American writer and poet in early 20th century Texas. His love of poetry came from being read to by his mother at a young age. However, his attempts to make a living by poetry were unsuccessful and he is today most remembered for his short stories and fiction. Nevertheless, Howard wrote hundreds of poems; many were published within his lifetime and the others published after his 1936 suicide.

A list of poems by Robert E. Howard (1906–1936), an American writer and poet in early 20th century Texas. His love of poetry came from being read to by his mother at a young age. However, his attempts to make a living by poetry were unsuccessful and he is today most remembered for his short stories and fiction. Nevertheless, Howard wrote hundreds of poems; many were published within his lifetime and the others published after his 1936 suicide.

A list of poems by Robert E. Howard (1906–1936), an American writer and poet in early 20th-century Texas. His love of poetry came from being read to by his mother at a young age. However, his attempts to make a living by poetry were unsuccessful and he is today most remembered for his short stories and fiction. Nevertheless, Howard wrote hundreds of poems; many were published within his lifetime and the others published after his 1936 suicide.












