
Robert Winthrop Simpson was a British-born rear-admiral of the Chilean Navy, who distinguished himself during the Latin American wars of independence and later in the War of the Confederation.

O'Higgins was a Chilean frigate famous for her actions under Captain Lord Cochrane.
USS Fredonia (1845) was an 800-ton bark that served the U.S. Navy as a transport and as a storeship. After several voyages to California by way of Cape Horn, she became the station warehouse in Arica, Chile, where she was destroyed by an earthquake.
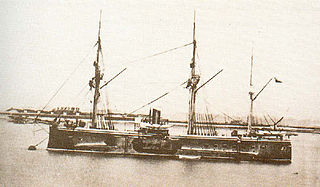
Blanco Encalada was a central battery ship built by Earle's Shipbuilding Co. in England for the Chilean Navy in 1875. She was nicknamed El Blanco. She participated actively in the War of the Pacific, her most important action being the capture of the Peruvian monitor Huáscar during the Battle of Angamos.

Águila was the first naval vessel of the Chilean Navy. She was later renamed Pueyrredón.

The corvette Abtao was a wooden ship built in Scotland during 1864 of 1.600 tons and 800 IHP. She fought in the War of the Pacific and was in service for the Chilean Navy until 1922.

Lautaro was initially the British East Indiaman Windham, built by Perry, Wells & Green at the Blackwall Shipyard for the East India Company (EIC) and launched in 1800. She made seven voyages to India, Ceylon, and China for the EIC. In 1809-10, the French captured her twice, but the British also recaptured her twice. The Chilean Navy bought her in 1818 and she then served in the Chilean Navy, taking part in several actions during the liberation wars in Chile and Peru. From 1824 she was a training ship until she was sold in 1828.

Esmeralda was a 44-gun frigate built in Port Mahón, Balearic Islands in 1791 for the Spanish Navy. The First Chilean Navy Squadron, under the command of Thomas Cochrane, captured her on the night of 5 November 1820. She was renamed Valdivia in Chilean service. She was beached at Valparaíso in June 1825.

The First Chilean Navy Squadron was the heterogeneous naval force that temporarily terminated Spanish colonial rule in the Pacific and protagonized the most important naval actions of in the Latin American wars of independence. The Chilean revolutionary government organized the squadron in order to carry the war to the Viceroyalty of Perú, then the center of Spanish power in South America, and thus secure the independence of Chile and Argentina.
Independencia was a 26-gun corvette of the First Chilean Navy Squadron.

Chacabuco was a 20-gun corvette of 450 tons built in 1815 in Boston, USA. She came to Coquimbo as Avon where investors in Copiapó, Chile, purchased her to use her as privateer vessel under the name Coquimbo. But as the businessmen drew back, the Chilean government bought the ship on 20 June 1818 for $36,000. She was renamed Chacabuco and commissioned to the Navy under the command of Captain Francisco Díaz.

Araucano was a 16- or 18-gun brigantine of the First Chilean Navy Squadron.

The impressive frigate Chile was built 1840 in Bordeaux, France, by order of the Chilean government, but without building supervision, the use of poorly dried timber that had been felled outside the normal winter season was the main cause of rot damage.

At the end of the Chilean Civil War of 1829–1830 the government decided to buy the brigantine-schooner Flora to confront a new attack of insurgents. She was renamed Colo Colo.
The frigate Monteagudo was involved in important events of the first decades of the Republics of Chile and Peru. As in many other cases, the origin of the ship is unknown, although it is known that she was named Las Caldas and later Milagro.
Montezuma was launched in Philadelphia in 1804. She came into British hands c.1807 after having been seized for attempting to evade the British East India Company's monopoly on British trade with India. She then initially traded with Charleston until 1811 when she went whaling in the Galápagos Islands. There the Americans captured her in 1813. Her captors sailed her to Valparaiso where the Spanish colonial government seized her.

The capture of the frigate Esmeralda was a naval action waged on the night of 5 and 6 November 1820. A division of boats with sailors and marines of the First Chilean Navy Squadron, commanded by Thomas Cochrane, stealthily advanced towards Callao and captured the ship through a boarding attack. Esmeralda was the flagship of Spanish fleet and the main objective of the operation. She was protected by a strong military defense that the royalists had organized in the port.
Los Andes vs Prueba was a single ship action fought in 1820, during the development of the Spanish American Wars of Independence. The battle was between the corvette Los Andes and the frigate Prueba, the first a Chilean privateer and the second a ship of the Spanish Navy. It lasted two days and occurred in two different places. There are differences between Chilean and Spanish historiography on the exact date, the starting place, the development and the result of the naval action.
The Battle of Callao was a confrontation during the War of the Confederation, between the Chilean blockade of Callao under the command of Commander Bynnon and the Confederate corsair fleet under Juan Blanchet.
Sesostris was launched at Hull in 1818. She traded with India, the Baltic, and Russia, carried troops for a Chilean military expedition against Peru, and transported convicts to New South Wales. She was broken up in 1843.











