
Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean and has a mean transport estimated at 100–150 Sverdrups, or possibly even higher, making it the largest ocean current. The current is circumpolar due to the lack of any landmass connecting with Antarctica and this keeps warm ocean waters away from Antarctica, enabling that continent to maintain its huge ice sheet.

Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nutrient-rich upwelled water stimulates the growth and reproduction of primary producers such as phytoplankton. The biomass of phytoplankton and the presence of cool water in those regions allow upwelling zones to be identified by cool sea surface temperatures (SST) and high concentrations of chlorophyll a.
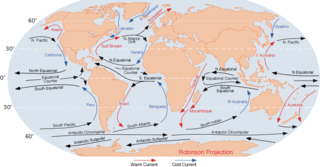
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.
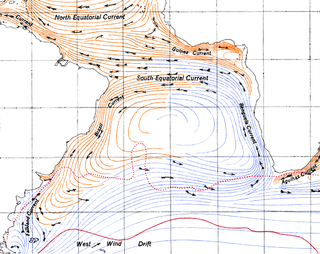
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela front in the north, at around 16°S. The current is driven by the prevailing south easterly trade winds. Inshore of the Benguela Current proper, the south easterly winds drive coastal upwelling, forming the Benguela Upwelling System. The cold, nutrient rich waters that upwell from around 200–300 m (656–984 ft) depth in turn fuel high rates of phytoplankton growth, and sustain the productive Benguela ecosystem.

The Isthmus of Tehuantepec is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as the Tehuantepec Route. The name is taken from the town of Santo Domingo Tehuantepec in the state of Oaxaca; this was derived from the Nahuatl term Tēcuāntepēc.

The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America. It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and extends 500–1,000 km (310–620 mi) offshore. The Humboldt Current is named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt even though it was discovered by José de Acosta 250 years before Humboldt. In 1846, von Humboldt reported measurements of the cold-water current in his book Cosmos.

The Canary Current is a wind-driven surface current that is part of the North Atlantic Gyre. This eastern boundary current branches south from the North Atlantic Current and flows southwest about as far as Senegal where it turns west and later joins the Atlantic North Equatorial Current. The current is named after the Canary Islands. The archipelago partially blocks the flow of the Canary Current.
Mountain jets are a type of jet stream created by surface winds channeled through mountain passes, sometimes causing high wind speeds and drastic temperature changes.

The California Current is a cold water Pacific Ocean current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur. It is considered an Eastern boundary current due to the influence of the North American coastline on its course. It is also one of six major coastal currents affiliated with strong upwelling zones, the others being the Humboldt Current, the Canary Current, the Benguela Current, the Oyashio Current, and the Somali Current. The California Current is part of the North Pacific Gyre, a large swirling current that occupies the northern basin of the Pacific.

The 1984 Pacific hurricane season featured numerous tropical cyclones, several of which were impactful to land. It was a busy hurricane season with 21 named storms, 13 hurricanes, and 7 major hurricanes, the latter of which are Category 3 or stronger cyclones on the Saffir–Simpson scale. This activity was unusual given the presence of a La Niña, which typically suppresses Central and East Pacific tropical cyclone activity, and only average sea surface temperatures. Seasonal activity began on May 17 and ended on November 8. This lies within the confines of a traditional hurricane season which begins on May 15 in the East Pacific and June 1 in the Central Pacific, and ends on November 30 in both basins. These dates conventionally delimit the period during each year when most tropical cyclones form.

Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary is a marine sanctuary located off the coast of California. It protects an area of 1,286 sq mi (3,331 km2) of marine wildlife. The administrative center of the sanctuary is on an offshore granite outcrop 4.5 sq mi (12 km2) by 9.5 sq mi (25 km2), located on the continental shelf off of California. The outcrop is, at its closest, 6 mi (10 km) from the sanctuary itself.

Tehuantepecer, or Tehuano wind, is a violent mountain-gap wind that travels through the Chivela Pass in southern Mexico, across the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. It is most common between October and February, with a summer minimum in July. It originates from eastern Mexico and the Bay of Campeche as a post-frontal northerly wind, accelerated southward by cold air damming, that crosses the isthmus and blows through the gap between the Mexican and Guatemalan mountains. The term dates back to at least 1929. This wind can reach gale, storm, even hurricane force. The leading edge of its outflow may form rope cloud over the Gulf of Tehuantepec. These winds can be observed on satellite pictures such as scatterometer wind measurements, they influence waves which then propagate as swell and are sometimes observed 1,600 km (1,000 mi) away. These strong winds bring cooler sub-surface waters to the surface of the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean and may last from a few hours to 6 days.

A parent to the Florida Current, the Loop Current is a warm ocean current that flows northward between Cuba and the Yucatán Peninsula, moves north into the Gulf of Mexico, loops east and south before exiting to the east through the Florida Straits and joining the Gulf Stream. The Loop Current is an extension of the western boundary current of the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Serving as the dominant circulation feature in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico, the Loop Currents transports between 23 and 27 sverdrups and reaches maximum flow speeds of from 1.5 to 1.8 meters/second.

The 1979 Pacific hurricane season was an inactive North Pacific hurricane season, featuring 10 named storms, 6 hurricanes, and 4 major hurricanes. All tropical cyclone activity this season was confined to the Eastern Pacific, east of 140°W. For the first time since 1977, no tropical cyclones formed in, or entered into the Central Pacific, between 140°W and the International Date Line.

Fog is a common weather phenomenon in the San Francisco Bay Area as well as along the entire coastline of California extending south to the northwest coast of the Baja California Peninsula. The frequency of fog and low-lying stratus clouds is due to a combination of factors particular to the region that are especially prevalent in the summer. Another type of fog, tule fog, can occur during the winter. There are occasions when both types can occur simultaneously in the Bay Area. The prevalence of fog in the San Francisco Bay Area has decreased, and this trend is typically attributed to climate change.

The Gulf of Tehuantepec is a large body of water on the Pacific coast of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, southeastern Mexico, at 16°N95°W. Many Pacific hurricanes form in or near this body of water. A strong, gale-force wind called the Tehuano periodically blows out over the waters of the Gulf of Tehuantepec, inducing strong upwelling of nutrient-rich waters which support abundant sea life.

The Somali Current is a warm ocean boundary current that runs along the coast of Somalia and Oman in the Western Indian Ocean and is analogous to the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean. This current is heavily influenced by the monsoons and is the only major upwelling system that occurs on a western boundary of an ocean. The water that is upwelled by the current merges with another upwelling system, creating one of the most productive ecosystems in the ocean.

The Papagayo jet, also referred to as the Papagayo Wind or the Papagayo Wind Jet, are strong intermittent winds that blow approximately 70 km north of the Gulf of Papagayo, after which they are named. The jet winds travel southwest from the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico to the Pacific Ocean through a pass in the Cordillera mountains at Lake Nicaragua. The jet follows the same path as the northeast trade winds in this region; however, due to a unique combination of synoptic scale meteorology and orographic phenomena, the jet winds can reach much greater speeds than their trade wind counterparts. That is to say, the winds occur when cold high-pressure systems from the North American continent meet warm moist air over the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico, generating winds that are then funneled through a mountain pass in the Cordillera. The Papagayo jet is also not unique to this region. There are two other breaks in the Cordillera where this same phenomenon occurs, one at the Chivela Pass in México and another at the Panama Canal, producing the Tehuano (Tehuantepecer) and the Panama jets respectively.
A Wind generated current is a flow in a body of water that is generated by wind friction on its surface. Wind can generate surface currents on water bodies of any size. The depth and strength of the current depend on the wind strength and duration, and on friction and viscosity losses, but are limited to about 400 m depth by the mechanism, and to lesser depths where the water is shallower. The direction of flow is influenced by the Coriolis effect, and is offset to the right of the wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere, and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. A wind current can induce secondary water flow in the form of upwelling and downwelling, geostrophic flow, and western boundary currents.



















