
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), referred to previously as spastic or nervous colon, and spastic bowel, is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms accompanied together that include abdominal pain and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms occur over a long time, often years. It has been classified into four main types depending on whether diarrhea is common, constipation is common, both are common (mixed/alternating), or neither occurs very often. IBS negatively affects quality of life and may result in missed school or work. Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS. IBS does not lead to malabsorption.
An antispasmodic is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms.
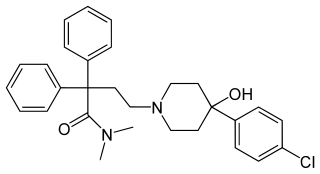
Loperamide, sold under the brand name Imodium, among others, is a medication used to decrease the frequency of diarrhea. It is often used for this purpose in inflammatory bowel disease and short bowel syndrome. It is not recommended for those with blood in the stool, mucus in the stool, or fevers. The medication is taken by mouth.
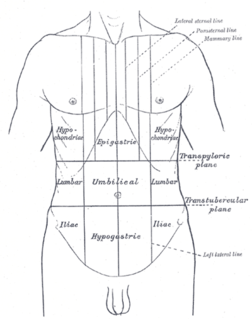
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.

Dicycloverine, also known as dicyclomine, sold under the brand name Bentyl in the US, is a medication that is used to treat spasms of the intestines such as occur in irritable bowel syndrome. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. While it has been used in baby colic and enterocolitis, evidence does not support these uses.
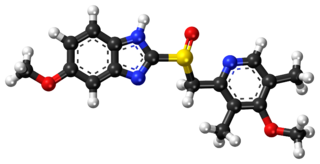
Esomeprazole, sold under the brand name Nexium among others, is a medication which reduces stomach acid. It is used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. Effectiveness is similar to other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.

Alosetron, sold under the brand name Lotronex among others, is a 5-HT3 antagonist used for the management of severe diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in women only.

Tegaserod is a 5-HT4 agonist manufactured by Novartis and sold under the names Zelnorm and Zelmac for the management of irritable bowel syndrome and constipation. Approved by the FDA in 2002, it was subsequently removed from the market in 2007 due to FDA concerns about possible adverse cardiovascular effects. Before then, it was the only drug approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration to help relieve the abdominal discomfort, bloating, and constipation associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Its use was also approved to treat chronic idiopathic constipation.

Blood in stool looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically originating from upper gastrointestinal bleeding; or to hematochezia, with a red color, typically originating from lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Evaluation of the blood found in stool depends on its characteristics, in terms of color, quantity and other features, which can point to its source, however, more serious conditions can present with a mixed picture, or with the form of bleeding that is found in another section of the tract. The term "blood in stool" is usually only used to describe visible blood, and not fecal occult blood, which is found only after physical examination and chemical laboratory testing.

Clorazepate, sold under the brand name Tranxene among others, is a benzodiazepine medication. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Clorazepate is an unusually long-lasting benzodiazepine and serves as a majoritive prodrug for the equally long-lasting desmethyldiazepam, which is rapidly produced as an active metabolite. Desmethyldiazepam is responsible for most of the therapeutic effects of clorazepate.

Rifaximin, sold under the brand name Xifaxan (USA) and Zaxine (Canada) among others, is an antibiotic medication used to treat travelers' diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, and hepatic encephalopathy. It has poor absorption when taken by mouth.

Methylscopolamine or methscopolamine, usually provided as the bromide or nitrate salt, is an oral medication used along with other medications to treat peptic ulcers by reducing stomach acid secretion. Proton pump inhibitors and antihistamine medications have made this use obsolete. It can also be used for stomach or intestinal spasms, to reduce salivation, and to treat motion sickness. Methscopolamine is also commonly used as a drying agent, to dry up post-nasal drip, in cold, irritable bowel syndrome and allergy medications

Chlordiazepoxide, trade name Librium among others, is a sedative and hypnotic medication of the benzodiazepine class; it is used to treat anxiety, insomnia and symptoms of withdrawal from alcohol and other drugs.

Lubiprostone is a medication used in the management of chronic idiopathic constipation, predominantly irritable bowel syndrome-associated constipation in women and opioid-induced constipation. The drug is owned by Mallinckrodt and is marketed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
Abdominal guarding is the tensing of the abdominal wall muscles to guard inflamed organs within the abdomen from the pain of pressure upon them. The tensing is detected when the abdominal wall is pressed. Abdominal guarding is also known as 'défense musculaire'.
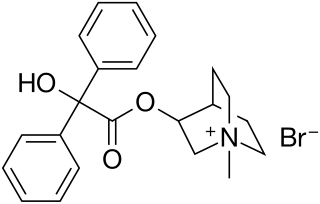
Clidinium bromide (INN) is an anticholinergic drug. It may help symptoms of cramping and abdominal/stomach pain by decreasing stomach acid, and slowing the intestines. It is commonly prescribed in combination with chlordiazepoxide using the brand name Normaxin.
Donnatal is a combination medication that provides natural belladonna alkaloids in a specific fixed ratio combined with phenobarbital to provide peripheral anticholinergic/antispasmodic action and mild sedation. Donnatal is manufactured for Concordia Pharmaceuticals by IriSys, LLC. It is available as tablets and 5 mL elixir. Active ingredients are listed as: phenobarbital (16.2 mg), hyoscyamine sulfate (0.1037 mg), atropine sulfate (0.0194 mg), and scopolamine hydrobromide (0.0065 mg). The latter two ingredients are found in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as belladonna.

Pinaverium bromide (INN) is a medication used for functional gastrointestinal disorders. It belongs to a drug group called antispasmodics and acts as a calcium channel blocker in helping to restore the normal contraction process of the bowel. It is most effective when taken for a full course of treatment and is not designed for immediate symptom relief or sporadic, intermittent use.

Tenapanor, used in form of tenapanor hydrochloride and sold under the brand name Ibsrela, is a treatment for adults with a disease of the gut called irritable bowel syndrome with constipation commonly referred to as IBS-C.

Eluxadoline, sold under the brand names Viberzi and Truberzi, is a medication taken by mouth for the treatment of diarrhea and abdominal pain in individuals with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). It was approved for use in the United States in 2015. The drug originated from Janssen Pharmaceutica and was developed by Actavis.
















